Compatibility Test Suite (CTS) is a free, commercial-grade test suite and tools used to help ensure that your devices are Android compatible. CTS is intended to be integrated into your daily workflow, such as through a continuous build system. CTS runs on a desktop machine and executes tests directly on attached devices or on an emulator. For an overview of Android compatibility, see Android compatibility program overview.
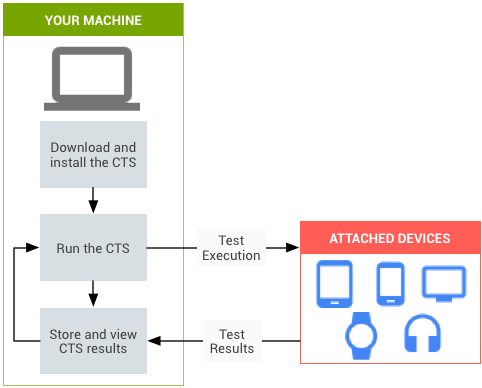
Figure 1. CTS automated testing.
Figure 1 shows the process of executing CTS automated tests:
- Download and install CTS. This step also involves setting up the test environment, the testing workstation, and the device you are testing or device under test (DUT)
- Run CTS automated tests.
- Store and review the results.
- Troubleshoot issues and rerun tests.
Use CTS to reveal incompatibilities early, and to ensure that your Android implementations remain compatible throughout the development process.
CTS components
CTS contains the following major components:
- Trade Federation
- A test harness and framework allow for the automated execution of tests.
- CTS automated tests
- Tests that use the Trade Federation framework and can be run using the Trade Federation test harness.
- CTS Verifier (CTS-V) tests
- Tests that must be run manually.
- CTS Verifier (CTS-V) app
- An app used to conduct CTS-V tests and collect CTS-V test results.
- Test case
An individual test executed on the DUT. Automated test cases are written in Java as JUnit tests and packaged Android APK files to run on the device target.
Test cases can be unit tests or functional tests. A unit test tests atomic units of code within the Android platform. For example, a unit test might test a single Android class.
A functional test exercises a combination of methods and classes used for a specific use case.
- Test configuration
A specific set of automated tests that are run on the DUT. Test configurations are XML files located in
WORKING_DIRECTORY/cts/tools/cts-tradefed/res/config. There are test configurations that contains all automated test cases and test configurations that contain a subset of test cases.- Test module
A test configuration consisting of a collection of test cases for the same feature area.
- Test plan
A test configuration consisting of a collection of test modules.
Test coverage
Test cases cover the following areas to ensure compatibility:
| Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Signature tests | For each Android release, there are XML files describing the signatures of all public APIs contained in the release. The CTS contains a utility to check those API signatures against the APIs available on the device. The results from signature checking are recorded in the test result XML file. |
| Platform API tests | Test the platform (core libraries and Android Application Framework) APIs as documented in the SDK Class Index to ensure API correctness, including correct class, attribute and method signatures, correct method behavior, and negative tests to ensure expected behavior for incorrect parameter handling. |
| Dalvik tests | The tests focus on testing the Dalvik executable format. |
| Platform data model | The CTS tests the core platform data model as exposed to application developers
through content providers, as documented in the
SDK
android.provider package (including contacts, browsers, and settings) |
| Platform intents | The CTS tests the core platform intents, as documented in the SDK Common intents. |
| Platform permissions | The CTS tests the core platform permissions, as documented in the
SDK
Manifest.permission. |
| Platform resources | The CTS tests for correct handling of the core platform resource types, as documented in the SDK Resource types overview. The CTS tests include tests for simple values, drawables, nine-patch, animations, layouts, styles and themes, and loading alternate resources. |
What's next
After reading this document, continue to Set up CTS.
