Mã AOSP di chuyển qua nhiều nhánh trước khi được kết hợp vào một bản phát hành chính thức. Hình 1 cho thấy các bước trong vòng đời phát hành này:
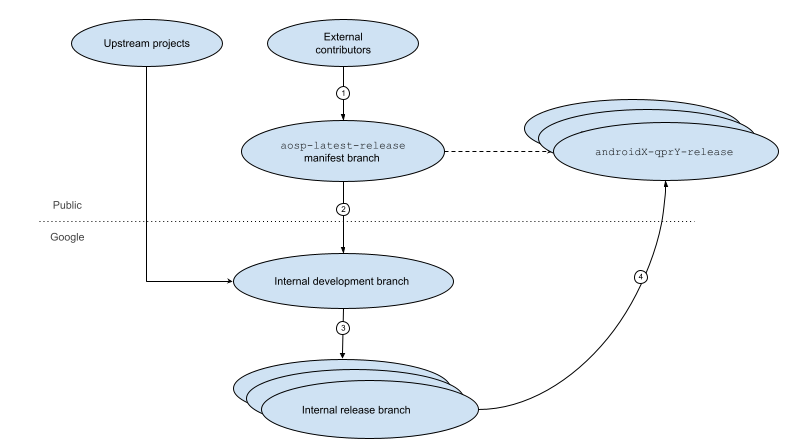
Hình 1. Vòng đời phát hành AOSP.
Sau đây là các bước trong vòng đời:
Người đóng góp bên ngoài có thể tải xuống và sửa đổi nhánh phát hành mới nhất cho thiết bị của họ, cũng như đề xuất thay đổi mã cho phiên bản AOSP tiếp theo trên nhánh này.
Để biết thông tin về vòng đời của các dự án ngược dòng, hãy xem phần Vòng đời của dự án ngược dòng.
Google xem xét và chọn lọc các thay đổi được đề xuất trên nhánh phát hành mới nhất vào nhánh phát triển nội bộ của Google (nếu được chấp nhận). Bạn chỉ có thể truy cập vào nhánh này trong Google và đây là nơi Google thêm các tính năng mới cho bản phát hành tiếp theo.
Theo định kỳ, một nhánh phát hành nội bộ sẽ được tạo từ nhánh phát triển nội bộ. Google có thể chọn lọc các thay đổi vào nhánh phát hành này để giải quyết các bản sửa lỗi và cải thiện hiệu suất .
Tại một thời điểm nào đó, Google sẽ đẩy mã từ nhánh phát hành nội bộ sang nhánh phát hành mới nhất (được chỉ định trong tệp kê khai
android-latest-release) để tạo bản sao chỉ có thể đọc của nhánh phát hành trên máy chủ AOSP công khai.
Vòng đời của dự án ngược
Mã dự án thượng nguồn sẽ chảy vào nhánh phát triển nội bộ và thực hiện các bước 3 và 4 trong sơ đồ trước. Mã nguồn thượng nguồn được phát hành trong nhánh phát hành tiếp theo. Dự án thượng nguồn là một dự án nguồn mở mà AOSP lấy mã từ đó. Ngoài các dự án như nhân Linux và WebKit, Google còn di chuyển một số dự án Android bán tự động như ART, các công cụ SDK Android và Bionic sang AOSP. Bạn có thể đóng góp trực tiếp cho một số dự án thượng nguồn. Để biết thông tin chi tiết, hãy xem bài viết Đóng góp cho dự án cấp trên.
