Untuk menerapkan update over-the-air (OTA), bootloader harus dapat mengakses disk RAM pemulihan selama booting. Jika perangkat
menggunakan image pemulihan AOSP yang tidak dimodifikasi, bootloader akan membaca 32 byte pertama
di partisi misc; jika data di sana cocok dengan boot-recovery, bootloader akan melakukan booting ke image recovery. Metode ini memungkinkan pekerjaan pemulihan
yang tertunda (misalnya, menerapkan OTA atau menghapus data) untuk terus
berlanjut hingga selesai.
Untuk mengetahui detail konten blok di flash yang digunakan untuk komunikasi oleh pemulihan dan bootloader, lihat bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h.
Perangkat dengan update A/B
Untuk mendukung update OTA di perangkat yang menggunakan update A/B, pastikan bootloader perangkat memenuhi kriteria berikut.
Kriteria umum
Semua partisi yang diupdate melalui OTA harus dapat diupdate saat sistem utama di-boot (dan tidak diupdate dalam pemulihan).
Untuk mem-boot partisi
system, bootloader meneruskan nilai berikut pada command line kernel:ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/init.Framework Android bertanggung jawab untuk memanggil
markBootSuccessfuldari HAL. Bootloader tidak boleh menandai partisi sebagai berhasil di-boot.
Dukungan untuk HAL kontrol booting
Bootloader harus mendukung HAL boot_control sebagaimana ditentukan dalam
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h. Pengupdate mengkueri
HAL kontrol booting,
mengupdate slot booting yang tidak digunakan, mengubah slot aktif menggunakan
HAL, dan melakukan booting ulang ke sistem operasi yang diupdate. Untuk mengetahui detailnya, lihat
Menerapkan HAL kontrol booting.
Dukungan untuk slot
Bootloader harus mendukung fungsi terkait partisi dan slot, termasuk:
Nama partisi harus menyertakan akhiran yang mengidentifikasi partisi mana yang termasuk dalam slot tertentu di bootloader. Untuk setiap partisi tersebut, ada variabel
has-slot:partition base nameyang sesuai dengan nilaiyes. Slot diberi nama secara alfabetis sebagai a, b, c, dll. yang sesuai dengan partisi dengan akhiran_a,_b,_c, dll. Bootloader harus memberi tahu sistem operasi slot mana yang di-boot menggunakan properti command lineandroidboot.slot_suffix. Properti ini disetel melalui bootconfig untuk perangkat yang diluncurkan dengan Android 12 atau yang lebih tinggi.Nilai
slot-retry-countdireset ke nilai positif (biasanya3), baik oleh HAL kontrol booting melalui callbacksetActiveBootSlotatau melalui perintahfastboot set_active. Saat mengubah partisi yang merupakan bagian dari slot, bootloader akan menghapus "berhasil di-boot" dan mereset jumlah percobaan ulang untuk slot.
Bootloader juga harus menentukan slot mana yang akan dimuat. Gambar menunjukkan contoh proses pengambilan keputusan.
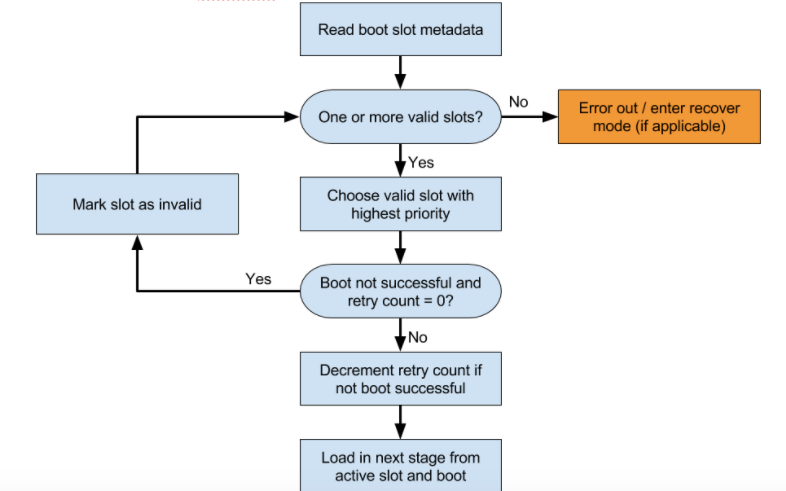
Tentukan slot yang akan dicoba. Jangan mencoba memuat slot yang ditandai
slot-unbootable. Slot ini harus konsisten dengan nilai yang ditampilkan oleh fastboot, dan disebut sebagai slot saat ini.Jika slot saat ini tidak ditandai sebagai
slot-successfuldan memilikislot-retry-count = 0, tandai slot saat ini sebagaislot-unbootable. Kemudian pilih slot lain yang tidak ditandaiunbootabledan ditandai sebagaislot-successful; slot ini sekarang menjadi slot yang dipilih. Jika tidak ada slot saat ini yang tersedia, lakukan booting ke pemulihan atau tampilkan pesan error yang bermakna kepada pengguna.Pilih
boot.imgyang sesuai dan sertakan jalur ke partisi sistem yang benar di command line kernel.Isi parameter command line kernel
slot_suffix.Booting. Jika tidak ditandai
slot-successful, kurangislot-retry-count.
Utilitas fastboot menentukan partisi mana yang akan di-flash saat menjalankan perintah flash apa pun. Misalnya, menjalankan perintah fastboot flash system system.img
terlebih dahulu akan mengkueri variabel current-slot, lalu menggabungkan hasilnya
ke sistem untuk membuat nama partisi yang harus di-flash
(system_a, system_b, dll.).
Saat menyetel slot saat ini menggunakan perintah fastboot set_active atau perintah
HAL kontrol booting setActiveBootSlot, bootloader harus memperbarui
slot saat ini, menghapus slot-unbootable dan slot-successful, serta mereset
jumlah percobaan ulang (ini adalah satu-satunya cara untuk menghapus slot-unbootable).
Perangkat tanpa update A/B
Untuk mendukung update OTA di perangkat yang tidak menggunakan update A/B (lihat Perangkat yang dapat diupdate Non-A/B), pastikan bootloader perangkat memenuhi kriteria berikut.
Partisi
recoveryharus berisi image yang dapat membaca image sistem dari beberapa partisi yang didukung (cache,userdata) dan menuliskannya ke partisisystem.Bootloader harus mendukung booting langsung ke mode pemulihan.
Jika update gambar radio didukung, partisi
recoveryjuga harus dapat mem-flash radio. Hal ini dapat dilakukan dengan salah satu dari dua cara berikut:Bootloader mem-flash radio. Dalam hal ini, Anda dapat melakukan reboot dari partisi pemulihan kembali ke bootloader untuk menyelesaikan update.
Gambar pemulihan mem-flash radio. Fungsi ini dapat disediakan sebagai library atau utilitas biner.
