Android 7.0 推出了原生程式庫的命名空間,可限制內部 API 的可見度,並解決應用程式意外使用平台程式庫而非自身程式庫的情況。如要瞭解應用程式專屬的變更,請參閱「在 Android 7.0 中使用私人 C/C++ 符號限制提升穩定性」Android 開發人員網誌文章。
建築
在 Android 7.0 以上版本中,系統程式庫與應用程式程式庫會分開。
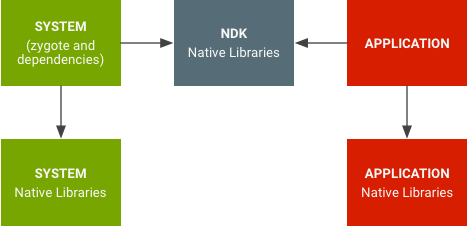
圖 1. 原生程式庫的命名空間。
原生程式庫的命名空間可防止應用程式使用私有平台原生 API (就像 OpenSSL 一樣)。此外,應用程式也不會再意外使用平台程式庫,而非自己的程式庫 (如 libpng 所示)。應用程式程式庫很難意外使用內部系統程式庫 (反之亦然)。
新增其他原生程式庫
除了標準公開原生程式庫外,晶片供應商 (從 Android 7.0 開始) 和裝置製造商 (從 Android 9 開始) 也可以選擇提供其他原生程式庫,只要將這些程式庫放在各自的程式庫資料夾中,並在 .txt 檔案中明確列出,應用程式就能存取這些程式庫。
程式庫資料夾如下:
/vendor/lib(適用於 32 位元) 和/vendor/lib64(適用於 64 位元),適用於晶片供應商的程式庫/system/lib(32 位元) 和/system/lib64(64 位元),適用於裝置製造商的程式庫
.txt 檔案如下:
/vendor/etc/public.libraries.txt適用於晶片供應商的程式庫/system/etc/public.libraries-COMPANYNAME.txt(適用於裝置製造商的程式庫),其中COMPANYNAME是指製造商的名稱 (例如awesome.company)。COMPANYNAME必須與[A-Za-z0-9_.-]+相符;英數字元、_、. (點) 和 -。如果某些程式庫來自外部解決方案供應商,裝置中可能會有多個這類 .txt 檔案。
裝置製造商在 system 分區中公開的原生程式庫必須命名為 lib*COMPANYNAME.so,例如 libFoo.awesome.company.so。換句話說,libFoo.so不得公開不含公司名稱後置字串的網域。
程式庫檔案名稱中的 COMPANYNAME 必須與列出程式庫名稱的 txt 檔案名稱中的 COMPANYNAME 相符。
屬於 AOSP 的原生程式庫不得設為公開 (預設為公開的標準公開原生程式庫除外)。應用程式只能存取晶片供應商或裝置製造商新增的其他程式庫。
從 Android 8.0 開始,供應商公開程式庫有下列額外限制和必要設定:
- 供應商中的原生程式庫必須正確標示,應用程式才能存取。如果任何應用程式 (包括第三方應用程式) 需要存取權,則必須在廠商專屬的
file_contexts檔案中,將程式庫標示為same_process_hal_file,如下所示:/vendor/lib(64)?/libnative.so u:object_r:same_process_hal_file:s0
libnative.so是原生程式庫的名稱。 - 程式庫不得直接或透過依附元件依附於 VNDK-SP 和 LLNDK 程式庫以外的系統程式庫。在
development/vndk/tools/definition/tool/datasets/eligible-list-<version>-release.csv找到 VNDK-SP 和 LLNDK 程式庫清單。
從 Android 15 開始,廠商公開程式庫可以放在廠商 APEX 中。封裝在供應商 APEX 中時,請在 APEX 資訊清單的 provideNativeLibs 屬性中列出程式庫。
更新應用程式,避免使用非公開原生程式庫
這項功能僅適用於以 SDK 24 以上版本為目標的應用程式;如需回溯相容性,請參閱表 1。 如果應用程式連結至私人的原生程式庫,會發生什麼情況。 應用程式可存取的 Android 原生程式庫清單 (也稱為公開原生程式庫) 列於 CDD 3.1.1 節。如果應用程式指定 API 級別 24 以上版本,且使用任何非公開程式庫,就必須更新。詳情請參閱「連結至平台程式庫的 NDK 應用程式 」。
更新應用程式的原生程式庫依附元件
如果應用程式指定 SDK 版本 31 (Android 12) 以上,就必須在應用程式資訊清單中使用 <uses-native-library> 標記,明確指定原生共用程式庫依附元件。如果裝置上沒有要求的程式庫,應用程式就不會安裝。安裝應用程式時,系統只會提供應用程式要求的原生共用程式庫。也就是說,應用程式無法存取未顯示在應用程式資訊清單中的原生共用程式庫。
