W poprzedniej wersji systemu widoku zewnętrznego (EVS) interfejs IEvsCameraStreamzdefiniował jedną metodę wywołania zwrotnego, która dostarczała tylko klatki obrazu wideo. Chociaż uprościło to implementacje klienta usługi EVS, utrudniło też klientom identyfikowanie incydentów związanych ze strumieniowaniem i odpowiednie ich przetwarzanie. Aby ulepszyć proces tworzenia EVS, AOSP zawiera teraz dodatkowe wywołanie zwrotne do przesyłania zdarzeń strumieniowych.
package android.hardware.automotive.evs@1.1; import @1.0::IEvsCameraStream; /** * Implemented on client side to receive asynchronous video frame deliveries. */ interface IEvsCameraStream extends @1.0::IEvsCameraStream { /** * Receives calls from the HAL each time a video frame is ready for inspection. * Buffer handles received by this method must be returned via calls to * IEvsCamera::doneWithFrame_1_1(). When the video stream is stopped via a call * to IEvsCamera::stopVideoStream(), this callback may continue to happen for * some time as the pipeline drains. Each frame must still be returned. * When the last frame in the stream has been delivered, STREAM_STOPPED * event must be delivered. No further frame deliveries may happen * thereafter. * * @param buffer a buffer descriptor of a delivered image frame. */ oneway deliverFrame_1_1(BufferDesc buffer); /** * Receives calls from the HAL each time an event happens. * * @param event EVS event with possible event information. */ oneway notify(EvsEvent event); };
Ta metoda zwraca odpowiedź EvsEventDesc, która zawiera 3 pola:
- Typ zdarzenia.
- Ciąg znaków identyfikujący źródło zdarzenia.
- 4 32-bitowe dane słowa zawierające możliwe informacje o zdarzeniu.
/** * Structure that describes informative events occurred during EVS is streaming */ struct EvsEvent { /** * Type of an informative event */ EvsEventType aType; /** * Device identifier */ string deviceId; /** * Possible additional information */ uint32_t[4] payload; };
Aby uniknąć rozbieżności w opisie bufora graficznego między EVS a innymi komponentami graficznymi Androida, BufferDesc został zdefiniowany na nowo w celu używania HardwareBuffer zaimportowanego z interfejsu android.hardware.graphics.common@1.2.
HardwareBuffer zawiera HardwareBufferDescription, który jest odpowiednikiem interfejsu HIDL w Android NDK
AHardwareBuffer_Desc, z użyciem uchwytu bufora.
/** * HIDL counterpart of AHardwareBuffer_Desc. * * An AHardwareBuffer_Desc object can be converted to and from a * HardwareBufferDescription object by memcpy(). * * @sa +ndk libnativewindow#AHardwareBuffer_Desc. */ typedef uint32_t[10] HardwareBufferDescription; /** * HIDL counterpart of AHardwareBuffer. * * AHardwareBuffer_createFromHandle() can be used to convert a HardwareBuffer * object to an AHardwareBuffer object. * * Conversely, AHardwareBuffer_getNativeHandle() can be used to extract a native * handle from an AHardwareBuffer object. Paired with AHardwareBuffer_Desc, * AHardwareBuffer_getNativeHandle() can be used to convert between * HardwareBuffer and AHardwareBuffer. * * @sa +ndk libnativewindow#AHardwareBuffer". */ struct HardwareBuffer { HardwareBufferDescription description; handle nativeHandle; } /** * Structure representing an image buffer through our APIs * * In addition to the handle to the graphics memory, need to retain * the properties of the buffer for easy reference and reconstruction of * an ANativeWindowBuffer object on the remote side of API calls. * Not least because OpenGL expect an ANativeWindowBuffer* for us as a * texture via eglCreateImageKHR(). */ struct BufferDesc { /** * HIDL counterpart of AHardwareBuffer_Desc. Please see * hardware/interfaces/graphics/common/1.2/types.hal for more details. */ HardwareBuffer buffer; /** * The size of a pixel in the units of bytes */ uint32_t pixelSize; /** * Opaque value from driver */ uint32_t bufferId; /** * Unique identifier of the physical camera device that produces this buffer. */ string deviceId; /** * Time that this buffer is being filled */ int64_t timestamp; /** * Frame metadata. This is opaque to EVS manager */ vec<uint8_t> metadata };
Uwaga: HardwareBufferDescription to tablica 10 32-bitowych słów. Możesz przesłać go jako element typu AHardwareBuffer_Desc i uzupełnić zawartość.
