A biometria oferece uma maneira mais conveniente, mas potencialmente menos segura, de confirmar sua identidade com um dispositivo. No modelo de autenticação em camadas, a autenticação primária (ou seja, modalidades baseadas em fatores de conhecimento, como PIN, padrão e senha) fornece o mais alto nível de segurança. A biometria está na camada secundária de autenticação, oferecendo um equilíbrio entre conveniência e segurança. O CDD do Android define três classes de força biométrica: Classe 3 (anteriormente Forte), Classe 2 (anteriormente Fraca) e Classe 1 (anteriormente Conveniência). Cada classe tem um conjunto de pré-requisitos, privilégios e restrições - consulte o CDD acima para obter mais detalhes. Todas as três classes podem se integrar com a tela de bloqueio, mas somente autenticadores fortes e fracos podem se integrar com as APIs android.hardware.biometrics. Esta tabela descreve cada autenticador e a funcionalidade que eles suportam.
| Autenticador | Tela de bloqueio | Integração de prompt biométrico | Armazenamento de chaves (chave baseada em tempo) | Armazenamento de chaves (chave baseada em operação) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIOMETRIC_STRONG (Classe 3) | Sim | Sim | Sim | Sim |
| BIOMETRIC_WEAK (Classe 2) | Sim | Sim | Não | Não |
| BIOMÉTRICA_CONVENIÊNCIA (Classe 1) | Sim | Não | Não | Não |
| DEVICE_CREDENCIAL | Sim | Sim | Sim | Sim (1) |
- Esta funcionalidade foi adicionada no Android 11, veja isto para mais detalhes
A estrutura do Android inclui suporte para autenticação biométrica de rosto e impressão digital. O Android pode ser personalizado para suportar outras modalidades biométricas (como Iris). No entanto, a integração biométrica dependerá da segurança biométrica, não da modalidade. Para obter mais detalhes sobre as especificações de segurança biométrica, consulte Medindo a segurança do desbloqueio biométrico .
Fonte
Android 11
- Apresenta a interface BiometricManager.Authenticators , que fornece constantes que os desenvolvedores podem usar para especificar os tipos de autenticação aceitos por seus aplicativos.
- Adiciona aação de intenção
ACTION_BIOMETRIC_ENROLL, que os desenvolvedores podem usar para direcionar o usuário a registrar um método de autenticação que atenda aos requisitos de seus aplicativos. - Adiciona o método
AuthenticationResult #getAuthenticationType (), que os desenvolvedores podem usar para verificar se o usuário autenticou usando uma credencial biométrica ou uma credencial de dispositivo. - Fornece suporte adicional para chaves de autenticação por uso na classe BiometricPrompt.
Android 10
- Apresenta a classe
BiometricManagerque os desenvolvedores podem usar para consultar a disponibilidade da autenticação biométrica. - Inclui integração de autenticação de impressão digital e facial para
BiometricPrompt
Android 9
- Inclui integração de impressão digital apenas para
BiometricPrompt. - Desaprova a classe FingerprintManager. Se seus aplicativos empacotados e do sistema usarem essa classe, atualize-os para usar
BiometricPrompteBiometricManager. - Atualizados os testes do verificador
FingerprintManagerCTS para testarBiometricPromptusandoBiometricPromptBoundKeysTest.
