Per implementare gli aggiornamenti over-the-air (OTA), il
bootloader deve essere in grado di accedere a un RAM disk di ripristino durante l'avvio. Se il dispositivo
utilizza un'immagine di ripristino AOSP non modificata, il bootloader legge i primi 32 byte
della partizione misc; se i dati corrispondono a boot-recovery, il
bootloader si avvia nell'immagine recovery. Questo metodo consente di completare
qualsiasi lavoro di ripristino in attesa (ad esempio, l'applicazione di un aggiornamento OTA o la rimozione di dati).
Per informazioni dettagliate sul contenuto di un blocco nella memoria flash utilizzato per le comunicazioni dal recupero e dal bootloader, consulta bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h.
Dispositivi con aggiornamenti A/B
Per supportare gli aggiornamenti OTA sui dispositivi che utilizzano gli aggiornamenti A/B, assicurati che il bootloader del dispositivo soddisfi i seguenti criteri.
Criteri generali
Tutte le partizioni aggiornate tramite un aggiornamento OTA devono essere aggiornabili durante l'avvio del sistema principale (e non aggiornate nel ripristino).
Per avviare la partizione
system, il bootloader passa il seguente valore nella riga di comando del kernel:ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/init.È responsabilità del framework Android chiamare
markBootSuccessfuldall'HAL. Il bootloader non deve mai contrassegnare una partizione come avviata correttamente.
Supporto per l'HAL di controllo dell'avvio
Il bootloader deve supportare l'HAL boot_control come definito in
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h. L'updater esegue query sull'HAL di controllo dell'avvio, aggiorna lo slot di avvio non in uso, modifica lo slot attivo utilizzando l'HAL e riavvia il sistema operativo aggiornato. Per maggiori dettagli, vedi
Implementazione dell'HAL
di controllo dell'avvio.
Supporto per gli slot
Il bootloader deve supportare le funzionalità relative a partizioni e slot, tra cui:
I nomi delle partizioni devono includere un suffisso che identifichi le partizioni appartenenti a uno slot specifico nel bootloader. Per ogni partizione di questo tipo, esiste una variabile corrispondente
has-slot:partition base namecon un valore diyes. Gli slot sono denominati in ordine alfabetico come a, b, c e così via, corrispondenti alle partizioni con il suffisso_a,_b,_ce così via. Il bootloader deve comunicare al sistema operativo lo slot di avvio utilizzando la proprietà della riga di comandoandroidboot.slot_suffix. Questa proprietà viene impostata tramite bootconfig per i dispositivi avviati con Android 12 o versioni successive.Il valore di
slot-retry-countviene reimpostato su un valore positivo (di solito3), tramite l'HAL di controllo dell'avvio tramite il callbacksetActiveBootSloto tramite il comandofastboot set_active. Quando modifichi una partizione che fa parte di uno slot, il bootloader cancella "avvio riuscito" e reimposta il numero di tentativi per lo slot.
Il bootloader deve anche determinare quale slot caricare. La figura mostra un esempio di processo decisionale.
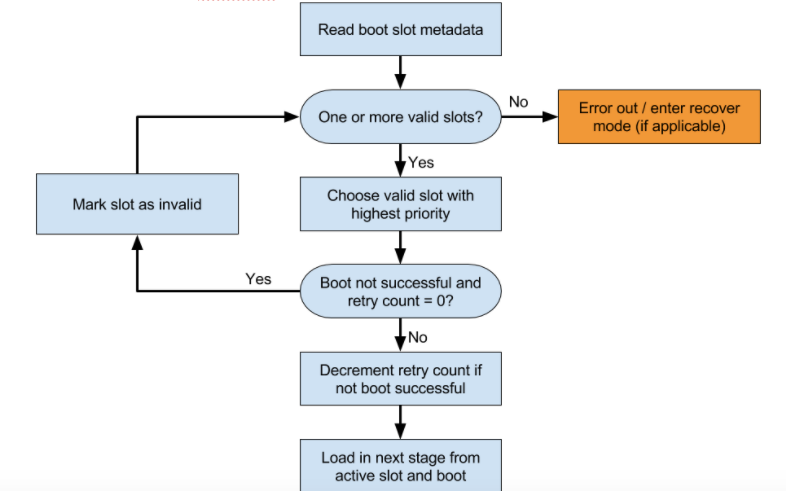
Determina quale slot tentare. Non tentare di caricare uno slot contrassegnato con
slot-unbootable. Questo slot deve essere coerente con i valori restituiti da fastboot ed è denominato slot corrente.Se lo slot attuale non è contrassegnato come
slot-successfule ha unslot-retry-count = 0, contrassegna lo slot attuale comeslot-unbootable. Poi seleziona un altro slot non contrassegnato conunbootablee contrassegnato conslot-successful; questo slot è ora quello selezionato. Se non è disponibile nessuno slot attuale, avvia il ripristino o mostra un messaggio di errore significativo all'utente.Seleziona il
boot.imgappropriato e includi il percorso della partizione di sistema corretta nella riga di comando del kernel.Compila il parametro della riga di comando del kernel
slot_suffix.Avvio. Se non è contrassegnato come
slot-successful, decrementaslot-retry-count.
L'utilità fastboot determina la partizione da flashare quando vengono eseguiti comandi flash. Ad esempio, l'esecuzione del comando fastboot flash system system.img
esegue prima una query sulla variabile current-slot, quindi concatena il risultato
al sistema per generare il nome della partizione da flashare
(system_a, system_b e così via).
Quando imposti lo slot corrente utilizzando il comando fastboot set_active o il comando
boot control HAL setActiveBootSlot, il bootloader deve aggiornare
lo slot corrente, cancellare slot-unbootable e slot-successful e reimpostare
il conteggio dei tentativi (questo è l'unico modo per cancellare slot-unbootable).
Dispositivi senza aggiornamenti A/B
Per supportare gli aggiornamenti OTA sui dispositivi che non utilizzano gli aggiornamenti A/B (vedi Dispositivi aggiornabili non A/B), assicurati che il bootloader del dispositivo soddisfi i seguenti criteri.
La partizione
recoverydeve contenere un'immagine in grado di leggere un'immagine di sistema da una partizione supportata (cache,userdata) e scriverla nella partizionesystem.Il bootloader deve supportare l'avvio diretto in modalità di ripristino.
Se gli aggiornamenti delle immagini della radio sono supportati, anche la partizione
recoverydeve essere in grado di eseguire il flashing della radio. Puoi farlo in due modi:Il bootloader lampeggia la radio. In questo caso, dovrebbe essere possibile riavviare dalla partizione di ripristino al bootloader per completare l'aggiornamento.
L'immagine di ripristino lampeggia sulla radio. Questa funzionalità può essere fornita come una libreria binaria o un'utilità.
