차세대 차량은 여러 화면을 지원하며 이 중 일부는 Android에서 작동하여 리치 콘텐츠를 제공할 수도 있습니다. 이 페이지에서는 계기판과 기타 디스플레이를 Android Automotive IVI 시스템에 통합하기 위한 주요 요소를 설명합니다.
Android의 외부 디스플레이
Android 10에서는 android.app.Presentation API를 사용하여 외부 디스플레이 사용을 지원합니다. 프레젠테이션은 보조 디스플레이에 콘텐츠를 표시하기 위한 고유한 대화상자입니다. 프레젠테이션은 생성 시 타겟 디스플레이와 연결되고 디스플레이 측정항목에 따라 컨텍스트 및 리소스 설정을 구성합니다.
계기판 디스플레이
Presentation API에는 다음 사항이 허용되므로 일반적인 계기판 디스플레이에 사용하기에 충분합니다.

Presentation API에는 다음이 필요하지 않습니다.
- 오디오 포커스 분리
- 전체 활동 또는 앱 실행
- 동시 사용자 입력 고려
- 터치 이벤트 처리
여러 디스플레이 사용에 관한 자세한 내용은 다중 디스플레이 개요를 참고하세요.
전제조건: Android WindowManager의 이전 개발 작업을 알고 있으면 도움이 됩니다.
지원되는 콘텐츠 유형
일부 차량에서는 Android가 계기판 그래픽을 직접 그리는 것은 원하지 않지만 세부 경로 안내나 음악 제목과 같은 정보 표시는 바랄 수 있습니다. Android는 여러 가지 방법으로 이러한 데이터를 전송할 수 있습니다. Android 기기는 계기판에 다음과 같이 콘텐츠를 전송할 수 있습니다.
- 메타데이터 기반으로(예:
CarVendorExtensionManager나VehicleNetworkService를 사용하여 CAN을 통해 메시지 전송). 계기판 시스템은 메타데이터에 기반하여 적절한 그래픽을 만들어야 합니다. - 실제 또는 가상 디스플레이에 그래픽 기반으로. 디스플레이는 게이지 클러스터 내의 전용 디스플레이이거나 완전한 그래픽 계기판 디스플레이의 일부일 수 있습니다.
그래픽 기반 계기판 디스플레이의 하드웨어 아키텍처의 예:
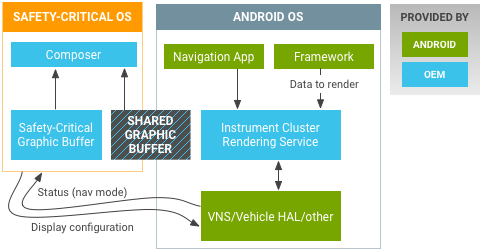
그림 2. Android Automotive 그래픽 기반 계기판 디스플레이 샘플
안전이 중요한(계기판 렌더링 담당) Android OS는 동일한 멀티코어 SoC에 있을 수 있습니다(예: 실시간 OS용 Cortex-R 및 Android용 Cortex-A 배치). 인터페이스는 이더넷 AVB(오디오 비디오 브리지)나 LVDS, HDMI일 수 있습니다. Android에서는 Graphics Instrument Cluster를 가상 디스플레이로 연결할 수 있으므로 디스플레이 HAL 구현의 하드웨어 아키텍처를 숨깁니다.
뒷좌석 제한사항
뒷좌석 엔터테인먼트의 경우 Presentation API에 다음과 같은 제한사항이 있습니다.
- 전체 활동을 표시할 수 없습니다(프레젠테이션은 대화상자임).
- 오디오 포커스는 1개만 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 동시 사용자가 없습니다.
- 외부 디스플레이에 직접적인 터치 이벤트가 없습니다(별도의 삽입 흐름 필요).
