
Android 提供預設的藍牙堆疊,同時支援傳統藍牙和藍牙低功耗 (BLE)。Android 裝置可透過藍牙建立個人區域網路,與附近的藍牙裝置傳送及接收資料。
在 Android 4.3 以上版本中,Android Bluetooth 堆疊可實作 BLE。如要完整使用 BLE API,請遵循 Android Bluetooth HCI 規定。搭載合格晶片的 Android 裝置可以實作傳統藍牙,也可以同時實作傳統藍牙和 BLE。BLE 無法與舊款藍牙晶片組回溯相容。
在 Android 8.0 中,藍牙堆疊完全符合藍牙 5 的資格。如要使用可用的藍牙 5 功能,裝置必須具備藍牙 5 認證的晶片組。
Android 架構
藍牙應用程式會透過 Binder 與藍牙程序通訊。藍牙程序會使用 Java Native Interface (JNI) 與藍牙堆疊通訊,並提供開發人員各種藍牙設定檔的存取權。下圖顯示藍牙堆疊的一般結構:
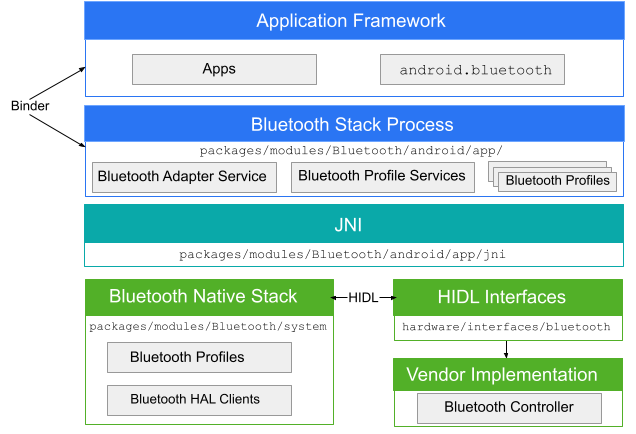
圖 1. Android 藍牙架構。
- 應用程式架構
- 在應用程式架構層級,應用程式程式碼會使用
android.bluetoothAPI 與藍牙硬體互動。在內部,這段程式碼會透過 Binder IPC 機制呼叫藍牙程序。 - 藍牙應用程式
- 藍牙應用程式位於
packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app,以 Android 應用程式的形式封裝,並在 Android 架構層實作藍牙設定檔。這個應用程式會透過 JNI 呼叫藍牙堆疊。 - JNI
- 與
android.bluetooth相關聯的 JNI 程式碼位於packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app/jni。發生特定藍牙作業時 (例如發現裝置),JNI 程式碼會呼叫藍牙堆疊。 - 藍牙堆疊
- AOSP 提供預設藍牙堆疊,位於
packages/modules/Bluetooth/system。堆疊會實作一般藍牙 HAL,並透過擴充功能和設定變更進行自訂。 - 廠商導入
- 供應商裝置會使用 HAL 介面定義語言 (HIDL) 與藍牙堆疊互動。
HIDL
HIDL 定義藍牙堆疊與供應商實作項目之間的介面。如要產生藍牙 HIDL 檔案,請將藍牙介面檔案傳遞至 HIDL 產生工具。介面檔案位於 hardware/interfaces/bluetooth。
藍牙堆疊開發
Android 藍牙堆疊是完全合格的藍牙堆疊。資格清單位於 Bluetooth SIG 網站 (需要登入),網址為 QDID 169365。
核心藍牙堆疊位於 packages/modules/Bluetooth 中。開發作業會在 AOSP 中進行,歡迎貢獻內容。
