次世代の車両では、複数の画面がサポートされます。また、Android がそれらの画面の一部を操作してリッチ コンテンツを提供することもあります。このページでは、インストルメント クラスタやその他のディスプレイを Android Automotive IVI システムに統合するための重要な要素について説明します。
Android の外部ディスプレイ
Android 10 では、android.app.Presentation API を使用して外部ディスプレイの使用をサポートします。プレゼンテーションとは、セカンダリ ディスプレイでコンテンツを表示するという目的に特化されたダイアログです。プレゼンテーションは作成時にターゲット ディスプレイに関連付けられ、ディスプレイの指標に従ってそのコンテキストとリソース構成が設定されます。
インストルメント クラスタ ディスプレイ
Presentation API は一般的な計器類(インストルメント クラスタ)のディスプレイに最適で、次図のような統合を可能にします。

Presentation API では、以下は不要です。
- 個別の音声フォーカス。
- アクティビティまたはアプリ全体の実行。
- 同時ユーザー入力の検討。
- タッチイベントの処理。
複数のディスプレイの使用について詳しくは、マルチディスプレイの概要をご覧ください。
前提条件: Android WindowManager の以前の開発の知識が役立ちます。
サポートされているコンテンツの種類
車両によっては、インストルメント クラスタの図まで Android で直接描画処理したくないが、ターンバイターンの案内や曲のタイトルといった情報は表示したいというケースがあります。そのようなデータはさまざまな方法で Android から送信できます。Android デバイスでは、以下のようにインストルメント クラスタのコンテンツを送信できます。
- メタデータベース(
CarVendorExtensionManagerやVehicleNetworkServiceを使用して CAN を通じてメッセージを送信するなど)。インストルメント クラスタ システムでは、メタデータに基づいて適切なグラフィックを作成する必要があります。 - グラフィックベース(物理的なディスプレイまたは仮想ディスプレイに対して)。ディスプレイは、ゲージクラスタ内の専用ディスプレイの場合もあれば、完全にグラフィカルなインストルメント クラスタ ディスプレイの一部である場合もあります。
グラフィック ベースのインストルメント クラスタ ディスプレイのハードウェア アーキテクチャの例は次のとおりです。
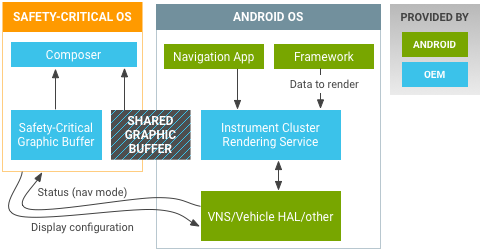
図 2. Android Automotive グラフィックベースのインストルメント クラスタ ディスプレイの例
セーフティ クリティカル OS(インストルメント クラスタのレンダリングを実行)と Android OS が、同じマルチコア SoC 上に搭載されていることがあります(たとえば、リアルタイム OS が専用の Cortex-R に、Android が Cortex-A に搭載されるなど)。インターフェースは、イーサネット AVB(音声ビデオブリッジ)、LVDS、HDMI のいずれでも構いません。Android では、グラフィック インストルメント クラスタは仮想ディスプレイとして接続され、Display HAL 実装の背後にあるハードウェア アーキテクチャを非表示にできます。
リアシートの制限事項
リアシート エンターテイメントの場合、Presentation API には次の制限があります。
- アクティビティ全体を投影することはできません(プレゼンテーションはダイアログの一種です)。
- 使用できる音声フォーカスは 1 つのみです。
- 同時ユーザーは存在しません。
- 外部ディスプレイに対する直接的なタッチイベントはありません(個別の挿入フローが必要です)。
