Se o blob da árvore de dispositivos (DTB, na sigla em inglês) ou da sobreposição de blob da árvore de dispositivos (DTBO, na sigla em inglês) estiver em uma partição exclusiva,
por exemplo, as partições dtb e dtbo, use a estrutura de tabela
e o formato de cabeçalho abaixo:
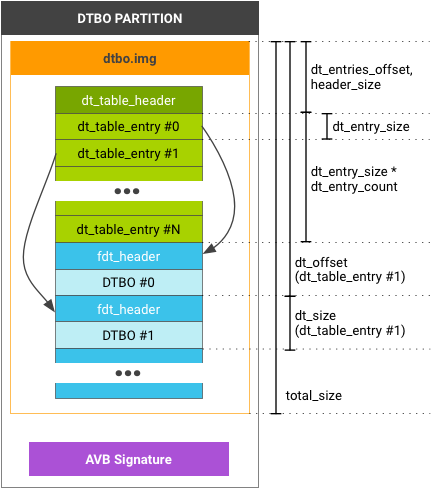
Figura 1. Exemplo de layout de partição DTB e DTBO.
Estruturas de dados
O dt_table_header é somente para a
partição dtb/dtbo. NÃO É POSSÍVEL anexar esse formato
após o final do image.gz. Se você tiver um único DTB ou DTBO, ainda
precisa usar esse formato (e o dt_entry_count em
dt_table_header é 1).
#define DT_TABLE_MAGIC 0xd7b7ab1e
struct dt_table_header {
uint32_t magic; // DT_TABLE_MAGIC
uint32_t total_size; // includes dt_table_header + all dt_table_entry
// and all dtb/dtbo
uint32_t header_size; // sizeof(dt_table_header)
uint32_t dt_entry_size; // sizeof(dt_table_entry)
uint32_t dt_entry_count; // number of dt_table_entry
uint32_t dt_entries_offset; // offset to the first dt_table_entry
// from head of dt_table_header
uint32_t page_size; // flash page size we assume
uint32_t version; // DTBO image version, the current version is 0.
// The version is incremented when the
// dt_table_header struct is updated.
};
struct dt_table_entry {
uint32_t dt_size;
uint32_t dt_offset; // offset from head of dt_table_header
uint32_t id; // optional, must be zero if unused
uint32_t rev; // optional, must be zero if unused
uint32_t custom[4]; // optional, must be zero if unused
};Para ler todos os dt_table_entry, use dt_entry_size,
dt_entry_count e dt_entries_offset. Exemplo:
my_read(entries_buf, header_addr + header->dt_entries_offset, header->dt_entry_size * header->dt_entry_count);
id, rev e custom em
dt_table_entry são identificações de hardware opcionais da árvore
de dispositivos que o carregador de inicialização pode usar para identificar de maneira eficiente o DTB ou o DTBO a ser carregado. Se o
bootloader precisar de mais informações, coloque-as no DTB ou DTBO, onde
o bootloader possa lê-las analisando o DTB ou DTBO (consulte o exemplo de código abaixo).
Exemplo de código
O exemplo de código a seguir verifica a identificação de hardware no carregador de inicialização.
- A função
check_dtbo()verifica a identificação do hardware. Primeiro, ele verifica os dados na estruturadt_table_entry(id,revetc.). Se esses dados não forem suficientes, os dadosdtbserão carregados na memória e o valor será verificado emdtb. - Os valores das propriedades
my_hw_informationesoc_idsão analisados no nó raiz (exemplo emmy_dtbo_1.dts).[my_dtbo_1.dts] /dts-v1/; /plugin/; / { /* As DTS design, these properties only for loader, won't overlay */ compatible = "board_manufacturer,board_model"; /* These properties are examples */ board_id = <0x00010000>; board_rev = <0x00010001>; another_hw_information = "some_data"; soc_id = <0x68000000>; ... }; &device@0 { value = <0x1>; status = "okay"; }; [my_bootloader.c] int check_dtbo(const dt_table_entry *entry, uint32_t header_addr) { ... if (entry->id != ... || entry->rev != ...) { ... } ... void * fdt_buf = my_load_dtb(header_addr + entry->dt_offset, entry->dt_size); int root_node_off = fdt_path_offset(fdt_buf, "/"); ... const char *my_hw_information = (const char *)fdt_getprop(fdt_buf, root_node_off, "my_hw_information", NULL); if (my_hw_information != NULL && strcmp(my_hw_information, ...) != 0) { ... } const fdt32_t *soc_id = fdt_getprop(fdt_buf, root_node_off, "soc_id", NULL); if (soc_id != NULL && *soc_id != ...) { ... } ... }
mkdtimg
mkdtimg é uma ferramenta para criar
imagens dtb/dtbo
(código-fonte
em system/libufdt no AOSP). mkdtimg oferece suporte a
vários comandos, incluindo create, cfg_create e
dump.
