Remote Key Provisioning (RKP) has been a part of AOSP since Android 12. Android 14 introduces a remote provisioning updatable module that increases feature resilience by improving the robustness of the service API and decreasing the time to introduce any improvements to it.
Motivation
Simplify the RKP service by packaging everything into an APEX.
Before Android 14, RKP was separated into an app,
RemoteProvisioner, and Keystore 2.0. The RemoteProvisioner app was
responsible for contacting the RKP backend, and Keystore 2.0 was responsible for
both storing the keys and communicating with HALs. This wasn't a good
architecture because RKP keys are significantly different from Keystore keys in
terms of attached metadata. Additionally, this required awkward modifications to
the Keystore framework code to alert RemoteProvisioner about potential
resource starvation.
RKP as a Mainline module is designed to improve on these points by neatly packing everything into an APEX.
Module boundary
The RKP Mainline APEX, com.android.rkpd, contains the Remote Key Provisioning
Daemon (RKPD) application and a remote provisioning system server component
(built with Java).
Stack architecture
Figure 1 illustrates the RKP stack architecture.
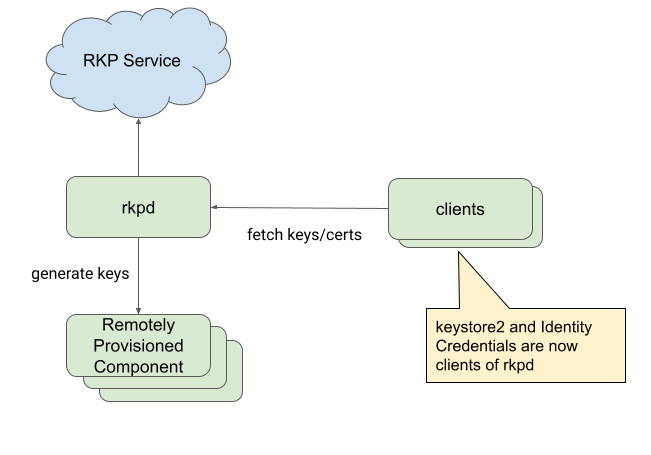
Figure 1. RKP stack architecture.
Internal architecture
Figure 2 illustrates the RKP internal architecture.
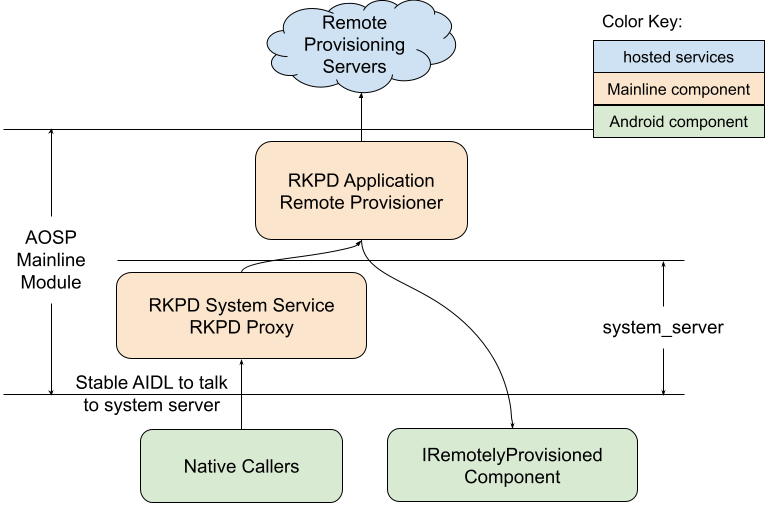
Figure 2. RKP internal architecture.
Additional information about the RKP internal architecture:
RKPD Mainline APEX -
com.android.rkpd- RKPD app (Java)
packages/modules/RemoteKeyProvisioning/app
- RKPD system server fragment (Java)
packages/modules/RemoteKeyProvisioning/system-server
- RKPD app (Java)
HAL interface/implementation (Rust/C++)
IRemotelyProvisionedComponenthardware/interfaces/security/keymint
Package format
The application and other functionalities of the module are packaged as APEX
file com.android.rkpd.
Dependencies
The RKP module continues to depend on the existence of
IRemotelyProvisionedComponent implementations to provide the attestation keys
and certificate requests.
Testing strategy
The AOSP version of the application APEX contains unit tests that OEMs can run.
