Android 13 introduces an ABI for user-space to communicate the requested MTE mode to the bootloader. You can use this to enable MTE on devices that have hardware support but don't ship with MTE enabled by default, or to disable MTE on devices that do ship with it.
Bootloader support
To support this ABI, your bootloader needs to read the
misc_memtag_message (defined in
bootloader_message.h) from the misc partition.
If a valid misc_memtag_message is found
(MISC_MEMTAG_MAGIC_HEADER matches, and the version number is supported),
the bootloader computes as follows:
memtag = (default_memtag && !(misc.memtag_mode & MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_OFF)) || misc.memtag_mode & MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG || misc.memtag_mode & MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_ONCE memtag_kernel = misc.memtag_mode & MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_KERNEL || misc.memtag_mode & MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_KERNEL_ONCE
default_memtag is the default memtag on or off setting for the
SKU. If memtag is true, the bootloader sets up MTE tag
reservation, enables tag checks in the lower exception levels, and
communicates the tag reserved region to the kernel with the devicetree (DT). If
memtag is false, the bootloader appends
arm64.nomte to the kernel command line.
If memtag_kernel is true, the bootloader appends
kasan=on to the kernel command line. Otherwise, it
appends kasan=off.
Bootloader must clear MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_ONCE and
MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_KERNEL_ONCE on every boot.
If the bootloader supports fastboot oem mte, the on argument should set the
MISC_MEMTAG_MODE_{MEMTAG, MEMTAG_ONLY, MEMTAG_OFF} flags to
(1, 0, 0), and the off argument should set them to (0, 0, 1),
while preserving the other flags.
Configure your product to build the mtectrl binary for userspace support.
And then set the ro.arm64.memtag.bootctl_supported system property to indicate
to the system that your bootloader supports the memtag message.
User interface
When the ro.arm64.memtag.bootctl_supported property is set, the Reboot with
MTE option in the Developer Options menu lets you reboot once with
MTE enabled. The target audience for this is app developers that want to test their apps with
MTE.
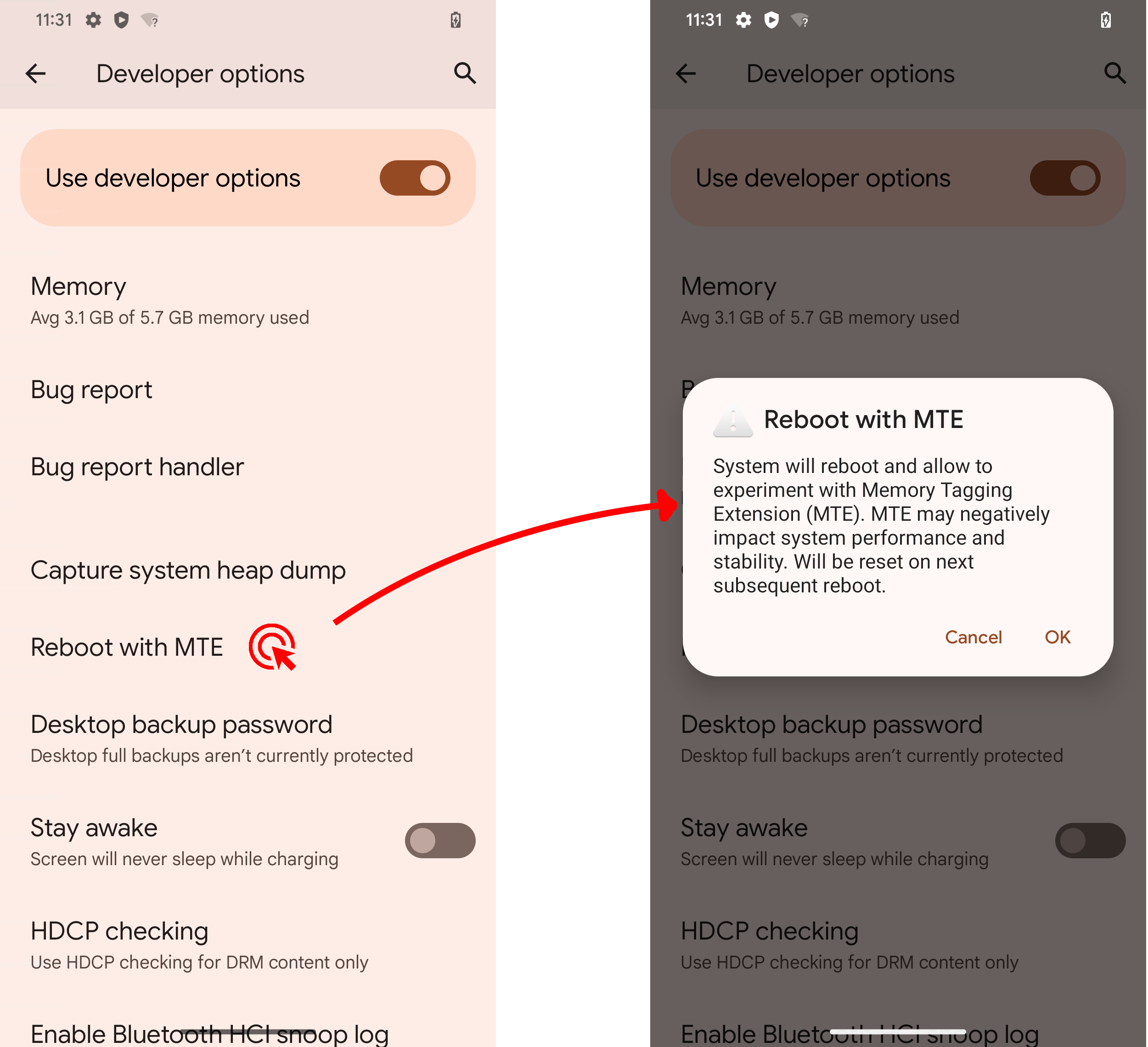
Figure 1. MTE developer option.
System property
For advanced use, the system property
arm64.memtag.bootctl can take a comma-separated list of the
following values:
-
memtagpersistently enables user-space MTE (setMISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG). -
memtag-onceenables user-space MTE once (setMISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_ONCE). -
memtag-kernelenables kernel-space MTE (setMISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_KERNEL). -
memtag-kernel-onceenables kernel-space MTE once (setMISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_KERNEL_ONCE). -
memtag-offdisables MTE (setMISC_MEMTAG_MODE_MEMTAG_OFF).
The setting is applied by the bootloader, so reboot the system after you make a change.
