AOSP 코드는 공식 출시에 병합되기 전에 여러 브랜치를 거칩니다. 그림 1은 이 출시 수명 주기의 다양한 단계를 보여줍니다.
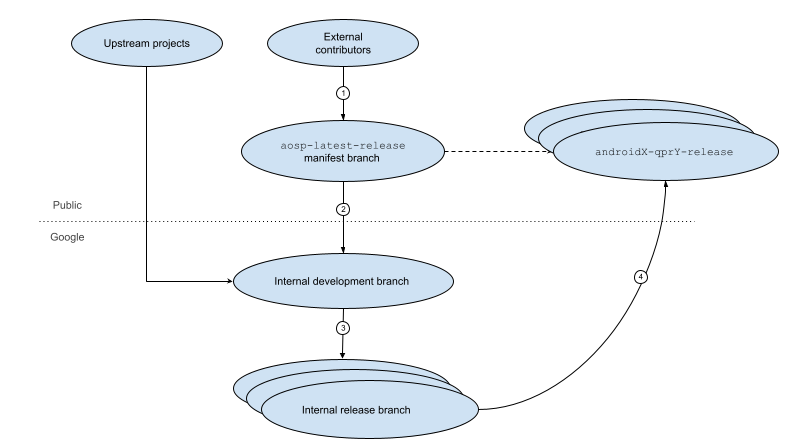
그림 1. AOSP 출시 수명 주기
수명 주기의 단계는 다음과 같습니다.
외부 참여자는 기기의 최신 출시 브랜치를 다운로드하여 수정할 수 있으며 이 브랜치에서 AOSP의 다음 버전에 관한 코드 변경사항을 제안할 수 있습니다.
업스트림 프로젝트의 수명 주기에 관한 자세한 내용은 업스트림 프로젝트 수명 주기를 참고하세요.
Google은 제안된 변경사항을 검토하고, 승인되면 최신 출시 브랜치의 제안된 변경사항을 Google의 내부 개발 브랜치에 체리픽합니다. 이 브랜치는 Google 내에서만 액세스할 수 있으며 Google에서 다음 출시의 새로운 기능을 추가하는 곳입니다.
내부 개발 브랜치에서 주기적으로 내부 출시 브랜치가 생성됩니다. Google은 버그 수정 및 성능 개선을 위해 이 출시 브랜치에서 변경사항을 선별할 수 있습니다 .
Google은 특정 시점에 내부 출시 브랜치의 코드를 최신 출시 브랜치 (
android-latest-release매니페스트에 지정됨)로 푸시하여 공개 AOSP 호스트에 출시 브랜치의 읽기 전용 사본을 만듭니다.
업스트림 프로젝트 수명 주기
업스트림 프로젝트 코드는 내부 개발 브랜치로 이동하고 위 다이어그램의 3단계와 4단계를 따릅니다. 업스트림 코드는 다음 출시 브랜치에 게시됩니다. 업스트림 프로젝트는 AOSP가 코드를 가져오는 오픈소스 프로젝트입니다. Google에서는 Linux 커널 및 WebKit과 같은 프로젝트 외에도 ART, Android SDK 도구, Bionic과 같은 일부 반자동 Android 프로젝트를 AOSP로 이전합니다. 일부 업스트림 프로젝트에 직접 참여할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 업스트림 프로젝트에 기여하기를 참고하세요.
