ערכת הכלים של ממשק המשתמש (UI) ברכב מספקת מסגרת לפיתוח ממשק משתמש, שבאמצעותה אפשר לוודא שאפליקציות ברכב (אפליקציות של Google וגם אפליקציות מערכת ואפליקציות של ספקים) יכולות להשיג את היעדים הבאים:
-
עקביות עצמית של ממשק המשתמש/חוויית המשתמש של מערכת הבידור. עקביות עצמית היא היכולת של משתמש לחזות איך לבצע אינטראקציה עם מערכת מידע ובידור על סמך חוויות קודמות של אינטראקציה עם אותה מערכת.
-
התאמה אישית. יצרני ציוד מקורי יכולים לשנות את העיצוב והסגנון של המערכת כדי לשלב בצורה הטובה ביותר את הפונקציונליות עם הפנים והחומרה של הרכב.
מידע נוסף על השילוב עם ספריית ממשק המשתמש שברכב זמין בדפים הבאים:
- שילוב ספריית ממשק המשתמש שברכב באפליקציות
- התאמה אישית של אפליקציות
- הוספת גופנים מותאמים אישית
- התאמה אישית של העדפות ממשק המשתמש ברכב
- CarUiListItem
- התאמה אישית של CarUiRecyclerView
- פתרון בעיות בשכבות-על של משאבים בסביבת זמן ריצה
- נתוני גרסה
- נספח א', עבודה עם RRO
- נספח ב', הנחיות להתאמה אישית
מידע על ספריית ממשק המשתמש שברכב
ספריית ממשק המשתמש שברכב היא ספרייה מקושרת באופן סטטי, שמספקת קבוצה של רכיבים ומשאבים שאפשר להשתמש בהם כדי להטמיע:
- אפליקציות מערכת ואפליקציות OEM (Gerrit)
- אפליקציות ל-Android Automotive (AAOS)
הספרייה הזו משמשת כ:
-
ממשק API להתאמה אישית לפי:
- הגדרת המשאבים שאפשר להתאים אישית, כולל צבעים, מאפיינים ורכיבים גרפיים שאפשר לצייר.
- התייחסות למשאבים כ-API עם ערבויות לתאימות לאחור.
- שכבת תאימות בין הפתרון לטווח הקצר שזמין ב-Android 9 וב-Android 10 לבין הפתרון לטווח הארוך שנמצא בפיתוח.
שכבות-על של משאבים
מערכת Android מספקת כרגע כמה דרכים להחיל התאמות אישיות בלי צורך לבצע עבודה נוספת במערכות המשנה והאפליקציות המושפעות:
-
שכבות-על בזמן ה-build ההתאמה האישית הזו חלה בזמן ה-build של קובץ האימג' של מערכת Android. במהלך ה-build, כל האפליקציות במערכת מקבלות משאבים מהתיקייה
resומתיקיותoverlayשהוגדרו בקובצי ה-makefile של היעד. -
שכבות-על דינמיות בסביבת זמן הריצה (RRO דינמי). חבילות ה-APK המיוחדות האלה מכילות רק משאבים וקובץ מניפסט כדי לציין על איזה APK יעד הן ישפיעו. קובצי RRO דינמיים עוברים הידור ופריסה בנפרד מתמונת המערכת, ואפשר להפעיל או להשבית אותם. כשהמערכת מבצעת חיפוש משאבים לאפליקציה ספציפית, היא גם בודקת אם יש כל קובץ RRO שמטרגט אותה, ואם קובץ ה-RRO מכיל משאב עם אותו שם.
-
שכבות-על סטטיות של זמן ריצה (RRO סטטי). המבנה שלהם דומה למבנה של RRO דינמי, והם תמיד מופעלים. כלומר, אי אפשר להסיר אותם או לעדכן אותם בלי לבצע שדרוג מלא של קובץ האימג' של המערכת. קובצי RRO סטטיים משמשים כשכבת ביניים בין שכבות-על בזמן ה-build לבין שכבות-על דינמיות בסביבת זמן הריצה.
בנוסף לרכיבי ממשק המשתמש, ספריית ממשק המשתמש ברכב מספקת מנגנון להצגת שכבת-על ישירה של משאבים (המקושר באופן סטטי לכל אפליקציה) עם משאבי ה-OEM, באמצעות קבוצה של RROs סטטיים. יצרני ציוד מקורי חייבים לספק תיקייה שמכילה את שכבות-העל של המשאבים שלהם ואת רשימת האפליקציות המטורגטות. במהלך ה-build, התשתית של ספריית ממשק המשתמש ברכב תשתמש במידע הזה כדי ליצור RRO סטטי אחד לכל אפליקציה שמוגדרת כמטרה.
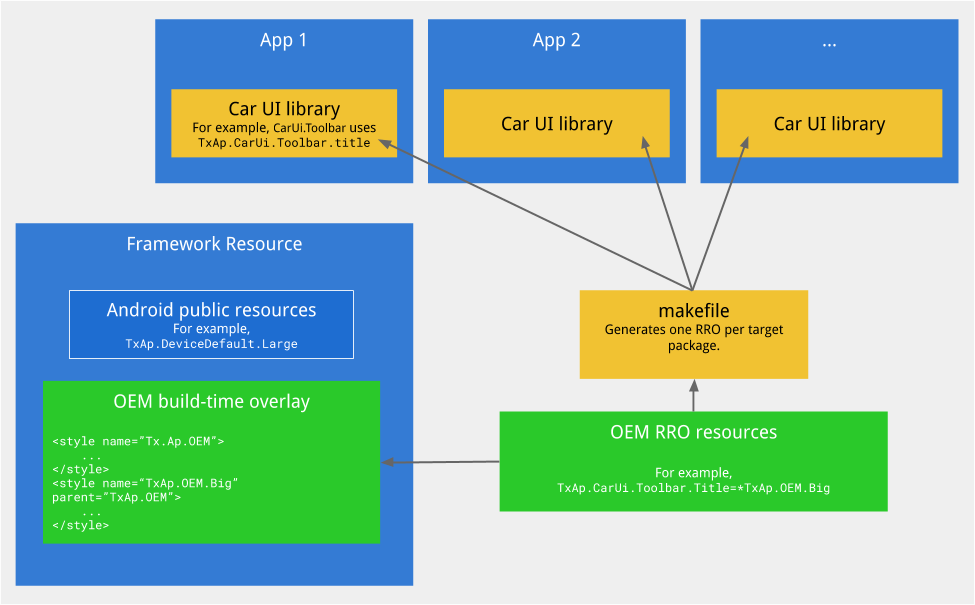
איור 1. רכיבים של ספריית ממשק המשתמש שברכב
בתמונה שלמעלה:
-
ירוק. התאמה אישית שמספקת יצרנית הציוד המקורי (OEM), שילוב של משאבי שכבת-על בזמן ה-build ובזמן הריצה.
-
צהוב. תמיכה שמספקת ספריית Car UI, כולל משאבים שאפשר להציב שכבה עליונה מעליהם , רכיבים (קוד Java) ותמיכה ב-build ליצירת קובצי ה-RRO הנדרשים.
-
כחול. יעדים ניתנים להתאמה אישית, כולל המסגרת, אפליקציות המערכת, אפליקציות הספקים ואפליקציות GAS שמשתמשות בספריית ממשק המשתמש שברכב כדי להתאים אישית רכיבי ממשק המשתמש.
