Android 9 支援 APK 金鑰輪替功能,可讓應用程式在 APK 更新期間變更簽署金鑰。為了讓輪替機制運作順利,APK 必須指出新舊簽署金鑰之間的信任層級。為了支援金鑰輪替,我們將 APK 簽名方案從 v2 更新為 v3,以便使用新舊金鑰。V3 會在 APK 簽署區塊中新增支援的 SDK 版本資訊和輪替證明結構體。
APK 簽署區塊
為維持與 v1 APK 格式的向下相容性,v2 和 v3 APK 簽名會儲存在 APK 簽署區塊中,位於 ZIP 中央目錄的正前方。
v3 APK 簽署區塊格式與 v2 相同。APK 的 v3 簽名會以 ID-value 組合的形式儲存,ID 為 0xf05368c0。
APK 簽署配置 v3 區塊
v3 配置表的設計與 v2 配置表非常相似。它採用相同的一般格式,並支援相同的簽名演算法 ID、金鑰大小和 EC 曲線。
不過,v3 配置文件會新增支援的 SDK 版本和輪替證明結構體的相關資訊。
格式
APK 簽署配置 v3 區塊會儲存在 APK 簽署區塊內,ID 為 0xf05368c0。
APK Signature Scheme v3 區塊的格式與 v2 相同:
- 長度前置碼序列的長度前置碼
signer:- 長度前置
signed data:- 長度前置碼序列的長度前置碼
digests:signature algorithm ID(4 個位元組)digest(長度前置)
- X.509 長度前置序列
certificates:- 長度前置碼 X.509
certificate(ASN.1 DER 格式)
- 長度前置碼 X.509
minSDK(uint32):如果平台版本低於這個數字,系統應忽略這個簽署者。maxSDK(uint32) - 如果平台版本高於此數字,應忽略此簽署者。- 長度前置碼序列的長度前置碼
additional attributes:ID(uint32)value(變長:額外屬性的長度 - 4 個位元組)ID - 0x3ba06f8cvalue -輪替證明結構體
- 長度前置碼序列的長度前置碼
minSDK(uint32) - 簽署資料區段中 minSDK 值的複本 - 如果目前平台不在範圍內,則用於略過此簽章的驗證。必須與已簽署資料值相符。maxSDK(uint32):簽署資料區段中 maxSDK 值的複本,用於在目前平台不在範圍內時略過驗證此簽章。必須與已簽署資料值相符。- 長度前置碼序列的長度前置碼
signatures:signature algorithm ID(uint32)- 長度前置
signature超過signed data
- 長度前置
public key(SubjectPublicKeyInfo、ASN.1 DER 格式)
- 長度前置
輪替證明和自信任舊憑證結構體
輪替證明結構體可讓應用程式輪替其簽署憑證,而不會在與其通訊的其他應用程式上遭到封鎖。為達成這項目標,應用程式簽章會包含兩個新的資料:
- 向第三方聲明,只要應用程式前身受到信任,應用程式的簽署憑證即可信任
- 應用程式仍信任的舊版簽署憑證
已簽署資料區段中的輪替證明屬性由單連結清單組成,每個節點都包含用於簽署先前應用程式版本的簽署憑證。這個屬性旨在包含概念性的輪替證明和自行信任的舊憑證資料結構。清單會依版本排序,其中最舊的簽署憑證會對應至根節點。證明輪替資料結構的做法,是讓每個節點中的憑證簽署清單中的下一個憑證,進而讓每個新金鑰都附上證明,證明該金鑰應與舊金鑰一樣值得信賴。
您可以透過在每個節點中新增標記,表示該節點在集合中的成員資格和屬性,來建構自信任舊版憑證資料結構。舉例來說,您可能會看到標記,指出系統信任特定節點的簽署憑證,可用於取得 Android 簽署權限。這個標記可讓使用舊版憑證簽署的其他應用程式,仍能獲得由使用新簽署憑證簽署的應用程式定義的簽章權限。由於整個旋轉證明屬性位於 v3 signer 欄位的已簽署資料區段,因此會受到用於簽署包含 APK 的金鑰保護。
