If your device tree blob (DTB) or device tree blob for overlay (DTBO) is in a unique partition,
for example, the dtb and dtbo partition, use the following table structure
and header format:
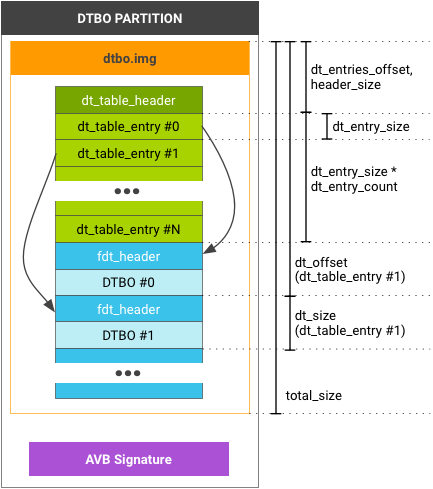
Figure 1. Example DTB and DTBO partition layout.
Data structures
The dt_table_header is only for the
dtb/dtbo partition; you CAN'T append this format
after the end of image.gz. If you have a single DTB or DTBO, you must
still use this format (and the dt_entry_count in
dt_table_header is 1).
#define DT_TABLE_MAGIC 0xd7b7ab1e
struct dt_table_header {
uint32_t magic; // DT_TABLE_MAGIC
uint32_t total_size; // includes dt_table_header + all dt_table_entry
// and all dtb/dtbo
uint32_t header_size; // sizeof(dt_table_header)
uint32_t dt_entry_size; // sizeof(dt_table_entry)
uint32_t dt_entry_count; // number of dt_table_entry
uint32_t dt_entries_offset; // offset to the first dt_table_entry
// from head of dt_table_header
uint32_t page_size; // flash page size we assume
uint32_t version; // DTBO image version, the current version is 0.
// The version is incremented when the
// dt_table_header struct is updated.
};
struct dt_table_entry {
uint32_t dt_size;
uint32_t dt_offset; // offset from head of dt_table_header
uint32_t id; // optional, must be zero if unused
uint32_t rev; // optional, must be zero if unused
uint32_t custom[4]; // optional, must be zero if unused
};To read all dt_table_entry, use the dt_entry_size,
dt_entry_count, and dt_entries_offset. Example:
my_read(entries_buf, header_addr + header->dt_entries_offset, header->dt_entry_size * header->dt_entry_count);
The id, rev, custom in
dt_table_entry are optional hardware identifications of the device
tree the bootloader can use to efficiently identify the DTB or DTBO to load. If the
bootloader requires additional information, put it in the DTB or DTBO where
bootloader can read it by parsing DTB or DTBO (see the sample code below).
Sample code
The following sample code checks the hardware identification in bootloader.
- The
check_dtbo()function checks the hardware identification. It first checks the data in structdt_table_entry(id,rev, etc.). If this data isn't enough, it loadsdtbdata into memory and checks the value indtb. - The values of
my_hw_informationandsoc_idproperties are parsed in the root node (example inmy_dtbo_1.dts).[my_dtbo_1.dts] /dts-v1/; /plugin/; / { /* As DTS design, these properties only for loader, won't overlay */ compatible = "board_manufacturer,board_model"; /* These properties are examples */ board_id = <0x00010000>; board_rev = <0x00010001>; another_hw_information = "some_data"; soc_id = <0x68000000>; ... }; &device@0 { value = <0x1>; status = "okay"; }; [my_bootloader.c] int check_dtbo(const dt_table_entry *entry, uint32_t header_addr) { ... if (entry->id != ... || entry->rev != ...) { ... } ... void * fdt_buf = my_load_dtb(header_addr + entry->dt_offset, entry->dt_size); int root_node_off = fdt_path_offset(fdt_buf, "/"); ... const char *my_hw_information = (const char *)fdt_getprop(fdt_buf, root_node_off, "my_hw_information", NULL); if (my_hw_information != NULL && strcmp(my_hw_information, ...) != 0) { ... } const fdt32_t *soc_id = fdt_getprop(fdt_buf, root_node_off, "soc_id", NULL); if (soc_id != NULL && *soc_id != ...) { ... } ... }
mkdtimg
mkdtimg is a tool for creating
dtb/dtbo images
(source
code at system/libufdt in AOSP). mkdtimg supports
several commands, including create, cfg_create, and
dump.
