請按照本頁的說明,整合 AAOS 偵錯限制控制器 (DRC)。
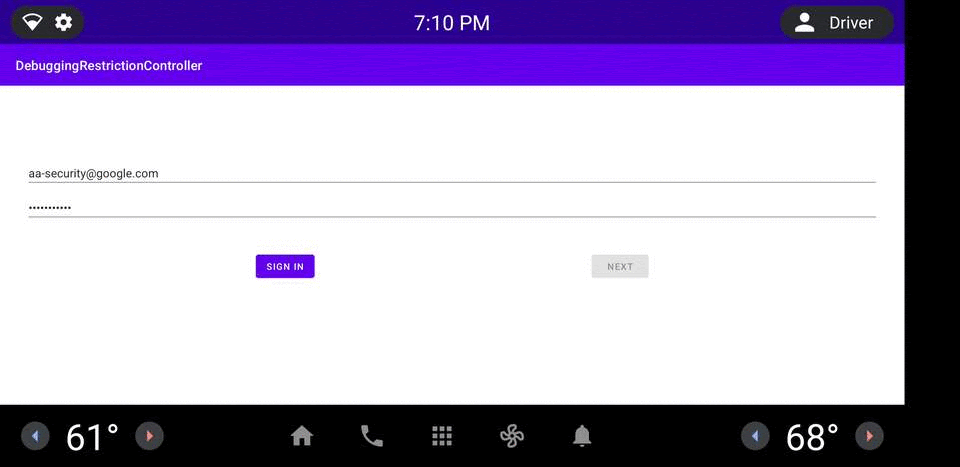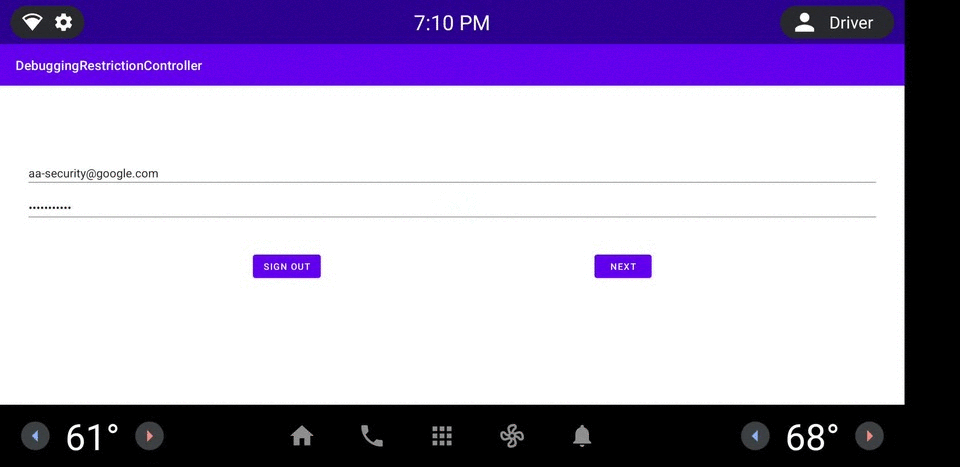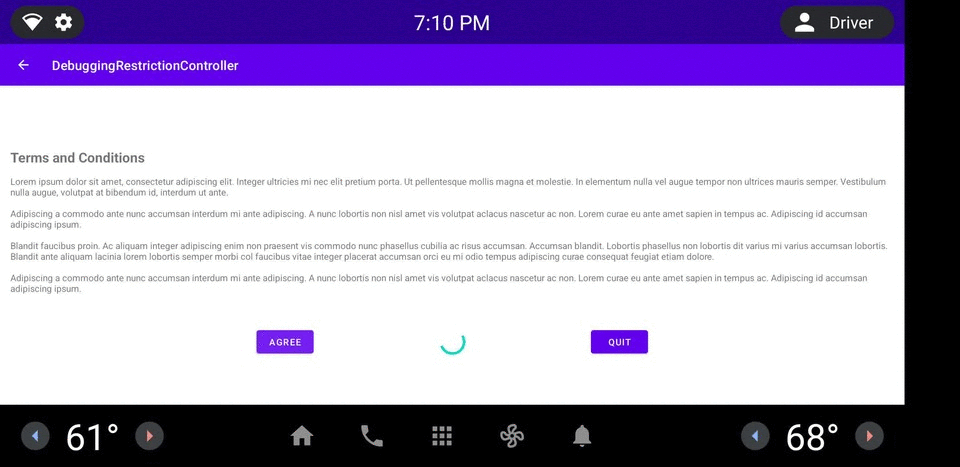