Produsen perangkat umumnya dianggap sebagai pemilik aset pribadi yang dibuat untuk setiap perangkat. Oleh karena itu, upaya engineering mereka sering kali berfokus pada perangkat; hanya sedikit atau tidak ada upaya yang dilakukan untuk menjaga konsistensi perangkat lain dalam ekosistem.
Sebaliknya, developer berupaya membuat aplikasi yang berfungsi di semua ponsel Android dalam ekosistem, terlepas dari spesifikasi teknis setiap perangkat. Perbedaan pendekatan ini dapat menyebabkan masalah fragmentasi, misalnya, kemampuan hardware ponsel tertentu tidak sesuai dengan ekspektasi yang ditetapkan oleh developer aplikasi. Jadi, jika API haptik berfungsi di beberapa ponsel Android, tetapi tidak di ponsel lain, hasilnya adalah ekosistem yang tidak konsisten. Itulah sebabnya konfigurasi hardware memainkan peran penting dalam memastikan bahwa produsen dapat menerapkan API haptik Android di setiap perangkat.
Halaman ini menyediakan checklist langkah demi langkah untuk menyiapkan kepatuhan hardware agar dapat menggunakan Android Haptics API secara optimal.
Gambar berikut mengilustrasikan pembangunan pengetahuan umum antara produsen perangkat dan developer, yang merupakan langkah penting dalam menciptakan ekosistem yang kohesif:
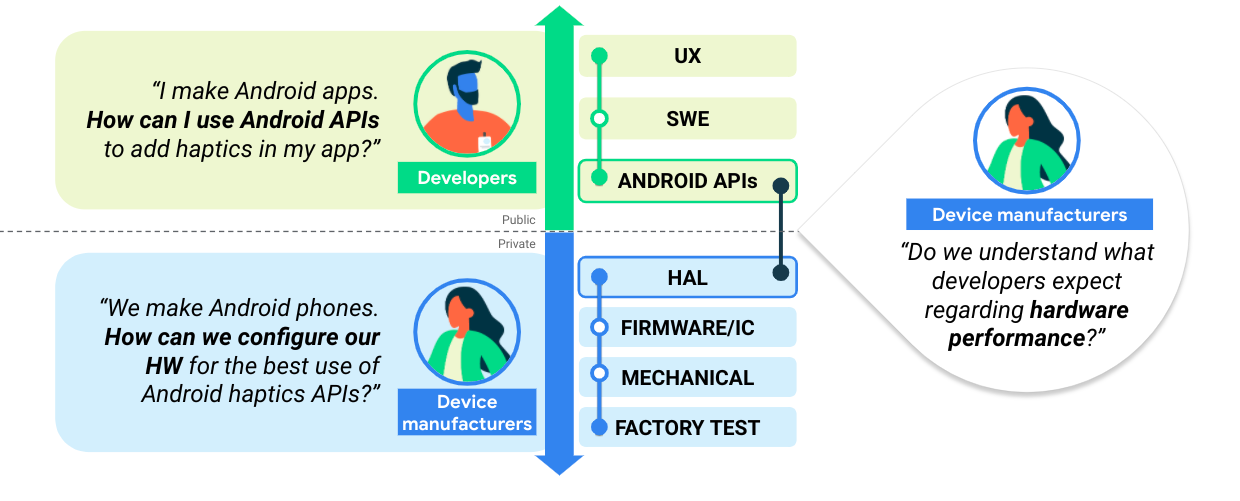
Gambar 1. Membangun pengetahuan antara produsen perangkat dan developer
Checklist penerapan haptik
-
- Daftar konstanta untuk menerapkan haptik.
-
- Panduan penerapan untuk primitif komposisi HAL.
Memetakan konstanta antara HAL dan API
- Memetakan rekomendasi antara konstanta API publik (bernama placeholder dalam framework) dan konstanta HAL, yang menerapkan placeholder.
- Lihat Prinsip desain untuk memandu pemetaan yang direkomendasikan untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut proses ini.
Menerapkan efek amplop linear per bagian (PWLE)
- Panduan penerapan untuk amplop amplitudo dan frekuensi.
-
- Petunjuk tentang efek haptik target. Gunakan petunjuk ini untuk melakukan pemeriksaan cepat pada hardware Anda.

