リモートキーのプロビジョニング(RKP)は、Android 12 以降、AOSP の一部です。Android 14 では、リモート プロビジョニングの更新可能なモジュールが導入され、サービス API の堅牢性を高めてサービス API の改善に要する時間を短縮することで、機能の復元性を高めています。
目的
すべてを APEX にパッケージ化することで、RKP サービスを簡素化します。
Android 14 より前では、RKP はアプリ RemoteProvisioner とキーストア 2.0 に分離されていました。RemoteProvisioner アプリが RKP バックエンドと通信し、Keystore 2.0 が鍵の保存と HAL との通信の両方を実施していました。RKP 鍵とキーストアの鍵は添付されるメタデータの点で大きく異なるため、これは良好なアーキテクチャではありません。さらに、RemoteProvisioner がリソース不足の可能性を警告するように、キーストア フレームワークのコードを不自然な形で変更する必要がありました。
Mainline モジュールとしての RKP は、これらの点を改善するように設計されており、すべてを APEX にうまく組み込むことができます。
モジュールの境界
RKP Mainline APEX(com.android.rkpd)には、Remote Key Provisioning Daemon(RKPD)アプリケーションと、リモート プロビジョニング システム サーバー コンポーネント(Java でビルド)が含まれています。
スタック アーキテクチャ
図 1 は、RKP スタックのアーキテクチャを示しています。
図 1. RKP スタックのアーキテクチャ。
内部アーキテクチャ
図 2 は、RKP 内部アーキテクチャを示しています。
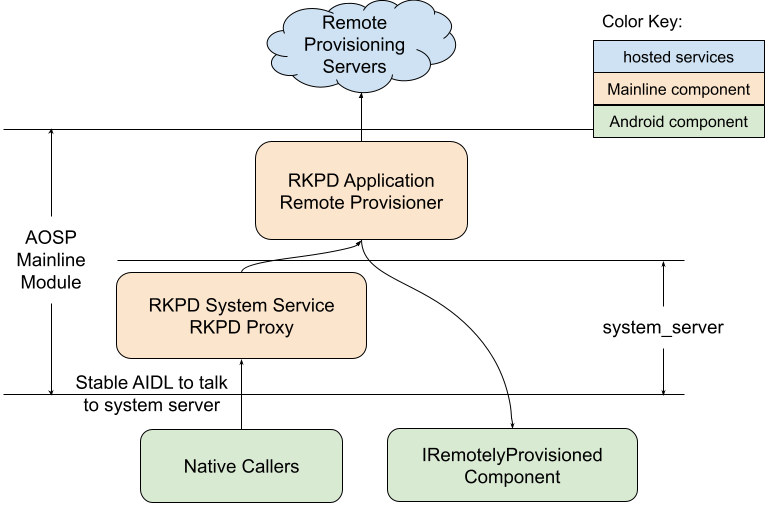
図 2. RKP 内部アーキテクチャ。
RKP 内部アーキテクチャに関する追加情報:
RKPD Mainline APEX -
com.android.rkpd- RKPD アプリ(Java)
packages/modules/RemoteKeyProvisioning/app
- RKPD システム サーバー フラグメント(Java)
packages/modules/RemoteKeyProvisioning/system-server
- RKPD アプリ(Java)
HAL インターフェース / 実装(Rust / C++)
IRemotelyProvisionedComponenthardware/interfaces/security/keymint
パッケージの形式
このモジュールのアプリケーションやその他の機能は、APEX ファイル com.android.rkpd としてパッケージ化されます。
依存関係
RKP モジュールは引き続き、証明書鍵と証明書リクエストの提供で IRemotelyProvisionedComponent 実装の存在に依存します。
テスト戦略
アプリ APEX の AOSP バージョンには、OEM が実行できる単体テストが含まれています。
