ยานพาหนะรุ่นถัดไปรองรับหน้าจอหลายจอ ซึ่งบางหน้าจออาจทำงานด้วย Android เพื่อแสดงเนื้อหาที่สมบูรณ์ หน้านี้อธิบายองค์ประกอบหลักในการผสานรวมแผงหน้าปัดและจอแสดงผลอื่นๆ เข้ากับระบบ IVI ของ Android Automotive
จอแสดงผลภายนอกใน Android
Android 10 ใช้ android.app.Presentation API เพื่อรองรับการใช้จอแสดงผลภายนอก การนำเสนอคือกล่องโต้ตอบที่ไม่ซ้ำกัน ซึ่งมีไว้เพื่อนำเสนอเนื้อหาบนจอแสดงผลรอง ระบบจะเชื่อมโยงการนำเสนอกับจอแสดงผลเป้าหมาย ณ เวลาที่สร้างขึ้น และกำหนดค่าบริบทและทรัพยากรตามเมตริกของจอแสดงผล
จอแสดงผลแผงหน้าปัด
Presentation API เพียงพอสำหรับการแสดงผลแผงหน้าปัดทั่วไป ซึ่งมีข้อจำกัดต่อไปนี้

Presentation API ไม่จำเป็นต้องมี
- โฟกัสเสียงแยกต่างหาก
- เพื่อเรียกใช้กิจกรรมหรือแอปทั้งหมด
- เพื่อพิจารณาอินพุตของผู้ใช้พร้อมกัน
- วิธีจัดการเหตุการณ์การแตะ
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้จอแสดงผลหลายจอได้ที่ภาพรวมจอแสดงผลหลายจอ
ข้อกําหนดเบื้องต้น: คุณควรมีความคุ้นเคยกับการพัฒนาWindowManager ของ Android เวอร์ชันก่อนหน้าบ้าง
ประเภทเนื้อหาที่รองรับ
รถยนต์บางรุ่นอาจไม่ต้องการให้ Android วาดกราฟิกแผงหน้าปัดเรือนไมล์โดยตรง แต่ยังคงต้องการแสดงข้อมูล เช่น คำแนะนำแบบเลี้ยวต่อเลี้ยวหรือชื่อเพลง Android สามารถส่งข้อมูลดังกล่าวได้หลายวิธี อุปกรณ์ Android สามารถส่งเนื้อหาหน้าปัดเป็นรูปแบบต่อไปนี้
- อิงตามข้อมูลเมตา เช่น ส่งข้อความผ่าน CAN ผ่าน
CarVendorExtensionManagerหรือVehicleNetworkServiceระบบคลัสเตอร์ของเครื่องมือวัดต้องสร้างกราฟิกที่เหมาะสมตามข้อมูลเมตา - กราฟิกเป็นพื้นฐาน ไปจนถึงจอแสดงผลจริงหรือเสมือนจริง จอแสดงผลอาจเป็นจอแสดงผลเฉพาะภายในหน้าปัด หรือเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของจอแสดงผลหน้าปัดแบบกราฟิกทั้งหมด
ตัวอย่างสถาปัตยกรรมฮาร์ดแวร์สำหรับจอแสดงผลหน้าปัดแบบกราฟิก
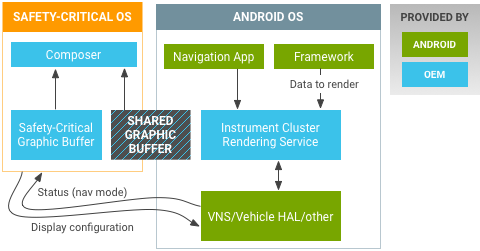
รูปที่ 2 ตัวอย่างจอแสดงผลหน้าปัดแบบกราฟิกของ Android Automotive
ระบบปฏิบัติการที่สำคัญต่อความปลอดภัย (มีหน้าที่แสดงผลคลัสเตอร์เครื่องมือ) และ Android อาจอยู่ใน SoC แบบหลายแกนเดียวกัน (เช่น ใช้ Cortex-R สำหรับระบบปฏิบัติการแบบเรียลไทม์โดยเฉพาะ และ Cortex-A สำหรับ Android) อินเทอร์เฟซอาจเป็น Ethernet AVB (Audio Video Bridge), LVDS หรือ HDMI ใน Android แผงหน้าปัดแบบกราฟิกจะเชื่อมต่อเป็นจอแสดงผลเสมือนได้ ซึ่งจะซ่อนสถาปัตยกรรมฮาร์ดแวร์ไว้เบื้องหลังการใช้งาน Display HAL
ข้อจำกัดของเบาะหลัง
สำหรับความบันเทิงบนที่นั่งด้านหลัง Presentation API มีข้อจำกัดต่อไปนี้
- โปรเจ็กต์กิจกรรมทั้งหมดไม่ได้ (การนำเสนอเป็นกล่องโต้ตอบ)
- โฟกัสเสียงใช้ได้เพียงรายการเดียว
- ไม่มีผู้ใช้ที่ใช้งานพร้อมกัน
- ไม่มีเหตุการณ์การสัมผัสโดยตรงสําหรับจอแสดงผลภายนอก (ต้องใช้ขั้นตอนการแทรกแยกต่างหาก)
