The Android kernel is based on an upstream Linux Long Term Supported (LTS) kernel. At Google, LTS kernels are combined with Android-specific patches to form Android Common Kernels (ACKs).
ACKs are built from the kernel/common repository. This repository is a superset of the upstream Linux kernel, with additional Android-specific patches.
ACKs that are 5.10 and higher are also known as *generic kernel images (GKI) kernels. GKI kernels support the separation of the hardware-agnostic generic core kernel code and GKI modules from hardware-specific vendor modules.
The interaction between the GKI kernel and vendor modules is enabled by the Kernel Module Interface (KMI) consisting of symbol lists identifying the functions and global data required by vendor modules. Figure 1 shows the GKI kernel and vendor module architecture:
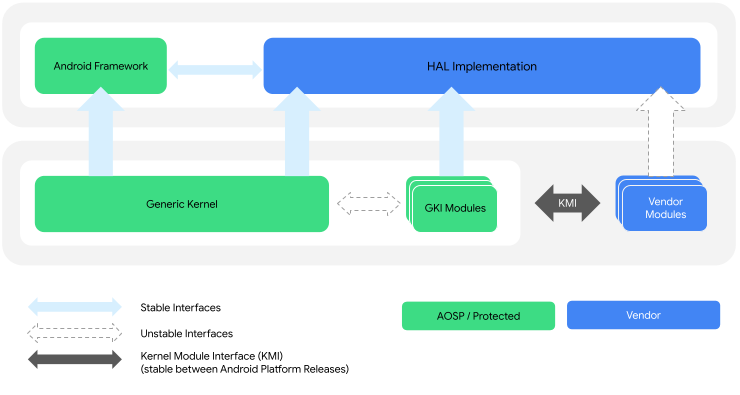
Figure 1. GKI kernel and vendor module architecture.
Kernel glossary
Following are terms used throughout the kernel documentation.
Kernel types
- Android Common Kernel (ACK)
- A kernel that is downstream of a LTS kernel and includes patches that are important to the Android community. These patches haven't been merged into Linux mainline or Long Term GKI kernels.
Kernel with versions of 5.10 and higher are also referred to as Generic Kernel Image (GKI) kernels.
- Android Open Source Project (AOSP) kernel
- See Android Common Kernel.
Android 12 features can't be backported to 4.19 kernels; the feature set would be similar to a device that launched with 4.19 on Android 11 and upgraded to Android 12.
- Generic Kernel Image (GKI) kernel
Any 5.10 and higher ACK kernel(aarch64 only). The GKI kernel has these two parts:
Generic kernel - The portion of the GKI kernel that is common across all devices.
GKI modules - Kernel modules built by Google that can be dynamically loaded on devices where applicable. These modules are built as artifacts of the GKI kernel and are delivered alongside GKI as the
system_dlkm_staging_archive.tar.gzarchive. GKI modules are signed by Google using the kernel build time key pair and are compatible only with the GKI kernel that they're built with.
- Kernel Module Interface (KMI) kernel
See GKI kernel.
- Long Term Supported (LTS) kernel
A Linux kernel that's supported for 2 to 6 years. LTS kernels are released once per year and are the basis for each of Google's Android Common Kernels.
Branch types
- ACK KMI kernel branch
- The branch for which GKI kernels are built. Branch names correspond
to kernel versions, such as
android15-6.6. - Android-mainline
- The primary development branch for Android features. When a new LTS kernel is declared upstream, the corresponding new GKI kernelGKI kernel is branched from android-mainline.
Linux mainline :The primary development branch for the upstream Linux kernels, including LTS kernels.
Other terms
- Certified boot image
- The kernel delivered in binary form (
boot.img) and flashed onto the device. This image is considered certified because contains embedded certificates so Google can verify that the device ships with a kernel certified by Google. - Dynamically loadable kernel module (DLKM)
- A module that can be dynamically loaded during device boot depending on the
needs of the device. GKI and vendor modules are both types of DLKMs. DLKMs are
released in
.koform and can be drivers or can deliver other kernel functionality. - GKI project
- A Google project addressing kernel fragmentation by separating common core kernel functionality from vendor-specific SoC and board support into loadable modules.
Generic Kernel Image (GKI) :A boot image certified by Google that contains a GKI kernel built from an ACK source tree and is suitable to be flashed to the boot partition of an Android-powered device.
- Kernel Module Interface (KMI)
- An interface between the GKI kernel and vendor modules allowing vendor modules to be updated independently of the GKI kernel. This interface consists of kernel functions and global data that have been identified as vendor/OEM dependencies using per-partner symbol lists.
- Vendor module
- A hardware-specific module developed by a partner and that contains SoC and device-specific functionality. A vendor module is a type of dynamically loadable kernel module.
What's next
If you're new to Android kernel development, start by reading the following:
- Long Term Stable Kernels - Background on upstream LTS kernels which feed into ACKs.
- Android Common Kernels - Background on ACKs.
If you're new to GKI kernel development, start by reading GKI development.