create
Use o comando create para criar uma
imagem dtb/dtbo:
mkdtimg create <image_filename> (<global-option>...) \
<ftb1_filename> (<entry1_option>...) \
<ftb2_filename> (<entry2_option>...) \
...
ftbX_filename gera um dt_table_entry na
imagem. entryX_options são os valores a serem atribuídos a
dt_table_entry. Esses valores podem ser um dos seguintes:
--id=<number|path> --rev=<number|path> --custom0=<number|path> --custom1=<number|path> --custom2=<number|path> --custom3=<number|path>
Os valores numéricos podem ser um dígito de 32 bits (como 68000) ou um número hexadecimal (como 0x6800). Como alternativa, especifique um caminho usando o formato:
<full_node_path>:<property_name>
Por exemplo, /board/:id. mkdtimg lê o valor
do caminho no arquivo DTB ou DTBO e atribui o valor (32 bits) a uma propriedade
relativa em dt_table_entry. Como alternativa, você pode definir um
global_option como opção padrão para todas as entradas. O valor
padrão de page_size em dt_table_header é 2048. Use
global_option --page_size=<number> para atribuir um valor
diferente.
Exemplo:
[board1.dts]
/dts-v1/;
/plugin/;
/ {
compatible = "board_manufacturer,board_model";
board_id = <0x00010000>;
board_rev = <0x00010001>;
another_hw_information = "some_data";
...
};
&device@0 {
value = <0x1>;
status = "okay";
};
mkdtimg create dtbo.img --id=/:board_id --custom0=0xabc \
board1.dtbo \
board2.dtbo --id=0x6800 \
board3.dtbo --id=0x6801 --custom0=0x123
- O primeiro
dt_table_entry(board1.dtbo)idé0x00010000ecustom[0]é0x00000abc. - O segundo
idé0x00006800, ecustom[0]é0x00000abc. - O terceiro
idé0x00006801, ecustom[0]é0x00000123. - Todos os outros usam o valor padrão (
0).
cfg_create
O comando cfg_create cria uma imagem com um arquivo de configuração no
formato a seguir:
# global options <global_option> ... # entries <ftb1_filename> # comment <entry1_option> # comment ... <ftb2_filename> <entry2_option> ... ...
As opções global_option e entryX_option precisam começar
com um ou mais caracteres de espaço. Essas opções são iguais às
opções create, sem o prefixo --. Linhas vazias ou
que começam com # são ignoradas.
Exemplo:
[dtboimg.cfg]
# global options
id=/:board_id
rev=/:board_rev
custom0=0xabc
board1.dtbo
board2.dtbo
id=0x6800 # override the value of id in global options
board2.dtbo
id=0x6801 # override the value of id in global options
custom0=0x123 # override the value of custom0 in global options
mkdtimg cfg_create dtbo.img dtboimg.cfg
O mkdtimg não processa o alinhamento de
arquivos .dtb/.dtbo, mas os anexa à imagem.
Quando você usa dtc para compilar .dts em
.dtb/.dtbo, é necessário adicionar a opção -a. Por
exemplo, adicionar a opção -a 4 adiciona padding para que o tamanho de
.dtb/.dtbo seja alinhado a 4 bytes.
Várias entradas de tabela de DT podem compartilhar um .dtb/.dtbo. Se
você usar o mesmo nome de arquivo para entradas diferentes, ele armazena apenas um conteúdo na
imagem com o mesmo dt_offset e dt_size. Isso é
útil ao usar hardwares diferentes com DTs idênticos.
despeje
Para imagens dtb/dtbo, use o comando dump
para imprimir as informações na imagem. Exemplo:
mkdtimg dump dtbo.img
dt_table_header:
magic = d7b7ab1e
total_size = 1300
header_size = 32
dt_entry_size = 32
dt_entry_count = 3
dt_entries_offset = 32
page_size = 2048
version = 0
dt_table_entry[0]:
dt_size = 380
dt_offset = 128
id = 00010000
rev = 00010001
custom[0] = 00000abc
custom[1] = 00000000
custom[2] = 00000000
custom[3] = 00000000
(FDT)size = 380
(FDT)compatible = board_manufacturer,board_model
...
