وفقًا لمستند تعريف التوافق مع Android، على المصنّعين الأصليين للأجهزة توفير طريقة لتفعيل تطوير التطبيقات. ومع ذلك، فإنّ توفير خيارات المطوّرين المشابهة للأجهزة الجوّالة داخل السيارات يجعل هذه السيارات عرضة للهجوم. يمكن الآن لمصنعي الأجهزة الأصليين حظر الوصول إلى خيارات المطوّرين باستخدام آلية رمز مميّز مشفّر تم التحقّق منه. على وجه التحديد، يمكن للمصنّع الأصلي للجهاز إجراء ما يلي:
- اضبط القيود التلقائية المطلوبة قبل بدء التشغيل لأول مرة.
- منح المطوّرين الإذن بأمان باستخدام الرموز المشفّرة إذا كان ذلك هو الخيار المفضّل
- تطبيق تغييرات القيود بعد مصادقة المطوّر وتفويضه
توضّح هذه المقالة عملية تنفيذ مرجعية تتألف من تطبيق تحكم في قيود تصحيح الأخطاء ومقدّمة نهاية لإصدار الرمز المميّز عن بُعد.
المصطلحات
بالإضافة إلى المصطلحات، يتم استخدام هذه المصطلحات في هذه المقالة:
- توقيع JSON على الويب (JWS)، كما هو محدّد في RFC 7515
- المعهد الوطني للمعايير والتكنولوجيا (NIST)
التصميم
يمكن لمصنّعي المعدّات الأصلية تفويض المطوّرين باستخدام رموز توقيع JSON على الويب (JWS) (RFC7515). في عملية التنفيذ المرجعية، تُصدر المصنّعين الأصليّين للأجهزة رموز الوصول ويستهلكها تطبيق التحكّم في القيود. تم تصميم رموز الوصول لمقاومة هجمات إعادة التشغيل والرموز المزورة.
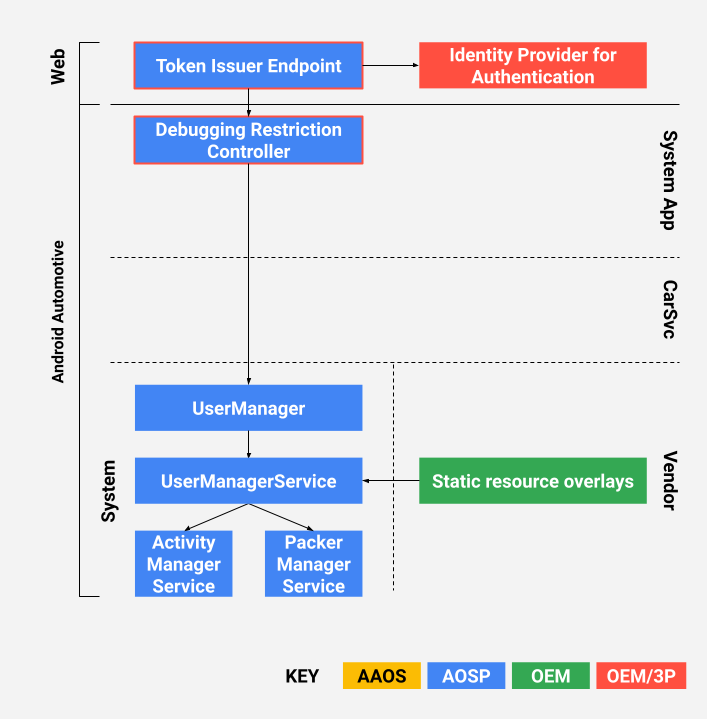
الشكل 1: التصميم
الدمج والضبط
على المصنّعين الأصليّين للأجهزة تحديد القيود التلقائية المطلوبة عند أول عملية تشغيل. ويتم ذلك باستخدام عدة طبقات موارد ثابتة لإلغاء الإعدادات التلقائية في إطار عمل AOSP.
يمكن ضبط القيود التلقائية لمستخدم النظام بلا واجهة مستخدم باستخدام سلسلة
config_defaultFirstUserRestrictions في
frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/config.xml، على سبيل المثال:
<!-- User restrictions set when the first user is created.
Note: Also update appropriate overlay files. -->
<string-array translatable="false" name="config_defaultFirstUserRestrictions">
<item>no_debugging_features</item>
</string-array>يمكن ضبط القيود التلقائية للسائقين والركاب والضيوف في
frameworks/base/core/res/res/xml/config_user_types.xml. يمكن لمصنّع المعدّات الأصلية (OEM) تراكب|
هذه السلاسل لضبط القيود التلقائية على كل نوع من المستخدمين على التوالي، على سبيل المثال:
<user-types> <full-type name="android.os.usertype.full.SECONDARY" > <default-restrictions no_debugging_features="true"/> </full-type> <full-type name="android.os.usertype.full.GUEST" > <default-restrictions no_debugging_features="true"/> </full-type> </user-types>
يتوفّر تطبيق مرجعي في الموقع التالي في AOSP:
packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController
الاختبار
تنصح Google المصنّعين الأصليّين للأجهزة بالبدء بالتطبيق المرجعي والبناء عليه.
- بعد ضبط القيود المطلوبة في ملفات التراكب، يمكنك تجميع AAOS و التحقّق من صحّة عمليات النقل المحدّدة. استخدِم التطبيق المرجعي والخدمة المحلية المزوّدة بتنسيق JWS للتحقّق من إعدادات الوصول.
- اضبط النظام لاستخدام خدمة السحابة الإلكترونية المزوّدة بتنسيق JWS (اختياري). تأكَّد من أنّك تلاحظ التدفق المطلوب في خدمة الخلفية.
