Android 9 includes support for obtaining the service name of a given HAL instance based on the device on which Vendor Test Suite (VTS) tests are running. Running VTS HAL tests that are service name aware enables developers to automate testing vendor extensions, multiple HALs, and multiple HAL instances on both target- and host-side VTS test runs.
About service names
Each instance of the running HAL service registers itself with a service name.
In previous versions of Android, developers running VTS HAL tests were
required to set the correct service name for the test client in
getService() or leave the name empty and fallback to the default
service name. Disadvantages to this approach included:
- Reliance on the test developer's knowledge to set the correct service name.
- Limited to testing against a single service instance by default.
- Manual maintenance of service names (i.e. because names are hard-coded, they must be manually updated if the service name changes.
In Android 9, developers can automatically get the service name for a given HAL instance based on the device under test. Advantages to this approach include support for testing:
- Vendor HAL extensions. For example, when a vendor has an implementation of camera.provider HAL that runs on vendor devices with a customized service name, VTS can identify the vendor instance and run the test against it.
- Multiple HAL instances. For example, when the
graphics.composerHAL has two instances (one with service name "default" and one with service name "vr"), VTS can identify both instances and run the test against each of them. - Multi-HAL testing. Used when testing multiple HALs with multiple instances For example, when running the VTS test that verifies how the KeyMint (previously Keymaster) and Gatekeeper HALs work together, VTS can test all combinations of service instances for those HALs.
Target-side tests
To enable service name awareness for target-side testing, Android
9 includes a customizable test environment
(VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase)
that provides interfaces to:
- Register targeting HAL(s) in the test.
- List all the registered HAL(s).
- Get service name(s) for registered HAL(s) provided by VTS framework.
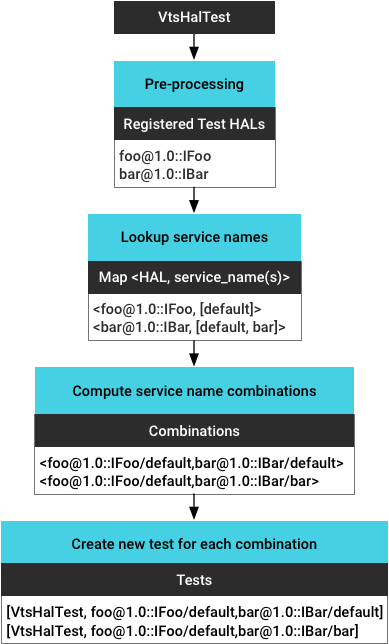
In addition, the VTS framework provides runtime support for:
- Pre-processing the test binary to get all registered test HAL(s).
- Identifying all running service instances and getting the service name for
each instance (retrieved based on
vendor/manifest.xml). - Calculating all instance combinations (to support multiple HAL testing).
- Generating a new test for each service instance (combination).
Example:
Set up service name aware target-side tests
To setup your test environment for target-side service name aware testing:
- Define a
testEnvironmentbased onVtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBaseand register test HALs:#include <VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase.h> class testEnvironment : public::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase { virtual void registerTestServices() override { registerTestService<IFoo>(); } };
- Use
getServiceName()provided by the test environment to pass service name:::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestBase::getService<IFoo>(testEnv->getServiceName<IFoo>("default")); // "default" is the default service name you want to use.
- Register the test environment in
main()andinitTest:int main(int argc, char** argv) { testEnv = new testEnvironment(); ::testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(testEnv); ::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); testEnv->init(argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); }
For additional examples, refer to
VtsHalCameraProviderV2_4TargetTest.cpp.
VTS host-side tests
VTS host-side tests run test scripts on host side instead of test binaries on the target device. To enable service name awareness for these tests, you can use host side templates to run the same test script multiple times against different parameters (similar to the gtest parameterized test).

- The hal test script specifies the targeting HAL service(s) in the test.
- The
hal_hidl_host_test(subclass ofparam_test) takes the registered testing HAL(s) from test script, identifies the corresponding service name(s) for the testing HAL, then generates service name combinations (for multi-HAL testing) as test parameters. It also provides a methodgetHalServiceName()which returns the corresponding service name according to the parameter passed to the current test case. - The param_test template supports logic to accept a list of parameters and run all the given test cases against each parameter. I.e. for each test case it generates N new parameterized test case (N = size of parameters), each with a given parameter.
Set up service name aware host-side tests
To setup your test environment for host-side service name aware testing:
- Specify the target HAL service in the test script:
TEST_HAL_SERVICES = { "android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo" }
- Call
getHalServiceName()and pass the name to init hal:self.dut.hal.InitHidlHal( target_type='foo', target_basepaths=self.dut.libPaths, target_version=1.0, target_package='android.hardware.foo', target_component_name='IFoo', hw_binder_service_name =self.getHalServiceName("android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo"), bits=int(self.abi_bitness))
For additional examples, refer to
VtsHalMediaOmxStoreV1_0HostTest.py.
Register test HALs
In previous versions of Android, VTS identified the testing HAL using the
<precondition-lshal> option configured in
AndroidTest.xml. This approach was difficult to maintain (as it
relied on developers to configure the test properly and update the
configuration accordingly) and inaccurate (as it contained only the package
and version info and not the interface info).
In Android 9, VTS identifies the testing HAL using service name awareness. The registered testing HALs are also useful for:
- Precondition checks. Before running a HAL test, VTS can confirm the testing HAL is available on the target device and skip the tests if it is not (refer to VTS testability check).
- Coverage measurement. VTS supports cross-process code coverage measurement via the knowledge about the testing HAL services it wants to measure (i.e. to flush the coverage for the hal service process).
