O gerenciador do TV Input Framework (TIF) funciona com a API de roteamento de áudio para oferecer suporte a mudanças flexíveis
no caminho do áudio. Quando um system on a chip (SoC) implementa a camada de abstração de hardware de TV (HAL), cada
entrada de TV (HDMI IN, sintonizador etc.) fornece TvInputHardwareInfo, que especifica informações de AudioPort para tipo e endereço de áudio.
- Os dispositivos de entrada/saída de áudio físicos têm um AudioPort correspondente.
- Os streams de saída/entrada de áudio do software são representados como AudioMixPort (classe filha de AudioPort).
O TIF usa informações do AudioPort para a API de roteamento de áudio.
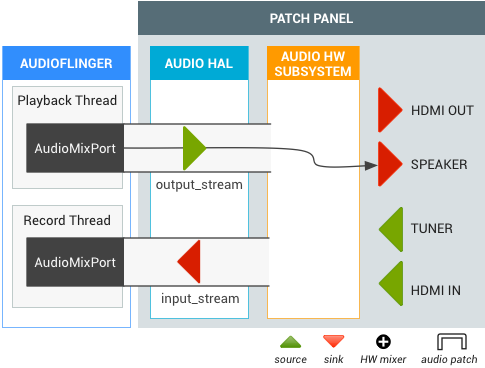
Figura 1. TV Input Framework (TIF)
Requisitos
Um SoC precisa implementar o HAL de áudio com o seguinte suporte à API de roteamento de áudio:
| Portas de áudio |
|
|---|---|
| Entrada padrão | O AudioRecord (criado com a fonte de entrada DEFAULT) precisa capturar a fonte de entrada nula virtual para a aquisição AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_DEFAULT no Android TV. |
| Loopback do dispositivo | Requer suporte a uma entrada AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK que seja uma mistura completa de toda a saída de áudio de toda a saída de TV (11 Khz, 16 bits mono ou 48 Khz, 16 bits mono). Usado apenas para captura de áudio. |
Dispositivos de áudio da TV
O Android oferece suporte aos seguintes dispositivos de áudio para entrada/saída de áudio de TV.
system/media/audio/include/system/audio.h
Observação:no Android 5.1 e versões anteriores, o caminho para
esse arquivo é: system/core/include/system/audio.h
/* output devices */ AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL = 0x400, AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_HDMI = AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_AUX_DIGITAL, /* HDMI Audio Return Channel */ AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_HDMI_ARC = 0x40000, /* S/PDIF out */ AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPDIF = 0x80000, /* input devices */ AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_AUX_DIGITAL = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x20, AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_HDMI = AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_AUX_DIGITAL, /* TV tuner input */ AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_TV_TUNER = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x4000, /* S/PDIF in */ AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_SPDIF = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x10000, AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK = AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN | 0x40000,
Extensão da HAL de áudio
A extensão HAL de áudio para a API de roteamento de áudio é definida da seguinte maneira:
system/media/audio/include/system/audio.h
Observação:no Android 5.1 e versões anteriores, o caminho para
esse arquivo é: system/core/include/system/audio.h
/* audio port configuration structure used to specify a particular configuration of an audio port */
struct audio_port_config {
audio_port_handle_t id; /* port unique ID */
audio_port_role_t role; /* sink or source */
audio_port_type_t type; /* device, mix ... */
unsigned int config_mask; /* e.g. AUDIO_PORT_CONFIG_ALL */
unsigned int sample_rate; /* sampling rate in Hz */
audio_channel_mask_t channel_mask; /* channel mask if applicable */
audio_format_t format; /* format if applicable */
struct audio_gain_config gain; /* gain to apply if applicable */
union {
struct audio_port_config_device_ext device; /* device specific info */
struct audio_port_config_mix_ext mix; /* mix specific info */
struct audio_port_config_session_ext session; /* session specific info */
} ext;
};
struct audio_port {
audio_port_handle_t id; /* port unique ID */
audio_port_role_t role; /* sink or source */
audio_port_type_t type; /* device, mix ... */
unsigned int num_sample_rates; /* number of sampling rates in following array */
unsigned int sample_rates[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_SAMPLING_RATES];
unsigned int num_channel_masks; /* number of channel masks in following array */
audio_channel_mask_t channel_masks[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_CHANNEL_MASKS];
unsigned int num_formats; /* number of formats in following array */
audio_format_t formats[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_FORMATS];
unsigned int num_gains; /* number of gains in following array */
struct audio_gain gains[AUDIO_PORT_MAX_GAINS];
struct audio_port_config active_config; /* current audio port configuration */
union {
struct audio_port_device_ext device;
struct audio_port_mix_ext mix;
struct audio_port_session_ext session;
} ext;
};
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/audio.h
struct audio_hw_device {
:
/**
* Routing control
*/
/* Creates an audio patch between several source and sink ports.
* The handle is allocated by the HAL and should be unique for this
* audio HAL module. */
int (*create_audio_patch)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
unsigned int num_sources,
const struct audio_port_config *sources,
unsigned int num_sinks,
const struct audio_port_config *sinks,
audio_patch_handle_t *handle);
/* Release an audio patch */
int (*release_audio_patch)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
audio_patch_handle_t handle);
/* Fills the list of supported attributes for a given audio port.
* As input, "port" contains the information (type, role, address etc...)
* needed by the HAL to identify the port.
* As output, "port" contains possible attributes (sampling rates, formats,
* channel masks, gain controllers...) for this port.