這類格式不允許多個簽署金鑰,也不允許不同的祖系簽署憑證匯集至單一憑證 (多個起始節點匯集至單一匯出端)。
格式
旋轉證明會儲存在 APK 簽署配置 v3 區塊內,ID 為 0x3ba06f8c。格式如下:
- 長度前置碼序列的長度前置碼
levels:- 長度前置字串
signed data(由先前憑證提供,如有)- 長度前置碼 X.509
certificate(ASN.1 DER 格式) signature algorithm ID(uint32) - 前一個層級中憑證所使用的演算法
- 長度前置碼 X.509
flags(uint32) - 標記,指出此憑證是否應位於 self-trusted-old-certs 結構體中,以及用於哪些作業。signature algorithm ID(uint32) - 必須與下一層級中已簽署資料部分的值相符。- 長度前置字元
signature在上述signed data上
- 長度前置字串
多個憑證
Google Play 不支援多個簽署者,也不會發布使用多個憑證簽署的應用程式。
驗證
在 Android 9 以上版本中,APK 可根據 APK Signature Scheme v3、v2 配置或 v1 配置進行驗證。較舊的平台會忽略 v3 簽章,並嘗試驗證 v2 簽章,然後再驗證 v1 簽章。
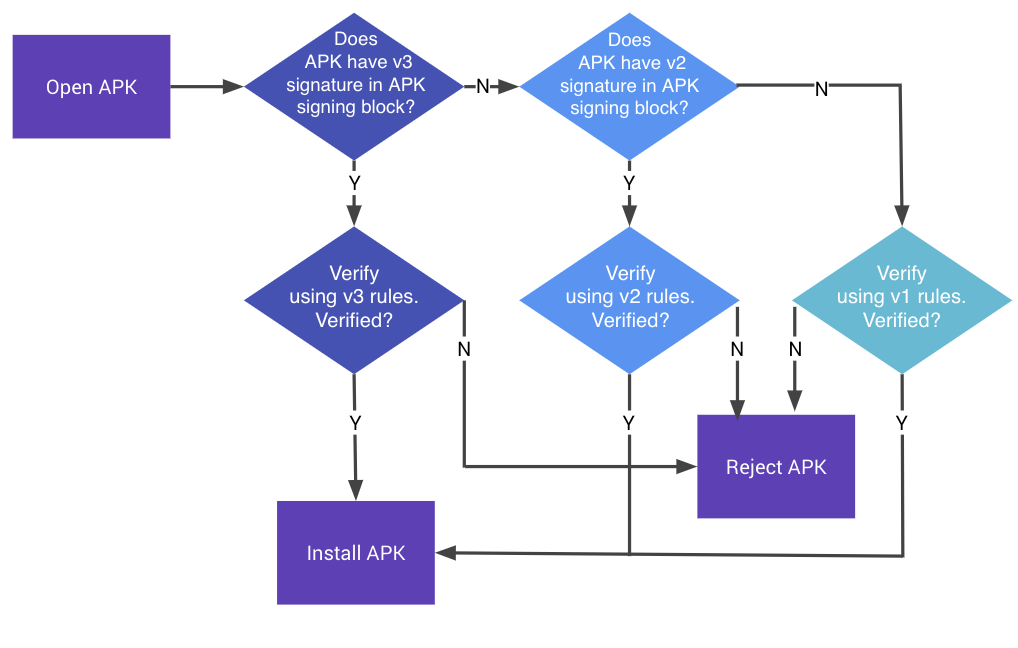
圖 1. APK 簽名驗證程序
APK 簽署配置 v3 驗證
- 找出 APK 簽署區塊,並確認:
- APK 簽署區塊的兩個大小欄位包含相同的值。
- ZIP 中央目錄後面緊接著 ZIP End of Central Directory 記錄。
- 在 ZIP End of Central Directory 後面沒有其他資料。
- 在 APK 簽署區塊中找出第一個 APK Signature Scheme v3 區塊。如果有 v3 區塊,請繼續執行步驟 3。否則,請改為使用 v2 配置驗證 APK。
- 針對 APK 簽名配置 v3 區塊中的每個
signer,其 SDK 最低和最高版本必須在目前平台的範圍內:- 從
signatures中選擇支援的最高級signature algorithm ID。強度排序取決於各實作/平台版本。 - 使用
public key驗證signatures與signed data的對應signature。(現在可以安全地剖析signed data)。 - 確認簽署資料中的最低和最高 SDK 版本,是否與
signer指定的版本相符。 - 請確認
digests和signatures中的簽章演算法 ID 排序清單相同。(這可避免簽章遭到剝離/新增)。 - 計算 APK 內容的摘要,使用與簽署演算法所用的摘要演算法相同的摘要演算法。
- 確認計算的摘要與
digests中的對應digest相同。 - 確認
certificates的第一個certificate的 SubjectPublicKeyInfo 與public key相同。 - 如果
signer有輪替證明屬性,請確認結構體有效,且這個signer是清單中的最後一個憑證。
- 從
- 如果在目前平台的範圍內找到了一個
signer,且步驟 3 針對該signer成功,驗證就會成功。
驗證
如要測試裝置是否正確支援 v3,請在 cts/hostsidetests/appsecurity/src/android/appsecurity/cts/ 中執行 PkgInstallSignatureVerificationTest.java CTS 測試。
