Android 11 supports a streaming-compatible signing scheme with the APK
signature scheme v4. The v4 signature is based on the Merkle hash tree
calculated over all bytes of the APK. The scheme follows the structure of the fs-verity
hash tree exactly (for example, zero-padding
the salt and zero-padding the last block). Android 11 stores the signature
in a separate file, <apk name>.apk.idsig. A v4 signature
requires a complementary v2 or v3 signature.
File format
All numeric fields are in little endian. All fields occupy exactly the number
of bytes as their sizeof(), with no implicit padding or alignment added.
The following helper struct simplifies the definitions:
template <class SizeT> struct sized_bytes { SizeT size; byte bytes[size]; };
Main file content:
struct V4Signature {
int32 version; // only version 2 is supported as of now
sized_bytes<int32> hashing_info;
sized_bytes<int32> signing_info;
sized_bytes<int32> merkle_tree; // optional
};hashing_info is the parameter used for hash tree
generation plus the root hash:
struct hashing_info.bytes {
int32 hash_algorithm; // only 1 == SHA256 supported
int8 log2_blocksize; // only 12 (block size 4096) supported now
sized_bytes<int32> salt; // used exactly as in fs-verity, 32 bytes max
sized_bytes<int32> raw_root_hash; // salted digest of the first Merkle tree page
};signing_info is the following struct:
struct signing_info.bytes {
sized_bytes<int32> apk_digest; // used to match with the corresponding APK
sized_bytes<int32> x509_certificate; // ASN.1 DER form
sized_bytes<int32> additional_data; // a free-form binary data blob
sized_bytes<int32> public_key; // ASN.1 DER, must match the x509_certificate
int32 signature_algorithm_id; // see the APK v2 doc for the list
sized_bytes<int32> signature;
};apk_digest is taken from the APK's v3 signing block. If that block isn't
present, it's taken from the v2 block (see apk_digest).
To create and verify, a signature code must serialize
the following data into binary blob and pass it into the
signing and verifying algorithm as the signed data:
struct V4DataForSigning {
int32 size;
int64 file_size; // the size of the file that's been hashed.
hashing_info.hash_algorithm;
hashing_info.log2_blocksize;
hashing_info.salt;
hashing_info.raw_root_hash;
signing_info.apk_digest;
signing_info.x509_certificate;
signing_info.additional_data;
};merkle_tree is the whole Merkle tree of the APK, calculated as described in the fs-verity
documentation.
Producers and consumers
The apksigner Android SDK tool generates the v4 signature file
if you run it with default parameters. You can disable v4 signing the same way
as the other signing schemes. The tool can also verify if the v4 signature is valid.
adb expects the .apk.idsig file to be present next to the APK when
running the adb install --incremental command. adb also uses the IDSIG
file to try incremental installation by default, and falls back to a regular installation if it's
missing or invalid.
When an installation session is created, the new streaming installation API
in PackageInstaller accepts the stripped
v4 signature as a separate argument when adding a file to the session.
At this point, signing_info is passed into IncFS as a
whole blob. IncFS extracts root hash from the blob.
When the installation session is being committed, PackageManagerService does
an ioctl call to retrieve the signing_info blob from IncFS, parses it,
and verifies the signature.
The Incremental Data Loader component streams the Merkle tree part
of the signature through the data loader native API. The
package service shell command install-incremental
accepts the stripped v4 signature file encoded as Base64 as a parameter for each
added file. The corresponding Merkle tree has to be sent into the command's
stdin.
apk_digest
apk_digest is the first available content digest in order:
- V3, 1 MB block, SHA2-512 (
CONTENT_DIGEST_CHUNKED_SHA512) - V3, 4 KB block, SHA2-256 (
CONTENT_DIGEST_VERITY_CHUNKED_SHA256) - V3, 1 MB block, SHA2-256 (
CONTENT_DIGEST_CHUNKED_SHA256) - V2, SHA2-512
- V2, SHA2-256
See length-prefixed sequence of length-prefixed signer in APK signature scheme v3.
Validation and testing
The APK validation process v4 is illustrated in the following figure:
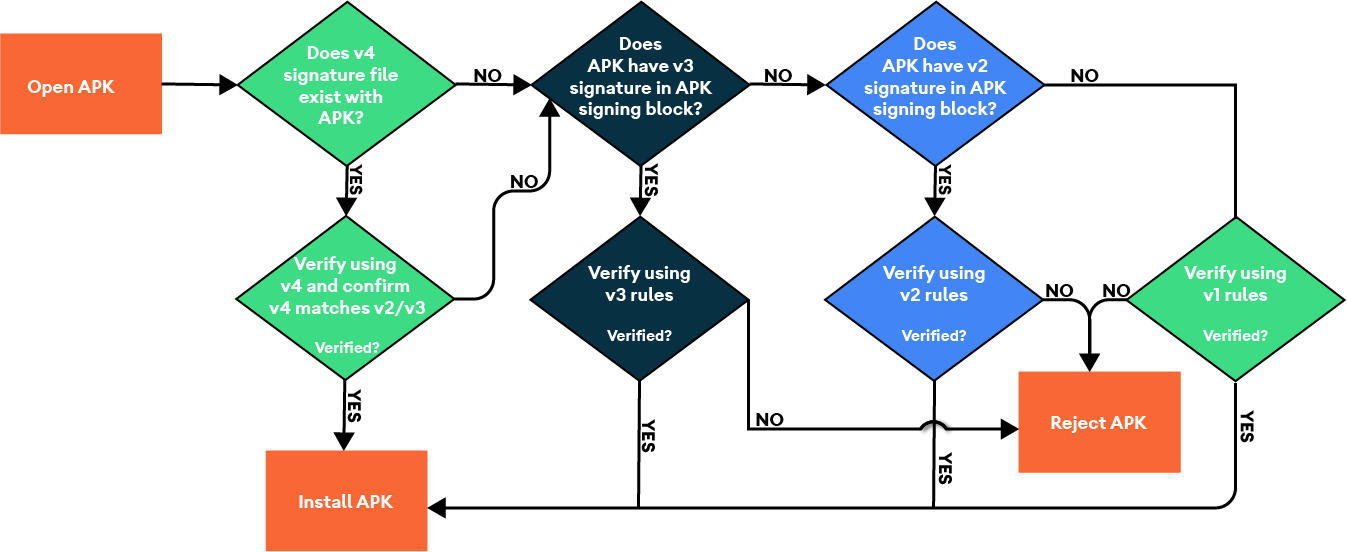
Figure 1. APK validation process v4.
Validate the implementation using feature unit tests and CTS:
CtsIncrementalInstallHostTestCases/android/cts/hostsidetests/incrementalinstall
Test the signature format
To test the signature format, set up a build environment and run the following manual tests:
$ atest PackageManagerShellCommandTest
PackageManagerShellCommandIncrementalTest
Test the signature format with Android SDK (ADB and apksigner)
Use this process test the signature format with Android SDK:
- Set up a build environment and ensure you've completed the implementation of IncFS.
- Flash the build on a target physical device or emulator.
- Generate or obtain an existing APK and then create a debug signing key.
- Sign and install the APK with v4 signature format
from the build-tools folder.
Sign
$ ./apksigner sign --ks debug.keystore game.apk
Install
$ ./adb install game.apk
Where these tests can be found
/android/cts/tests/tests/content/src/android/content/pm/cts/PackageManagerShellCommandIncrementalTest.java