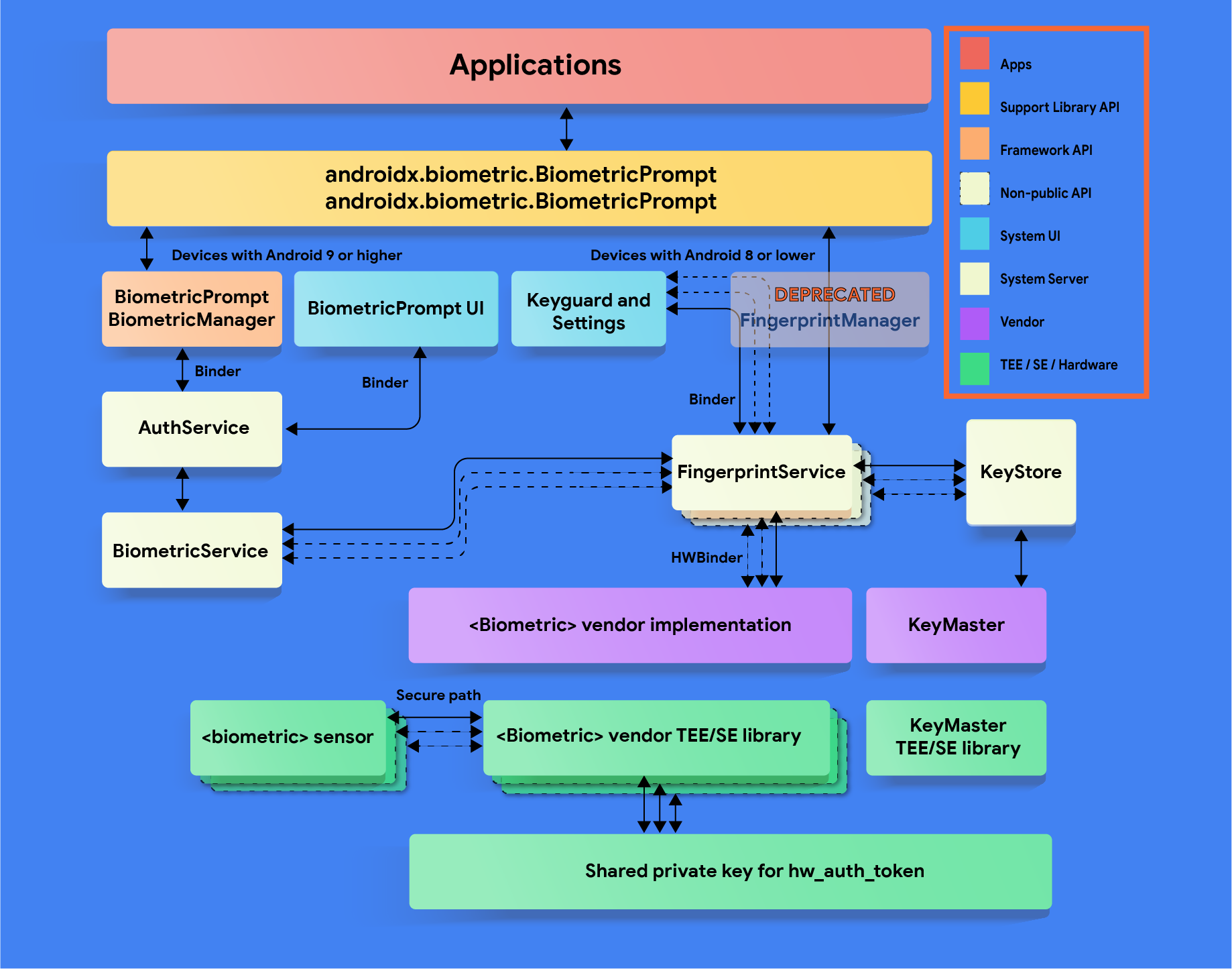
Implementação
Para garantir que usuários e desenvolvedores tenham uma experiência biométrica perfeita, integre sua pilha biométrica às APIs BiometricPrompt , BiometricManager e ACTION_BIOMETRIC_ENROLL . Os dispositivos com sensores biométricos devem atender a esses requisitos de resistência .
