进行硬件评估时,需要针对具体评估定义三种触感反馈效果,分别标为效果 1、2 和 3。
效果 1:预定义的短时触感反馈常量
VibrationEffect.EFFECT_CLICK 常量是在 HAL 和 API 之间映射常量部分中提供的 HAL-API 映射内的基准效果(即共同标准)。该常量与最常用的效果 HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_PRESS 进行映射。评估此效果有助于确定目标设备是否已准备好提供清晰触感反馈。
效果 2:短时自定义触感反馈效果
VibrationEffect.createOneShot(20,255) 常量适用于自定义触感反馈效果。对于单次短时自定义脉冲,在指定持续时间时,建议的最大阈值是 20 毫秒。不建议单次脉冲的持续时间超过 20 毫秒,因为这样的脉冲会被视为蜂鸣振动。
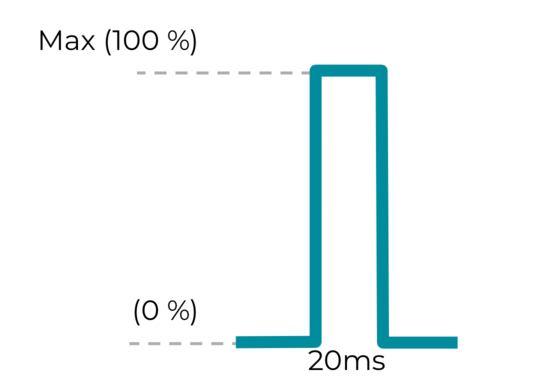
图 19. 短时自定义触感反馈效果
效果 3:具有振幅变体的长时自定义触感反馈效果
VibrationEffect.createWaveform(timings[], amplitudes[], int
repeat) 常量适用于具有振幅变体的长时自定义触感反馈效果。能否为自定义触感反馈效果生成不同的振幅是评估设备是否有能力提供丰富触感反馈的指标之一。推荐的 timings [] 和 amplitudes [] 分别是 {500, 500} 和 {128, 255},表示振幅会从 50% 增加到 100%,并且采样周期为 500 毫秒。