create
Use the create command to create a
dtb/dtbo image:
mkdtimg create <image_filename> (<global-option>...) \
<ftb1_filename> (<entry1_option>...) \
<ftb2_filename> (<entry2_option>...) \
...
ftbX_filename generates a dt_table_entry in the
image. entryX_options are the values to assign to
dt_table_entry. These values can be any of the following:
--id=<number|path> --rev=<number|path> --custom0=<number|path> --custom1=<number|path> --custom2=<number|path> --custom3=<number|path>
Number values can be a 32-bit digit (such as 68000) or a hex number (such as 0x6800). Alternatively, you can specify a path using the format:
<full_node_path>:<property_name>
For example, /board/:id. mkdtimg reads the value
from the path in the DTB or DTBO file and assigns the value (32-bit) to a relative
property in dt_table_entry. Alternatively, you can give a
global_option as a default option for all entries. The default
value of page_size in dt_table_header is 2048; use
global_option --page_size=<number> to assign a different
value.
Example:
[board1.dts]
/dts-v1/;
/plugin/;
/ {
compatible = "board_manufacturer,board_model";
board_id = <0x00010000>;
board_rev = <0x00010001>;
another_hw_information = "some_data";
...
};
&device@0 {
value = <0x1>;
status = "okay";
};
mkdtimg create dtbo.img --id=/:board_id --custom0=0xabc \
board1.dtbo \
board2.dtbo --id=0x6800 \
board3.dtbo --id=0x6801 --custom0=0x123
- First
dt_table_entry(board1.dtbo)idis0x00010000andcustom[0]is0x00000abc. - Second
idis0x00006800andcustom[0]is0x00000abc. - Third
idis0x00006801andcustom[0]is0x00000123. - All others use the default value (
0).
cfg_create
The cfg_create command creates an image with a config file in
the following format:
# global options <global_option> ... # entries <ftb1_filename> # comment <entry1_option> # comment ... <ftb2_filename> <entry2_option> ... ...
Options global_option and entryX_option must start
with one or more space characters (these options are the same as
create options, without the -- prefix). Empty lines or
lines beginning with # are ignored.
Example:
[dtboimg.cfg]
# global options
id=/:board_id
rev=/:board_rev
custom0=0xabc
board1.dtbo
board2.dtbo
id=0x6800 # override the value of id in global options
board2.dtbo
id=0x6801 # override the value of id in global options
custom0=0x123 # override the value of custom0 in global options
mkdtimg cfg_create dtbo.img dtboimg.cfg
mkdtimg doesn't handle alignment for
.dtb/.dtbo files but rather appends them to the image.
When you use dtc to compile .dts to
.dtb/.dtbo, you must add option -a. For
example, adding the option -a 4 adds padding so the size of
.dtb/.dtbo aligns to 4 bytes.
Several DT table entries can share a .dtb/.dtbo. If
you use the same filename for different entries, it stores only one content in
the image with same dt_offset and dt_size. This is
useful when using different hardware with identical DTs.
dump
For dtb/dtbo images, use the dump
command to print the information in the image. Example:
mkdtimg dump dtbo.img
dt_table_header:
magic = d7b7ab1e
total_size = 1300
header_size = 32
dt_entry_size = 32
dt_entry_count = 3
dt_entries_offset = 32
page_size = 2048
version = 0
dt_table_entry[0]:
dt_size = 380
dt_offset = 128
id = 00010000
rev = 00010001
custom[0] = 00000abc
custom[1] = 00000000
custom[2] = 00000000
custom[3] = 00000000
(FDT)size = 380
(FDT)compatible = board_manufacturer,board_model
...