*/
int (*get_audio_port)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
struct audio_port *port);
/* Set audio port configuration */
int (*set_audio_port_config)(struct audio_hw_device *dev,
const struct audio_port_config *config);
Testando DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK
Para testar DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK para monitoramento de TV, use o código de teste a seguir. Depois de executar o
teste, o áudio capturado é salvo em /sdcard/record_loopback.raw, onde você pode ouvi-lo
usando FFmpeg.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_ROUTING" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
AudioRecord mRecorder;
Handler mHandler = new Handler();
int mMinBufferSize = AudioRecord.getMinBufferSize(RECORD_SAMPLING_RATE,
AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT);;
static final int RECORD_SAMPLING_RATE = 48000;
public void doCapture() {
mRecorder = new AudioRecord(MediaRecorder.AudioSource.DEFAULT, RECORD_SAMPLING_RATE,
AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO, AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT, mMinBufferSize * 10);
AudioManager am = (AudioManager) getSystemService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);
ArrayList<AudioPort> audioPorts = new ArrayList<AudioPort>();
am.listAudioPorts(audioPorts);
AudioPortConfig srcPortConfig = null;
AudioPortConfig sinkPortConfig = null;
for (AudioPort audioPort : audioPorts) {
if (srcPortConfig == null
&& audioPort.role() == AudioPort.ROLE_SOURCE
&& audioPort instanceof AudioDevicePort) {
AudioDevicePort audioDevicePort = (AudioDevicePort) audioPort;
if (audioDevicePort.type() == AudioManager.DEVICE_IN_LOOPBACK) {
srcPortConfig = audioPort.buildConfig(48000, AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_DEFAULT,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_DEFAULT, null);
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Found loopback audio source port : " + audioPort);
}
}
else if (sinkPortConfig == null
&& audioPort.role() == AudioPort.ROLE_SINK
&& audioPort instanceof AudioMixPort) {
sinkPortConfig = audioPort.buildConfig(48000, AudioFormat.CHANNEL_OUT_DEFAULT,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_DEFAULT, null);
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Found recorder audio mix port : " + audioPort);
}
}
if (srcPortConfig != null && sinkPortConfig != null) {
AudioPatch[] patches = new AudioPatch[] { null };
int status = am.createAudioPatch(
patches,
new AudioPortConfig[] { srcPortConfig },
new AudioPortConfig[] { sinkPortConfig });
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Result of createAudioPatch(): " + status);
}
mRecorder.startRecording();
processAudioData();
mRecorder.stop();
mRecorder.release();
}
private void processAudioData() {
OutputStream rawFileStream = null;
byte data[] = new byte[mMinBufferSize];
try {
rawFileStream = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(new File("/sdcard/record_loopback.raw")));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Can't open file.", e);
}
long startTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimeMs < 5000) {
int nbytes = mRecorder.read(data, 0, mMinBufferSize);
if (nbytes <= 0) {
continue;
}
try {
rawFileStream.write(data);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "Error on writing raw file.", e);
}
}
try {
rawFileStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "Exit audio recording.");
}
Localize o arquivo de áudio capturado em /sdcard/record_loopback.raw e ouça usando
FFmpeg:
adb pull /sdcard/record_loopback.rawffmpeg -f s16le -ar 48k -ac 1 -i record_loopback.raw record_loopback.wavffplay record_loopback.wav
Casos de uso
Esta seção inclui casos de uso comuns para áudio de TV.
Sintonizador de TV com saída de alto-falante
Quando um sintonizador de TV fica ativo, a API de roteamento de áudio cria um patch de áudio entre o sintonizador e a saída padrão (por exemplo, o alto-falante). A saída do sintonizador não requer decodificação, mas a saída de áudio final é misturada com o output_stream de software.
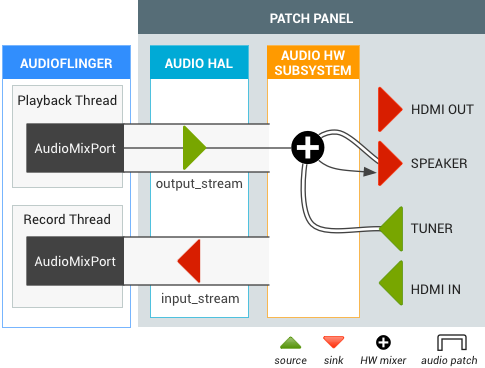
Figura 2. Patch de áudio para sintonizador de TV com saída de alto-falante.
HDMI OUT durante a TV ao vivo
Um usuário está assistindo TV ao vivo e muda para a saída de áudio HDMI (Intent.ACTION_HDMI_AUDIO_PLUG). O dispositivo de saída de todos os output_streams muda para a porta HDMI_OUT, e o gerenciador TIF muda a porta de destino do patch de áudio do sintonizador para a porta HDMI_OUT.
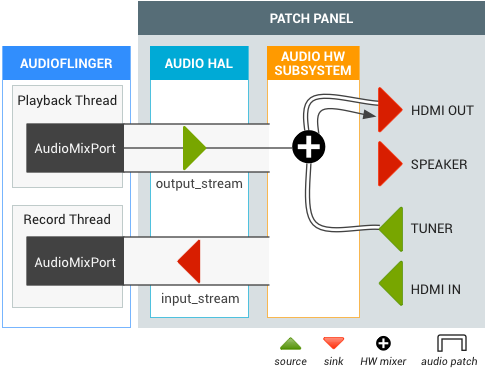
Figura 3. Patch de áudio para HDMI OUT da TV ao vivo.