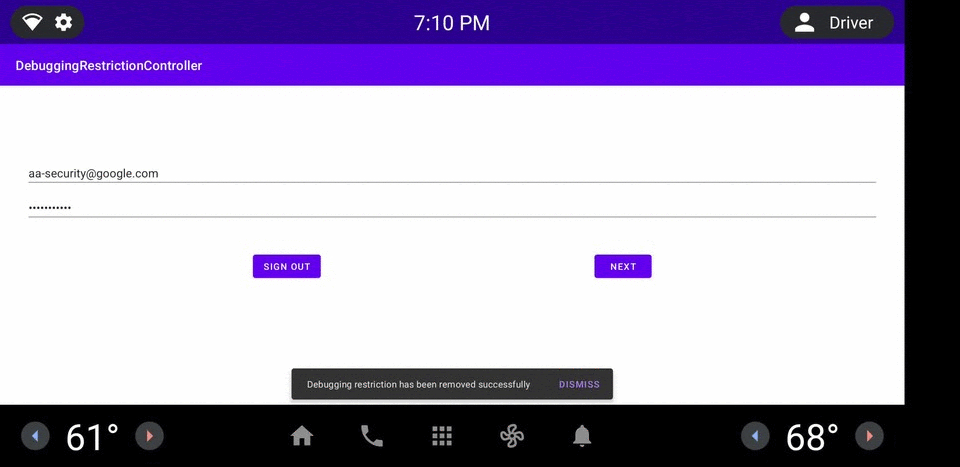
圖 1. DRC 應用程式範例。
建築
DRC 架構如圖 2 所示。以紅色標示的元件 (權杖發出者和 DRC) 會附帶可自訂的參考實作項目。
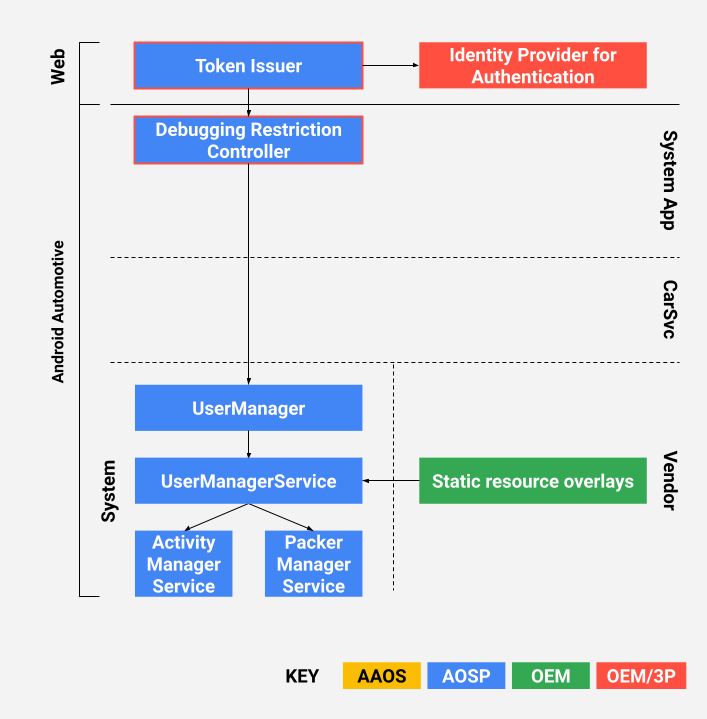
圖 2. DRC 架構。
什麼是 DRC?