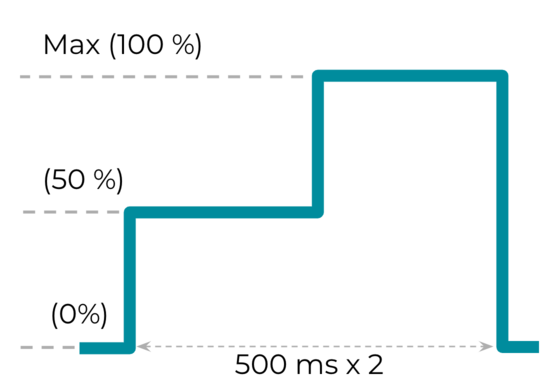
图 20. 具有振幅变体的长时自定义触感反馈效果
如需检查效果 3 的振幅控制硬件功能,请使用 Vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl() 方法。结果必须为 true,才能按照预期使用不同振幅执行 VibrationEffect.createWaveform。
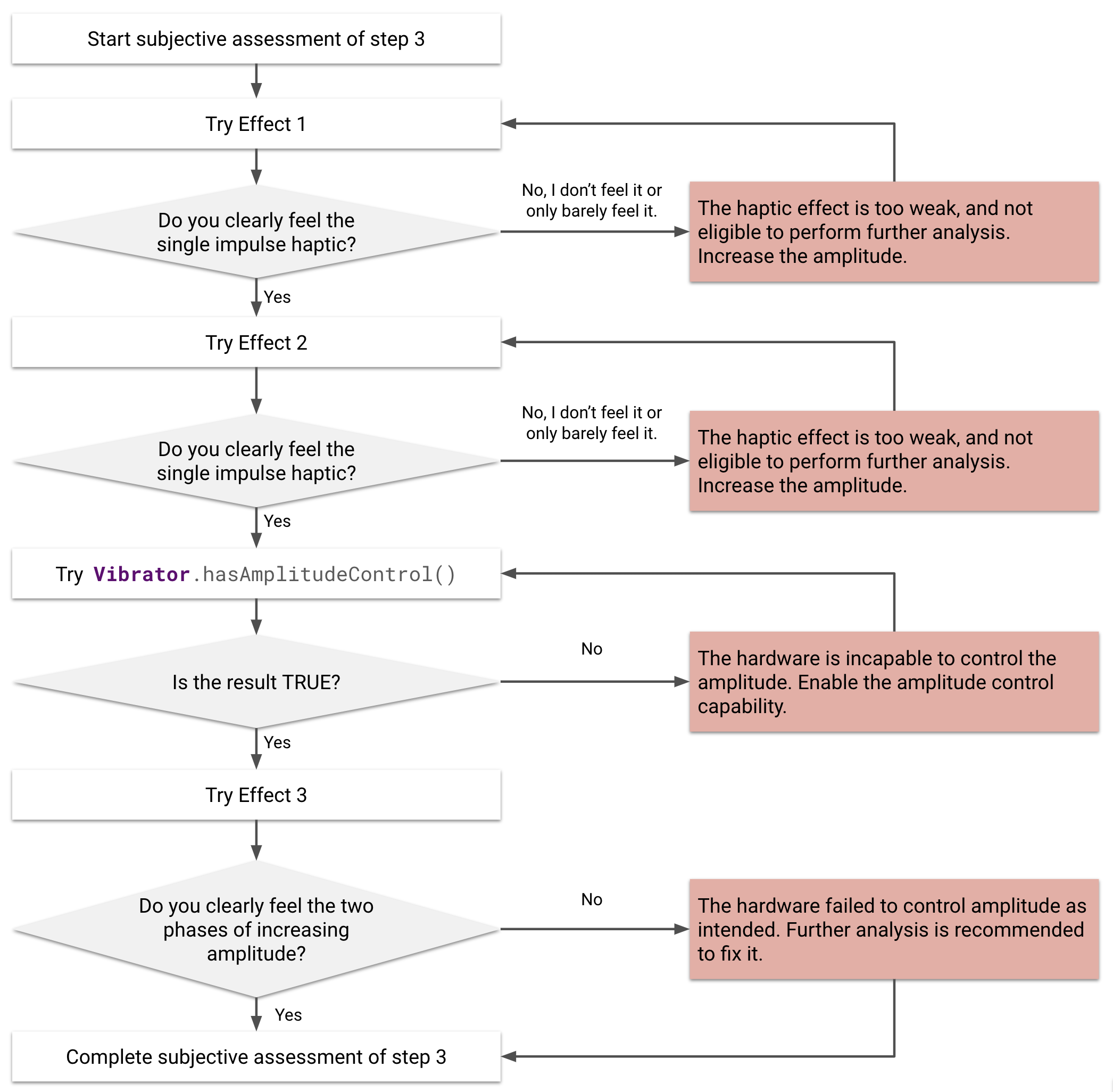
图 21. 对触感反馈效果 1、2 和 3 的主观评估
执行主观评估
若要快速完成一致性检查,请先执行主观评估。主观评估的目标是观察触感反馈效果的振幅,以确定设备能否生成具有人类可感知振幅的触感反馈。
围绕此概念产生的具体问题类似于:设备能否按预期为用户生成可感知的触感反馈效果?回答此问题有助于您避免失败的触感反馈,包括无法感知的触感反馈(用户感受不到)或意外的触感反馈(波形不产生预期的模式)。
执行高级评估
强烈建议执行高级质量评估。高级质量评估可表征处理触感反馈效果的可量化属性,以便实现高质量触感反馈。完成后,设备制造商就应该能够诊断当前的触感反馈状态,这意味着他们可以设定目标以提高整体质量。请参阅硬件评估。
