為配合主幹穩定開發模型,並確保生態系統的平台穩定性,我們將於 2026 年起,在第 2 季和第 4 季將原始碼發布至 AOSP。如要建構及貢獻 AOSP,建議使用 android-latest-release,而非 aosp-main。android-latest-release 資訊清單分支版本一律會參照推送至 AOSP 的最新版本。詳情請參閱「Android 開放原始碼計畫變更」一文。
版本生命週期
透過集合功能整理內容
你可以依據偏好儲存及分類內容。
AOSP 程式碼會先經過不同分支,再合併為正式版本。圖 1 顯示這項發布生命週期的各個步驟:
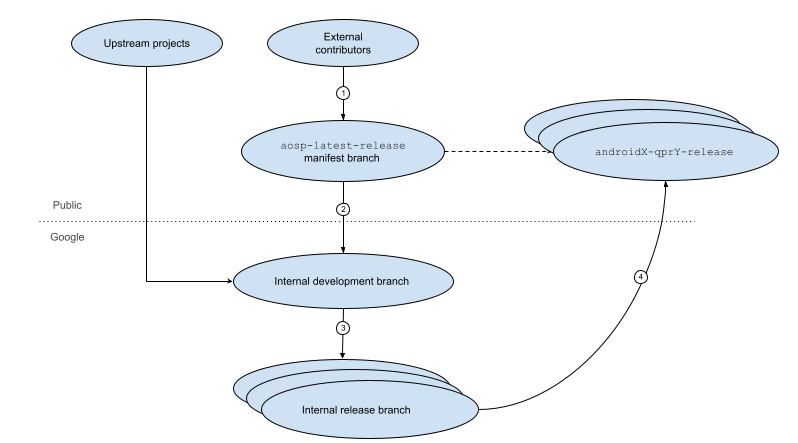
圖 1. Android 開放原始碼計畫發布生命週期。
生命週期中的步驟如下:
外部貢獻者可以下載及修改裝置的最新發布分支,並針對這個分支提出下一個 AOSP 版本的程式碼變更。
如要瞭解上游專案的生命週期,請參閱「上游專案生命週期」。
Google 會審查並挑選最新發布分支中提出的變更,將其納入 Google 的內部開發分支。這個分支只能在 Google 內存取,也是 Google 為下一個版本新增新功能的地方。
內部開發分支會定期建立內部版本分支。Google 可能會在這個版本分支中挑選變更,以便修正錯誤並提升效能。
在某個時間點,Google 會將內部發布分支的程式碼推送至最新的發布分支 (在 android-latest-release 資訊清單中指定),以便在公開的 AOSP 主機上建立發布分支的唯讀副本。
上游專案生命週期
上游專案程式碼會流入內部開發分支,並按照上方圖表中的步驟 3 和 4 進行。上游程式碼會在下一個發布分支中發布。上游專案是 AOSP 從中提取程式碼的開放原始碼專案。除了 Linux 核心和 WebKit 等專案之外,Google 也將部分半自動 Android 專案 (例如 ART、Android SDK 工具和 Bionic) 遷移至 AOSP。您可以直接為某些上游專案做出貢獻。詳情請參閱「為上游專案做出貢獻」。
這個頁面中的內容和程式碼範例均受《內容授權》中的授權所規範。Java 與 OpenJDK 是 Oracle 和/或其關係企業的商標或註冊商標。
上次更新時間:2025-07-27 (世界標準時間)。
[[["容易理解","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["確實解決了我的問題","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["其他","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["缺少我需要的資訊","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["過於複雜/步驟過多","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["過時","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["翻譯問題","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["示例/程式碼問題","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["其他","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["上次更新時間:2025-07-27 (世界標準時間)。"],[],[]]

