實作裝置樹狀結構疊加層 (DTO) 時,需要分割、建構、劃分及執行裝置樹狀結構 (DT)。實作完成後,您也必須維持兩個 DT 之間的相容性,並決定確保每個 DT 分區安全性的策略。
分割 DT
首先,請將 DT 分成兩部分:
- 主要 DT。僅限 SoC 的部分和預設設定,由 SoC 供應商提供。
- 重疊 DT。ODM/OEM 提供的裝置專屬設定。
分割 DT 後,請務必確保主要 DT 和疊加 DT 相容,以便合併主要 DT 和疊加 DT,為裝置產生完整的 DT。如要瞭解 DTO 格式和規則的詳細資訊,請參閱「DTO 語法」。如要瞭解多個 DT,請參閱使用多個 DT。
建構主要和重疊 DT
如要建構主要 DT:
- 將主要 DT
.dts編譯為.dtb檔案。 - 將
.dtb檔案刷入可供開機載入器執行階段存取的分區 (詳情請參閱 [分區 DT](#partition))。
如要建構重疊 DT:
- 將疊加 DT
.dts編譯成.dtbo檔案。雖然這個檔案格式與格式化為扁平 DT 的.dtb檔案相同,但不同的副檔名可將其與主要 DT 區分開來。 - 將
.dtbo檔案刷入可供開機載入器執行階段存取的分區 (詳情請參閱 [分區 DT](#partition))。
如要瞭解如何使用 DTC 編譯,以及在主機上驗證 DTO 結果,請參閱「編譯及驗證」。
分區 DT
在快閃記憶體中,找出可供系統啟動載入程式存取且信任的位置,放置 .dtb 和 .dtbo。
主要 DT 的範例位置:
- 啟動分區的一部分,附加至核心 (
image.gz) - 在專屬分割區 (
dtb) 中分隔 DT Blob (.dtb)
疊加層 DT 的範例位置:
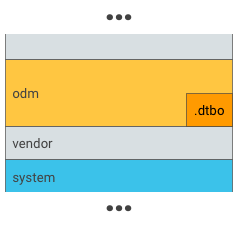
圖 1. 將 .dtbo 放入 odm 分區 (只有在開機載入器能夠從 odm 分區的檔案系統載入資料時,才需要這麼做)。
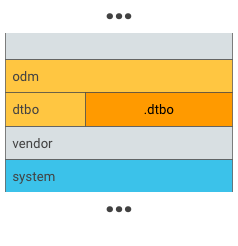
圖 2. 將 .dtbo 放入專屬分割區,例如 dtbo 分割區。
注意:疊加 DT 分割區的大小取決於裝置,以及主要 DT Blob 頂端需要變更的量。通常 8 MB 就已足夠,日後如有需要,還可擴充。
對於支援無縫 (A/B) 更新的裝置,請 A/B 測試主要 DT 和疊加 DT 分區:
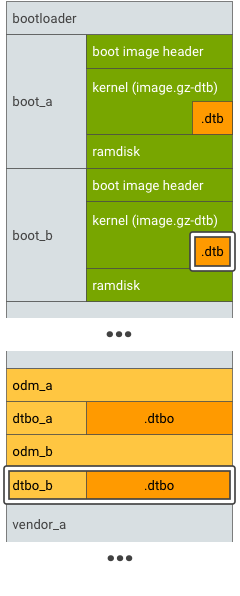
圖 3. DTBO 分區 A/B,範例 1。
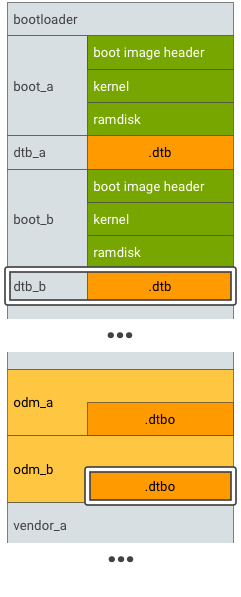
圖 4. DTBO 分區 A/B 測試,範例 2。
在系統啟動載入程式中執行
如要執行:
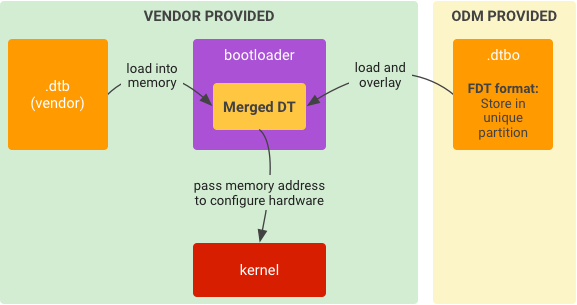
圖 5. 系統啟動載入程式中 DTO 的典型執行階段實作方式。
- 將儲存空間中的
.dtb載入記憶體。 - 將儲存空間中的
.dtbo載入記憶體。 - 將
.dtb覆蓋在.dtbo上,合併成 DT。 - 根據合併 DT 的記憶體位址啟動核心。
維持相容性
主要 DTB (來自 SoC 供應商) 會視為 DTBO 的 API 介面。將 DT 分成 SoC 通用部分和裝置專屬部分後,您必須確保這兩部分日後能相互相容,包括:
- 主要 DT 中的 DT 定義。例如節點、屬性、標籤。主要 DT 的任何定義變更都可能觸發疊加 DT 的變更。舉例來說,如要修正主要 DT 中的節點名稱,請定義對應至原始節點名稱的「別名」標籤 (避免變更疊加 DT)。
- 重疊顯示 DT 商店位置。例如分割區名稱、儲存格式。
確保安全性
系統啟動載入程式必須確保 DTB 或 DTBO 安全無虞、未經修改且未損毀。 您可以使用任何解決方案保護 DTB 或 DTBO,例如 VBoot 1.0 中的開機映像檔簽章,或 AVB HASH 頁尾 (VBoot 2.0)。
- 如果 DTB 或 DTBO 位於獨立分區,您可以將該分區新增至 AVB 的信任鏈。信任鏈結從受硬體保護的信任根開始,延伸至啟動載入程式,後者會驗證 DTB 或 DTBO 分區的完整性和真實性。
- 如果 DTB 或 DTBO 位於現有分割區 (例如
odm分割區),該分割區應位於 AVB 的信任鏈中。(DTBO 分區可以與odm分區共用公開金鑰)。
詳情請參閱「驗證開機程序」。

