The Vendor Native Development Kit (VNDK) requires several changes to a codebase to separate concerns between vendor and system. Use the following guide to enable VNDK in a vendor/OEM codebase.
Build system libraries
The build system contains several types of objects including libraries (shared, static, or header) and binaries.
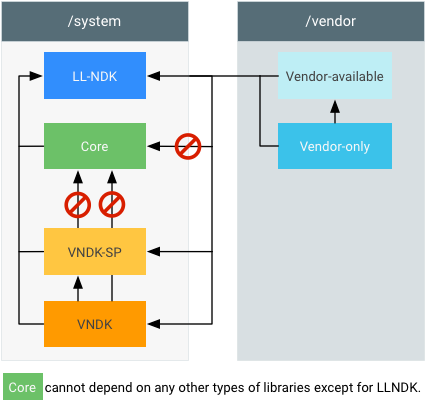
Figure 1. Build system libraries.
corelibraries are used by the system image, on the system image. These libraries can't be used byvendor,vendor_available,vndk, orvndk-splibraries.cc_library { name: "libThatIsCore", ... }
vendor-only(orproprietary) libraries are used by the vendor image, on the vendor image.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorOnly", proprietary: true, # or: vendor: true, # (for things in AOSP) ... }
vendor_availablelibraries are used by the vendor image, on the vendor image (may contain duplicates ofcore).cc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorAvailable", vendor_available: true, ... }
vndklibraries are used by the vendor image, on the system image.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndk", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, } ... }
vndk-splibraries are used by the vendor image, and also by the system image indirectly.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndkSp", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, support_system_process: true, } ... }
llndklibraries are used by both the system and vendor images.cc_library { name: "libThatIsLlndk", llndk: { symbol_file: "libthatisllndk.map.txt" } ... }
When a lib is marked as vendor_available:true, it's built
twice:
- Once for platform (and thus installed to
/system/lib) - Once for vendor (and thus installed to
/vendor/libor VNDK APEX)
The vendor versions of libs are built with -D__ANDROID_VNDK__.
Private system components that may change significantly in future versions of
Android are disabled with this flag. In addition, different libraries export a
different set of headers (such as liblog). Options specific to a
vendor variant of a target can be specified in an Android.bp file
in:
target: { vendor: { … } }Enable VNDK for a codebase
To enable the VNDK for a codebase:
- Determine eligibility by calculating the required sizes of
vendor.imgandsystem.imgpartitions. - Enable
BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current. You can add toBoardConfig.mkor build components with it directly (for example,m -j BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current MY-LIB).
After enabling BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current, the build system
enforces the following dependency and header requirements.
Manage dependencies
A vendor object that depends on a core component
that doesn't exist in vndk or as a vendor object
must be resolved using one of the following options:
- The dependency can be removed.
- If the
corecomponent is owned byvendor, it can be marked asvendor_availableorvendor. - A change making the core object part of the
vndkmay be upstreamed to Google.
In addition, if a core component has dependencies on a
vendor component, the vendor component must be made
into a core component or the dependency must be
removed in another way (for example, by removing the dependency or by moving the
dependency into a vendor component).
Manage headers
Global header dependencies must be removed to enable the build system to know
whether to build the headers with or without -D__ANDROID_VNDK__.
For example, libutils headers such as utils/StrongPointer.h can
still be accessed using the header library
libutils_headers.
Some headers (such as unistd.h) can no longer be included transitively
but can be included locally.
Finally, the public part of private/android_filesystem_config.h
has been moved to cutils/android_filesystem_config.h. To manage
these headers, do one of the following:
- Remove the dependency to
private/android_filesystem_config.hby replacing allAID_*macros withgetgrnam/getpwnamcalls if possible. For example:(uid_t)AID_WIFIbecomesgetpwnam("wifi")->pw_uid.(gid_t)AID_SDCARD_Rbecomesgetgrnam("sdcard_r")->gr_gid.
private/android_filesystem_config.h. - For hard-coded AIS, include
cutils/android_filesystem_config.h.