EvsEventDesc to struktura enum EvsEventType, która zawiera listę kilku zdarzeń strumieniowych i 32-bitowy ładunek słowa, w którym deweloper może umieścić dodatkowe informacje. Na przykład deweloper może umieścić kod błędu dla zdarzenia błędu przesyłania strumieniowego.
/** * Types of informative streaming events */ enum EvsEventType : uint32_t { /** * Video stream is started */ STREAM_STARTED = 0, /** * Video stream is stopped */ STREAM_STOPPED, /** * Video frame is dropped */ FRAME_DROPPED, /** * Timeout happens */ TIMEOUT, /** * Camera parameter is changed; payload contains a changed parameter ID and * its value */ PARAMETER_CHANGED, /** * Master role has become available */ MASTER_RELEASED, };
Dostarczanie klatek
W nowej wersji BufferDesc, IEvsCameraStream wprowadza też nowe metody wywołania, aby odbierać ramki i zdarzenia strumieniowania z implementacji usługi.
/** * Implemented on client side to receive asynchronous streaming event deliveries. */ interface IEvsCameraStream extends @1.0::IEvsCameraStream { /** * Receives calls from the HAL each time video frames are ready for inspection. * Buffer handles received by this method must be returned via calls to * IEvsCamera::doneWithFrame_1_1(). When the video stream is stopped via a call * to IEvsCamera::stopVideoStream(), this callback may continue to happen for * some time as the pipeline drains. Each frame must still be returned. * When the last frame in the stream has been delivered, STREAM_STOPPED * event must be delivered. No further frame deliveries may happen * thereafter. * * A camera device delivers the same number of frames as number of * backing physical camera devices; it means, a physical camera device * sends always a single frame and a logical camera device sends multiple * frames as many as the number of backing physical camera devices. * * @param buffer Buffer descriptors of delivered image frames. */ oneway deliverFrame_1_1(vec<BufferDesc> buffer); /** * Receives calls from the HAL each time an event happens. * * @param event EVS event with possible event information. */ oneway notify(EvsEventDesc event); };
Nowsza wersja metody wywołania zwrotnego ramki została zaprojektowana w celu dostarczania wielu opisów bufora. Dlatego implementacje kamer EVS mogą przesyłać wiele klatek za pomocą jednego wywołania, jeśli zarządzają wieloma źródłami.
Ponadto poprzedni protokół informujący o końcu strumienia, który polegał na wysyłaniu ramki null, został wycofany i zastąpiony zdarzeniem STREAM_STOPPED.
