您可以使用 Android 模擬器建立 Android 裝置的模擬環境,執行自訂 Android 系統映像檔。此外,您還可以在 Android Emulator 模擬中新增多螢幕支援功能。
Android Emulator 架構
Android Emulator 會在名為 Android 虛擬裝置 (AVD) 的虛擬機器中執行 Android 作業系統。每個 AVD 都包含完整的 Android 軟體堆疊,執行方式與實體裝置相同。圖 1 說明 Android Emulator 的高層級架構。如要進一步瞭解模擬器,請參閱「在 Android Emulator 上執行應用程式」。
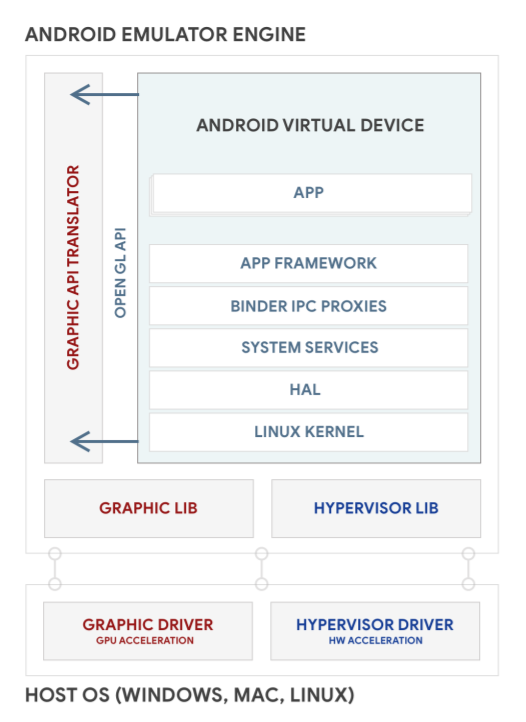
圖 1. Android Emulator 架構。
建構 AVD 映像檔
每個 AVD 都包含 Android 系統映像檔,可在該 AVD 中執行。AVD 管理工具包含部分系統映像檔。您也可以從原始碼建構自訂 AVD 系統映像檔,並建立裝置模擬器來執行這些映像檔。
如要建構及執行 AVD 系統映像檔,請按照下列步驟操作:
下載 Android 原始碼:
mkdir aosp-android-latest-release; cd aosp-android-latest-releaserepo init -urepo sync -j24
如要建構其他 Android 版本,請在公開 Android 存放區中尋找分支名稱。這些值會對應至「Android 產品代號、標記和版本號碼」。
建構 AVD 系統映像檔。這與建構 Android 裝置系統映像檔的程序相同。舉例來說,如要建構 x86 64 位元 AVD,請執行下列指令:
source ./build/envsetup.shlunch sdk_phone_x86_64make -j32在 Android 模擬器中執行 AVD 系統映像檔:
emulator
如要進一步瞭解如何執行模擬器,請參閱「指令列啟動選項」。圖 2 顯示 Android Emulator 執行 AVD 的範例:
圖 2. Android 模擬器執行 AVD。
分享 AVD 系統映像檔,供其他使用者搭配 Android Studio 使用
請按照下列操作說明,與他人共用 AVD 系統映像檔。他們可以使用 Android Studio 搭配 AVD 系統映像檔,開發及測試應用程式。
建立其他
sdk和sdk_repo套件:如果是 Android 13 以上版本,請使用
emu_img_zip指令:$ make emu_img_zip這會產生
sdk-repo-linux-system-images-eng.[username]].zip檔案。如果是 Android 12 以下版本,請使用
sdk_repo指令:$ make -j32 sdk sdk_repomake sdk sdk_repo指令會在aosp-android-latest-release/out/host/linux-x86/sdk/sdk_phone_x86下建立兩個檔案:sdk-repo-linux-system-images-eng.[username].ziprepo-sys-img.xml
將檔案託管在使用者可存取的位置,並取得該檔案的網址,做為 AVD 系統映像檔網址。
sdk-repo-linux-system-images-eng.[username].zip如果是 Android 12 以下版本,請視需要編輯
repo-sys-img.xml:- 將
<sdk:url>更新為 AVD 系統映像檔網址。 - 如要瞭解檔案的其他更新,請參閱 sdk-sys-img-03.xsd。
- 將檔案代管在使用者可存取的位置,並取得網址,做為「自訂更新網站網址」。
repo-sys-img.xml
- 將
如要使用自訂 AVD 映像檔,請在 SDK 管理工具中執行下列操作:
-
這會將自訂 AVD 系統映像檔新增至「系統映像檔」頁面。
下載並選取自訂 AVD 系統映像檔,建立 AVD。
新增多螢幕支援功能
Android 10 強化了多螢幕功能,可支援更多使用情境,例如自動和電腦模式。Android Emulator 也支援多螢幕模擬功能。因此您不必設定實際硬體,就能建立特定的多螢幕環境。
如要為 AVD 新增多螢幕支援功能,請進行下列變更,或從這些 CL 中挑選。
將下列幾行程式碼新增至
build/target/product/sdk_phone_x86.mk檔案,即可將多螢幕供應商新增至建構作業:PRODUCT_ARTIFACT_PATH_REQUIREMENT_WHITELIST := \ system/lib/libemulator_multidisplay_jni.so \ system/lib64/libemulator_multidisplay_jni.so \ system/priv-app/MultiDisplayProvider/MultiDisplayProvider.apk \ PRODUCT_PACKAGES += MultiDisplayProvider在
device/generic/goldfish/data/etc/advancedFeatures.ini檔案中加入以下程式碼,啟用多螢幕功能標記:MultiDisplay = on
如要瞭解最新的模擬器功能和發布資訊,請參閱下列來源:
