ওভার-দ্য-এয়ার (OTA) আপডেটগুলি বাস্তবায়ন করতে, বুটলোডারকে অবশ্যই বুট করার সময় একটি পুনরুদ্ধার RAM ডিস্ক অ্যাক্সেস করতে সক্ষম হতে হবে। যদি ডিভাইসটি একটি অপরিবর্তিত AOSP রিকভারি ইমেজ ব্যবহার করে, বুটলোডার misc পার্টিশনের প্রথম 32 বাইট পড়ে; যদি সেখানে ডেটা boot-recovery সাথে মেলে, বুটলোডার recovery চিত্রে বুট করে। এই পদ্ধতিটি যেকোন মুলতুবি পুনরুদ্ধারের কাজকে সক্ষম করে (উদাহরণস্বরূপ, একটি OTA প্রয়োগ করা বা ডেটা অপসারণ) সম্পূর্ণ করা চালিয়ে যেতে।
পুনরুদ্ধার এবং বুটলোডার দ্বারা যোগাযোগের জন্য ব্যবহৃত ফ্ল্যাশে ব্লকের বিষয়বস্তুর বিশদ বিবরণের জন্য, bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h দেখুন।
A/B আপডেট সহ ডিভাইস
A/B আপডেট ব্যবহার করে এমন ডিভাইসে OTA আপডেট সমর্থন করতে, ডিভাইস বুটলোডার নিম্নলিখিত মানদণ্ড পূরণ করে তা নিশ্চিত করুন।
সাধারণ মানদণ্ড
একটি OTA এর মাধ্যমে আপডেট করা সমস্ত পার্টিশন আপডেট করা উচিত যখন মূল সিস্টেম বুট করা হয় (এবং পুনরুদ্ধারের সময় আপডেট করা হয় না)।
systemপার্টিশন বুট করার জন্য, বুটলোডার কার্নেল কমান্ড লাইনে নিম্নলিখিত মান পাস করে:ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/init।HAL থেকে
markBootSuccessfulকল করার দায়িত্ব Android ফ্রেমওয়ার্কের। বুটলোডার কখনোই কোনো পার্টিশনকে সফলভাবে বুট হয়েছে বলে চিহ্নিত করা উচিত নয়।
বুট কন্ট্রোল HAL এর জন্য সমর্থন
বুটলোডারকে অবশ্যই boot_control HAL সমর্থন করতে হবে যা hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h এ সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয়েছে। আপডেটার বুট কন্ট্রোল HAL-কে জিজ্ঞাসা করে, ব্যবহার না করা বুট স্লট আপডেট করে, HAL ব্যবহার করে সক্রিয় স্লট পরিবর্তন করে এবং আপডেট করা অপারেটিং সিস্টেমে রিবুট করে। বিস্তারিত জানার জন্য, বুট কন্ট্রোল HAL বাস্তবায়ন দেখুন।
স্লট জন্য সমর্থন
বুটলোডার অবশ্যই পার্টিশন এবং স্লটের সাথে সম্পর্কিত কার্যকারিতা সমর্থন করবে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে:
পার্টিশনের নামগুলির মধ্যে একটি প্রত্যয় অন্তর্ভুক্ত করা আবশ্যক যা বুটলোডারের একটি নির্দিষ্ট স্লটের কোন পার্টিশনগুলিকে চিহ্নিত করে। এই ধরনের প্রতিটি পার্টিশনের জন্য, একটি সংশ্লিষ্ট ভেরিয়েবল has-slot:
yesএর মান সহhas-slot: partition base name।_a,_b,_c, ইত্যাদি প্রত্যয় যুক্ত পার্টিশনের সাথে সঙ্গতিপূর্ণ a, b, c, ইত্যাদি বর্ণানুক্রমিকভাবে স্লটগুলির নামকরণ করা হয়। বুটলোডারকে অপারেটিং সিস্টেমকে জানাতে হবে কোন স্লটটি কমান্ড লাইন প্রপার্টিandroidboot.slot_suffixব্যবহার করে বুট করা হয়েছে। অ্যান্ড্রয়েড 12 বা উচ্চতর সংস্করণের সাথে লঞ্চ হওয়া ডিভাইসগুলির জন্য বুট কনফিগারেশনের মাধ্যমে এই বৈশিষ্ট্যটি সেট করা হয়েছে।slot-retry-countমানটিকে একটি ধনাত্মক মান (সাধারণত3) এ রিসেট করা হয়, হয় বুট কন্ট্রোল HAL দ্বারাsetActiveBootSlotকলব্যাকের মাধ্যমে অথবাfastboot set_activeকমান্ডের মাধ্যমে। একটি স্লটের অংশ একটি পার্টিশন পরিবর্তন করার সময়, বুটলোডার "সফলভাবে বুট করা" সাফ করে এবং স্লটের জন্য পুনরায় চেষ্টা গণনা পুনরায় সেট করে।