車輛主機包含 DRC 應用程式 (請參閱 packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController 中的參考實作項目)。參考應用程式包含從權杖發出者接收存取權杖、驗證權杖,然後根據權杖中指定的內容套用偵錯限制變更的邏輯。邏輯包含車輛端的基本使用者體驗元素。
什麼是符記發出者?
這是一項會發出以密碼編譯簽署的存取權權杖的網頁服務 (請參閱 packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController/server 中的參考實作項目)。參考網頁服務是可部署的 Firebase Cloud 函式 (如要瞭解詳情,請參閱「Cloud Functions for Firebase」)。
必要條件
部署參考實作項目前,請務必完成下列工作。
準備用來簽署存取權杖的憑證
憑證發出者會產生 JSON Web Signature (JWS) 做為存取權杖。為確保最佳相容性,參考發證機構僅支援 RS256 演算法 (含 SHA256 的 RSA 簽章)。為方便金鑰輪替,請使用憑證鏈結 (而非單一憑證) 簽署存取權權杖。一般來說,憑證鏈結應包含根 CA 憑證、中繼 CA 憑證和終端實體憑證。
簽署 JWS 權杖的終端實體憑證與標準 TLS 憑證無異。您可以向 DigiCert 等公開 CA 購買憑證,也可以使用自行簽署的根 CA 憑證或硬體安全模組,維護自己的憑證鏈結。終端實體憑證應為含有主體別名 (SAN) 擴充功能的 X509v3 憑證。SAN 擴充功能包含符記發出者的識別碼 (例如主機名稱)。最後,由於權杖發出者只支援 RS256,因此應優先使用 RSA 憑證,而非 EC 憑證。
Google 提供殼層指令碼,可在 packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController/server/genkey.sh 中產生自行簽署的憑證。
設定 Firebase
參照憑證發出者使用 Firebase 驗證和 Firebase Cloud Function。
如要設定 Firebase 帳戶,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 如要建立 Firebase 專案,請參閱「將 Firebase 新增至 Android 專案」一文。
- 如要啟用部分 Firebase 驗證工具,請參閱「如何開始使用 Firebase 驗證?」。
- 如要新增空白的 Firebase Cloud 函式,請參閱「開始使用」一文。
- 如果尚未完成,請安裝
Node.js、NPM 和 Firebase 工具,以便編譯及部署權杖發出者。
整合 DRC 應用程式
參考的 DRC 應用程式位於 packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController 中。您可以使用 Soong 在 AOSP 中建構已組合的應用程式,也可以使用 Gradle 建構未組合的應用程式。
套裝建構
如要建構套件應用程式,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 將
applicationId、projectId和apiKey從google-services.json複製到packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController/soong/FirebaseApplication.java。這樣一來,DRC 應用程式就能正確連線至 Firebase。 - 請在
packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController/soong/BuildConfig.java中更新這些常數:TOKEN_USES_SELF_SIGNED_CA會指出是否使用自行簽署的根憑證授權單位憑證。啟用後,DRC 應用程式只會信任ROOT_CA_CERT中指定的 PEM 編碼根憑證授權單位憑證。TOKEN_ISSUER_API_NAME是 Firebase 雲端函式的名稱,應與您先前在 Firebase 控制台中建立的雲端函式相符。TOKEN_ISSUER_HOSTNAME應與將為存取權存取權杖簽署的終端實體憑證中的主體別名相符。DRC_TEST_EMAIL和DRC_TEST_PASSWORD是選用測試帳戶的憑證,如果您已啟用電子郵件/密碼登入功能,這些憑證可以在 Firebase 中預先提供。這些值僅用於檢測設備測試。
應用程式現在已設定為使用您的 Firebase 帳戶和憑證。在 Android 9 以上版本中,您必須設定特權權限許可清單。許可清單中至少必須包含 android.permission.MANAGE_USERS。例如:
<permissions> <privapp-permissions package="com.android.car.debuggingrestrictioncontroller"> <permission name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> <permission name="android.permission.MANAGE_USERS"/> </privapp-permissions> </permissions>
未組合的版本
未組合的 DRC 版本會使用 Gradle 編譯應用程式。