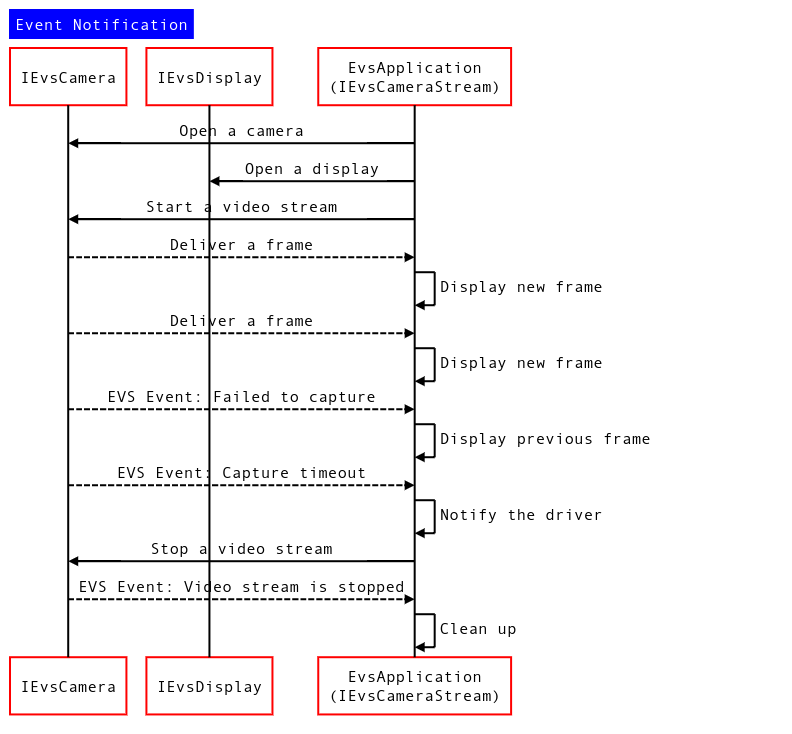
Rysunek 1. Schemat sekwencji powiadomienia o zdarzeniu
Używanie mechanizmu powiadomień o zdarzeniach i ramkach
Zidentyfikowanie wersji interfejsu IEvsCameraStream zaimplementowanego przez klienta
Usługa może zidentyfikować wersję przychodzącego interfejsu IEvsCameraStream zaimplementowanego przez klienta, próbując przekształcić:
using IEvsCameraStream_1_0 = ::android::hardware::automotive::evs::V1_0::IEvsCameraStream; using IEvsCameraStream_1_1 = ::android::hardware::automotive::evs::V1_1::IEvsCameraStream; Return<EvsResult> EvsV4lCamera::startVideoStream( const sp<IEvsCameraStream_1_0>& stream) { IEvsCameraStream_1_0 aStream = stream; // Try to downcast. This succeeds if the client implements // IEvsCameraStream v1.1. IEvsCameraStream_1_1 aStream_1_1 = IEvsCameraStream_1_1::castFrom(aStream).withDefault(nullptr); if (aStream_1_1 == nullptr) { ALOGI("Start a stream for v1.0 client."); } else { ALOGI("Start a stream for v1.1 client."); } // Start a video stream ... }
notify()
EvsEvent jest przekazywany przez wywołanie zwrotne notify(), a klient może określić jego typ na podstawie elementu discriminator, jak pokazano poniżej:
Return<void> StreamHandler::notify(const EvsEvent& event) { ALOGD("Received an event id: %u", event.aType); // Handle each received event. switch(event.aType) { case EvsEventType::ERROR: // Do something to handle an error ... break; [More cases] } return Void(); }
Używanie BufferDesc
AHardwareBuffer_Desc
to typ danych Android NDK, który reprezentuje natywny bufor sprzętowy, który można powiązać z podstawami EGL/OpenGL i Vulkan. Zawiera większość metadanych bufora z poprzedniego elementu EVS BufferDesc, dlatego zastępuje go w nowej definicji BufferDesc. Ponieważ jest on zdefiniowany jako tablica w interfejsie HIDL, nie można bezpośrednio indeksować zmiennych członkowskich.
Zamiast tego możesz przypisać tablicy typ AHardwareBuffer_Desc, jak pokazano poniżej:
BufferDesc bufDesc = {}; AHardwareBuffer_Desc* pDesc = reinterpret_cast<AHardwareBuffer_Desc *>(&bufDesc.buffer.description); pDesc->width = mVideo.getWidth(); pDesc->height = mVideo.getHeight(); pDesc->layers = 1; pDesc->format = mFormat; pDesc->usage = mUsage; pDesc->stride = mStride; bufDesc_1_1.buffer.nativeHandle = mBuffers[idx].handle; bufDesc_1_1.bufferId = idx;
