무선 업데이트(OTA)를 지원하려면 부트로더가 부팅 중에 복구 RAM 디스크에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다. 기기에서 수정되지 않은 AOSP 복구 이미지를 사용하면 부트로더는 misc 파티션의 처음 32바이트를 읽습니다. 그 데이터가 boot-recovery와 일치하면 부트로더는 recovery 이미지로 부팅됩니다. 이 메서드를 사용하면 대기 중인 복구 작업(예: OTA 적용 또는 데이터 삭제)이 계속 완료될 수 있습니다.
복구 및 부트로더에서 통신에 사용되는 플래시의 블록 콘텐츠에 관한 자세한 내용은 bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h를 참고하세요.
A/B 업데이트 기기
A/B 업데이트를 사용하는 기기에서 OTA 업데이트를 지원하려면 기기 부트로더가 다음 기준을 충족해야 합니다.
일반 기준
OTA를 통해 업데이트된 모든 파티션은 기본 시스템이 부팅되는 동안 업데이트할 수 있어야 합니다(복구 시 업데이트되지 않음).
system파티션을 부팅하기 위해 부트로더는 커널 명령줄에 다음 값을 전달합니다.ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/initHAL에서
markBootSuccessful을 호출하는 것은 Android 프레임워크의 책임입니다. 부트로더는 파티션을 부팅 완료로 절대 표시해서는 안 됩니다.
부팅 제어 HAL 지원
부트로더는 hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h에 정의된 boot_control HAL을 지원해야 합니다. 업데이터는 부팅 제어 HAL을 쿼리하고 현재 사용하지 않는 부팅 슬롯을 업데이트하며 HAL을 사용하여 활성 슬롯을 변경한 후 업데이트된 운영체제로 재부팅합니다. 자세한 내용은 부팅 제어 HAL 구현을 참고하세요.
슬롯 지원
부트로더는 다음을 비롯하여 파티션 및 슬롯과 관련된 기능을 지원해야 합니다.
파티션 이름에는 부트로더에서 특정 슬롯에 속하는 파티션을 식별하는 접미사가 포함되어야 합니다. 이러한 각 파티션에는 값이
yes인 상응하는 변수has-slot:partition base name이 있습니다. 슬롯의 이름은 접미사가_a,_b,_c등인 파티션에 상응하는 a, b, c 등 알파벳순으로 지정됩니다. 부트로더는 명령줄 속성androidboot.slot_suffix를 사용하여 부팅된 슬롯을 운영체제에 알려야 합니다. 이 속성은 Android 12 이상으로 출시되는 기기의 bootconfig를 통해 설정됩니다.slot-retry-count값은setActiveBootSlot콜백을 통해 부팅 제어 HAL에서 또는fastboot set_active명령어를 통해 양의 값(보통3)으로 재설정됩니다. 슬롯의 일부인 파티션을 수정할 때 부트로더는 'successfully booted'를 삭제하고 슬롯의 재시도 횟수를 재설정합니다.
부트로더는 로드할 슬롯도 결정합니다. 그림은 결정 프로세스 예를 보여 줍니다.
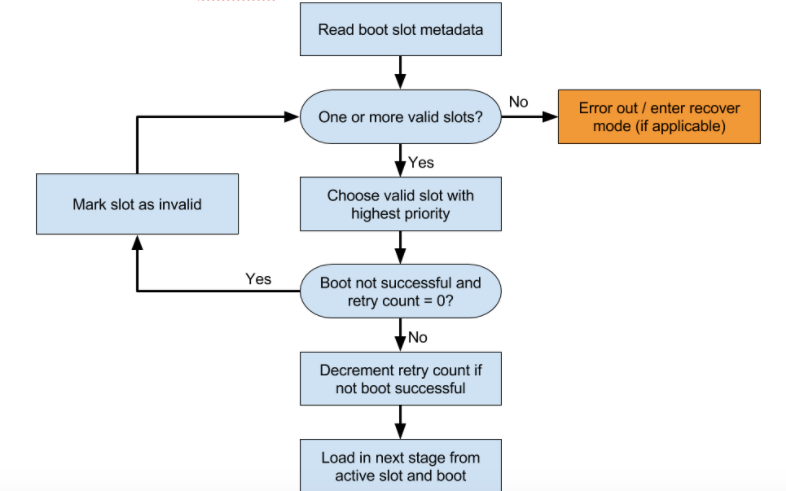
시도할 슬롯을 결정합니다.
slot-unbootable로 표시된 슬롯을 로드해서는 안 됩니다. 이 슬롯은 빠른 부팅에서 반환한 값과 일치해야 하고 현재 슬롯이라고 합니다.현재 슬롯이
slot-successful로 표시되지 않고slot-retry-count = 0을 보유하면 현재 슬롯을slot-unbootable로 표시합니다. 그런 다음unbootable로 표시되지 않고slot-successful로 표시된 다른 슬롯을 선택합니다. 이제 이 슬롯이 선택된 슬롯입니다. 사용 가능한 현재 슬롯이 없는 경우 복구로 부팅하거나 사용자에게 도움이 되는 오류 메시지를 표시합니다.적절한
boot.img를 선택하고 커널 명령줄에서 올바른 시스템 파티션 경로를 포함합니다.커널 명령줄
slot_suffix매개변수를 채웁니다.부팅합니다.
slot-successful로 표시되지 않으면slot-retry-count를 줄입니다.
fastboot 유틸리티는 플래시 명령어를 실행할 때 플래시할 파티션을 결정합니다. 예를 들어 fastboot flash system system.img 명령어를 실행하면 먼저 current-slot 변수를 쿼리하고 결과를 시스템에 연결하여 플래시해야 하는 파티션의 이름을 생성합니다(system_a, system_b 등).
빠른 부팅 set_active 명령어나 부팅 제어 HAL setActiveBootSlot 명령어를 사용하여 현재 슬롯을 설정할 때 부트로더는 현재 슬롯을 업데이트하고 slot-unbootable과 slot-successful을 삭제하고 재시도 횟수를 재설정합니다(slot-unbootable을 삭제하는 유일한 방법).
A/B 업데이트가 없는 기기
A/B 업데이트를 사용하지 않는 기기에서 OTA 업데이트를 지원하려면(A/B 업데이트가 불가능한 기기 참고) 기기 부트로더가 다음 기준을 충족해야 합니다.
recovery파티션에는 지원되는 일부 파티션 (cache,userdata)에서 시스템 이미지를 읽고system파티션에 쓸 수 있는 이미지가 있어야 합니다.부트로더는 복구 모드로 바로 재부팅할 수 있도록 지원해야 합니다.
라디오 이미지 업데이트가 지원된다면
recovery파티션도 라디오를 플래시할 수 있어야 합니다. 이는 다음 두 가지 방법 중 하나를 통해 이루어질 수 있습니다.부트로더가 라디오를 플래시합니다. 이 경우 복구 파티션에서 부트로더로 재부팅하여 업데이트를 완료합니다.
복구 이미지가 라디오를 플래시합니다. 이 기능은 바이너리 라이브러리나 유틸리티로 제공될 수 있습니다.
