Android supports multiple users settings, apps, and data. Android Automotive relies on Android's multi-user support to provide a shared device experience, wherein each device user is intended to be used by a different physical person. In Android 10 and higher, Android Automotive supports these types of users:
- Headless system user. The headless system user runs in the background and hosts all system services. For Automotive, the system user isn't intended to be used, nor directly accessed, by a physical person.
- Regular user. Automotive devices are shared devices and each user is intended to be used by a different physical person. Android users can have different roles. See Roles and restrictions for more information. In Automotive, all regular users are secondary users.
- Guest user. Automotive users can include temporary users, such as friends, who borrow a vehicle. To accommodate uses like this, Android Automotive provides a guest user with access to all components needed to use the vehicle. Only one guest user can be defined on a device at a time.
The following diagram illustrates how the Automotive headless system user mode supports the multi-user experience:
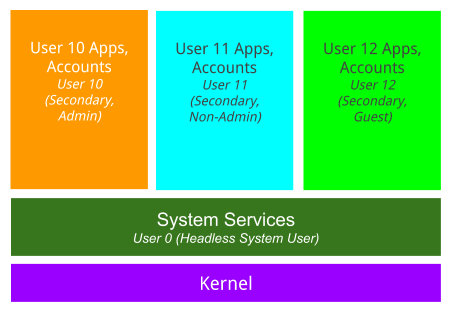
Figure 1. Multi-user experience.
To learn more, see Android Automotive multi-user.
Roles and restrictions
Vehicles are shared devices that may be driven by different people. Each person can have their own user, each with their own apps and data. However, a vehicle owner may not want all users to have the same ability to modify the device. Therefore, Automotive supports the concept of providing users with different roles and restrictions. The following user roles are supported:
- Admin. By default, regular users with the role of admin can perform every task. Admin users can grant the admin role to other users.
- Non-admin. By default, regular users with the role non-admin can't factory data reset the device, grant themselves an admin role, or delete other users.
- Guest. By default, a guest user can neither factory data reset the device nor delete other users. By default, a guest user has other restrictions, such as not being able to modify (add or remove) accounts, install apps, or apply a lockscreen. By default, guest is also ephemeral.
As stated above, each role has a default set of restrictions so that a new user created with that role has the same respective restrictions.