如要建立未內含的版本,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 確認您已安裝 Android SDK。
- 在應用程式根目錄中建立名為
local.properties的文字檔案。 - 設定 Android SDK 的位置:
sdk.dir=path/to/android/sdk
- 如要設定 Firebase,請將
google-services.json複製到packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController/app。Gradle 會剖析檔案,並自動設定其餘內容。 - 定義環境變數。如同套件建構作業,您必須指定:
$TOKEN_USES_SELF_SIGNED_CA:true 或 false;$ROOT_CA_CERT:PEM 編碼根 CA 憑證的路徑;$TOKEN_ISSUER_API_NAME:Firebase Cloud 函式的名稱;$TOKEN_ISSUER_HOST_NAME:憑證中的 SAN;$DRC_TEST_EMAIL和$DRC_TEST_EMAIL:測試帳戶的憑證,僅限偵錯版本。
- 如要使用 Gradle 建構應用程式,請執行以下指令:
$ ./gradlew build
整合權杖發出者
參照憑證發出者是 Node.js 中實作的 Firebase Cloud 函式。只有經過驗證的使用者才能呼叫此函式。在部署應用程式之前,您必須設定用於簽署 JWS 權杖的私密金鑰和憑證。
- 將下列內容填入 JSON 檔案:
{ "key": "---BEGIN PRIVATE KEY---\nRSA_PRIVATE_KEY\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n", "certificates.0": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\nTOKEN_SIGNING_CERT\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n", "certificates.1": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\nINTERMEDIATE_CA_CERT\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n", "certificates.2": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\nROOT_CA_CERT\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n", "expiration": "30m", "issuer": "Debugging Access Token Issuer", "audience": "IHU" }
憑證的順序為先列出終端實體憑證,最後是根 CA 憑證。您可以自訂到期期限,如果發出的權杖需要一段時間才能由 DRC 應用程式接收及使用,則可以將到期期限設為較長的時間。系統不支援權杖撤銷。
- 將設定上傳至 Firebase:
- 部署 Firebase Cloud 函式:
- 如要管理及監控權杖發出者,請參閱「管理函式部署和執行階段選項」。
$ firebase functions:config:set api_config="$(cat YOUR_CONFIG.json)"
$ firebase deploy --only functions
設定預設限制
您可以在第一次啟動前套用預設限制。您可以使用靜態資源覆蓋層來執行這項操作,藉此覆寫 Android 架構中的預設值。限制可分別套用至不同類型的使用者。如要瞭解不同類型的使用者,請參閱「多使用者支援」。
無頭系統使用者的預設限制可透過 frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/config.xml 中的 config_defaultFirstUserRestrictions 字串陣列設定。設定這項限制後,系統會自動停用 Android Debug Bridge (ADB),直到移除限制為止,例如:
<string-array translatable="false" name="config_defaultFirstUserRestrictions"> <item>no_debugging_features</item> </string-array>
您可以在 frameworks/base/core/res/res/xml/config_user_types.xml 中設定一般使用者 (例如駕駛員和乘客) 和訪客的預設限制。您可以重疊這些字串,分別為各類型使用者設定預設限制,例如:
<user-types> <full-type name="android.os.usertype.full.SECONDARY" > <default-restrictions no_debugging_features="true"/> </full-type> <full-type name="android.os.usertype.full.GUEST" > <default-restrictions no_debugging_features="true"/> </full-type> </user-types>