বুটলোডারকে কোন স্লট লোড করতে হবে তাও নির্ধারণ করা উচিত। চিত্রটি একটি উদাহরণ সিদ্ধান্ত প্রক্রিয়া দেখায়।
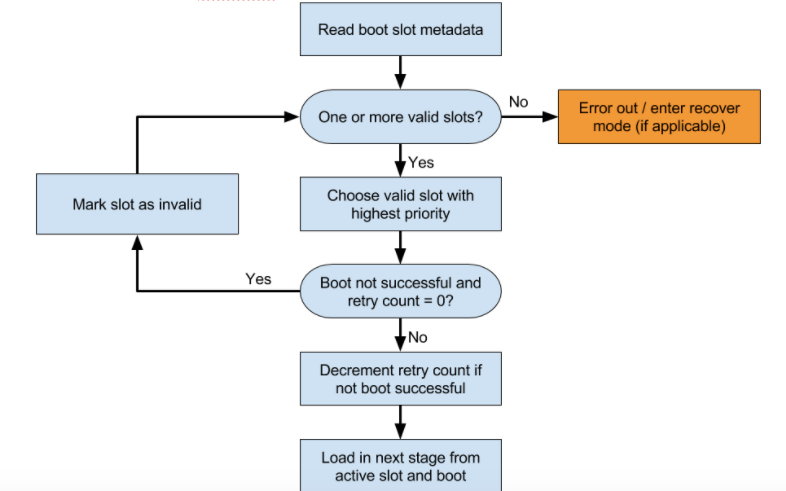
কোন স্লট চেষ্টা করতে হবে তা নির্ধারণ করুন।
slot-unbootableচিহ্নিত স্লট লোড করার চেষ্টা করবেন না। এই স্লটটি fastboot দ্বারা প্রত্যাবর্তিত মানগুলির সাথে সামঞ্জস্যপূর্ণ হওয়া উচিত এবং এটিকে বর্তমান স্লট হিসাবে উল্লেখ করা হয়৷যদি বর্তমান স্লটটিকে
slot-successfulহিসাবে চিহ্নিত না করা হয় এবং একটিslot-retry-count = 0থাকে, তাহলে বর্তমান স্লটটিকেslot-unbootableহিসাবে চিহ্নিত করুন। তারপরে একটি ভিন্ন স্লট নির্বাচন করুন যাunbootableনয় এবংslot-successfulহিসাবে চিহ্নিত করা হয়েছে; এই স্লটটি এখন নির্বাচিত স্লট। কোনো বর্তমান স্লট উপলব্ধ না হলে, পুনরুদ্ধারের জন্য বুট করুন বা ব্যবহারকারীকে একটি অর্থপূর্ণ ত্রুটি বার্তা প্রদর্শন করুন।উপযুক্ত
boot.imgনির্বাচন করুন এবং কার্নেল কমান্ড লাইনে সিস্টেম পার্টিশন সংশোধন করার পাথ অন্তর্ভুক্ত করুন।কার্নেল কমান্ড লাইন
slot_suffixপরামিতি পূরণ করুন।বুট.
slot-successfulচিহ্নিত না হলে,slot-retry-countহ্রাস করুন।
fastboot ইউটিলিটি নির্ধারণ করে যে কোন ফ্ল্যাশ কমান্ড চালানোর সময় কোন পার্টিশনটি ফ্ল্যাশ করতে হবে। উদাহরণ স্বরূপ, fastboot flash system system.img কমান্ড চালালে প্রথমে current-slot ভেরিয়েবলকে প্রশ্ন করা হয় তারপর ফ্ল্যাশ করা পার্টিশনের নাম তৈরি করতে ফলাফলটিকে সিস্টেমের সাথে সংযুক্ত করে ( system_a , system_b , ইত্যাদি)।
fastboot set_active কমান্ড বা বুট কন্ট্রোল HAL setActiveBootSlot কমান্ড ব্যবহার করে বর্তমান স্লট সেট করার সময়, বুটলোডারকে বর্তমান স্লট আপডেট করতে হবে, ক্লিয়ার slot-unbootable এবং slot-successful , এবং পুনরায় চেষ্টা গণনা রিসেট করতে হবে (এটি slot-unbootable সাফ করার একমাত্র উপায়)।
A/B আপডেট ছাড়া ডিভাইস
A/B আপডেটগুলি ব্যবহার করে না এমন ডিভাইসগুলিতে OTA আপডেটগুলিকে সমর্থন করতে ( নন-A/B আপডেটযোগ্য ডিভাইসগুলি দেখুন), নিশ্চিত করুন যে ডিভাইস বুটলোডার নিম্নলিখিত মানদণ্ডগুলি পূরণ করে৷
recoveryপার্টিশনে এমন একটি ইমেজ থাকা উচিত যা কিছু সমর্থিত পার্টিশন (cache,userdata) থেকে একটি সিস্টেম ইমেজ পড়তে এবংsystemপার্টিশনে লিখতে সক্ষম।বুটলোডারের উচিত সরাসরি রিকভারি মোডে বুট করা।
রেডিও ইমেজ আপডেট সমর্থিত হলে,
recoveryপার্টিশন রেডিও ফ্ল্যাশ করতে সক্ষম হওয়া উচিত। এটি দুটি উপায়ের একটিতে সম্পন্ন করা যেতে পারে:বুটলোডার রেডিও ফ্ল্যাশ করে। এই ক্ষেত্রে, আপডেটটি সম্পূর্ণ করতে পুনরুদ্ধার পার্টিশন থেকে বুটলোডারে পুনরায় বুট করা সম্ভব হবে।
পুনরুদ্ধারের চিত্রটি রেডিও ফ্ল্যাশ করে। এই কার্যকারিতা একটি বাইনারি লাইব্রেরি বা ইউটিলিটি হিসাবে প্রদান করা যেতে পারে.