Para integrar sua pilha biométrica com as BiometricManager APIs BiometricPrompt
- Certifique-se de que seu
<Modality>Serviceesteja registrado corretamente comBiometricServicepor meio do método IBiometricService#registerAuthenticator e implemente a interfaceIBiometricAuthenticator. Modalidades comuns (impressão digital, face) se estendem de uma superclasse comum. Se você precisar integrar uma modalidade não suportada, siga o exemplo de impressão digital / face e as diretrizes do CDD para biometria. - Certifique-se de que sua nova modalidade tenha suporte adequado no SystemUI . Existem interfaces de usuário padrão do
BiometricPromptpara impressão digital e rosto. Isso deve incluir qualquer alteração de layout ou tema necessária para o seu dispositivo. Ou seja, alterações de layout correspondentes para um sensor de impressão digital na tela.
Para integrar sua pilha biométrica com a API ACTION_BIOMETRIC_ENROLL:
- Modifique o BiometricEnrollActivity para apresentar seu fluxo de inscrição. Observe que sua biometria pode ser apresentada apenas se atender à força solicitada. Se o seu dispositivo suporta mais de um, esta ação deve apresentar uma lista que o usuário pode escolher.
Diretrizes de implementação de HAL
Siga estas diretrizes biométricas de HAL para garantir que os dados biométricos não vazem e sejam removidos quando um usuário for removido de um dispositivo:
- Certifique-se de que os dados biométricos brutos ou derivados (como modelos) nunca sejam acessíveis de fora do ambiente isolado seguro (como o TEE ou Secure Element). Todos os dados armazenados devem ser criptografados com uma chave específica do dispositivo conhecida apenas pelo TEE (Trusted Execution Environment). Se o hardware oferecer suporte, limite o acesso do hardware ao ambiente isolado seguro e proteja-o com uma política SELinux. Torne o canal de comunicação (por exemplo, SPI, I2C) acessível apenas ao ambiente isolado seguro com uma política SELinux explícita em todos os arquivos do dispositivo.
- A aquisição, registro e reconhecimento biométricos devem ocorrer dentro do ambiente seguro e isolado para evitar violações de dados e outros ataques. Este requisito aplica-se apenas à biometria Classe 3 (anteriormente Forte) e Classe 2 (anteriormente Fraca) .
- Para se proteger contra ataques de repetição, assine modelos biométricos com uma chave privada específica do dispositivo. Para o Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), no mínimo, assine um modelo com o caminho absoluto do sistema de arquivos, grupo e ID biométrico, de modo que os arquivos de modelo fiquem inoperantes em outro dispositivo ou para qualquer pessoa que não seja o usuário que os registrou no mesmo dispositivo . Por exemplo, evite copiar dados biométricos de um usuário diferente no mesmo dispositivo ou de outro dispositivo.
- Se você precisar armazenar dados fora do TEE, use o caminho do sistema de arquivos fornecido pelo
setActiveUser() HIDL methodou forneça outra maneira de apagar todos os dados do modelo de usuário quando o usuário for removido. O motivo é proteger o vazamento de dados do usuário. Os dispositivos que não usam esse caminho devem ser limpos após a remoção do usuário. É exigido pelo CDD que os dados biométricos e arquivos derivados sejam armazenados criptografados - especialmente se não for em TEE Se isso for inviável devido aos requisitos de armazenamento do ambiente isolado seguro, adicione ganchos para garantir a remoção dos dados quando o usuário for removido é apagado. Consulte LockSettingsService.removeBiometricsForUser()
Costumização
Se o seu dispositivo for compatível com várias biometrias, o usuário poderá especificar um padrão nas configurações. Sua implementação do BiometricPrompt deve preferir a biometria Classe 3 (anteriormente Strong) como padrão, a menos que o usuário a substitua explicitamente . )
Validação
Sua implementação biométrica deve passar nos seguintes testes:
- Gerente Biométrico CTS
- CTS BiometricPrompt (sanidade, testes aprofundados dependem do verificador)
- Seção de teste biométrico CtsVerifier : Deve passar individualmente com cada modalidade que o dispositivo suporta
Além disso, se o seu dispositivo suportar uma biometria que tenha um AOSP HIDL ( fingerprint@2.1 , fingerprint@2.2 , face1.0 ), ele deverá passar no teste VTS relevante ( fingerprint , face )
