Android 7.0 为原生库引入了命名空间,以限制内部 API 的可见性,并解决应用意外使用平台库(而非它们自己的库)的问题。请参阅通过 Android 7.0 中的私有 C/C++ 符号限制提升稳定性这篇 Android 开发者博文,了解针对应用的更改。
架构
在 Android 7.0 及更高版本中,系统库与应用库是分开的。
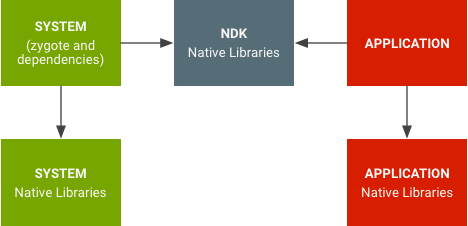
图 1. 原生库的命名空间
原生库的命名空间可防止应用使用私有平台的原生 API(例如使用 OpenSSL)。该命名空间还可以避免应用意外使用平台库(而非它们自己的库)的问题(如使用 libpng 时)。应用库很难意外使用内部系统库(反之亦然)。
添加其他原生库
除了标准的公共原生库之外,芯片供应商(从 Android 7.0 起)和设备制造商(从 Android 9 起)还可以选择提供可供应用访问的其他原生库,方法是将它们放在相应的库文件夹中,并在 .txt 文件中显式列出它们。
库文件夹是:
/vendor/lib(对于芯片供应商的 32 位库)和/vendor/lib64(对于芯片供应商的 64 位库)/system/lib(对于设备制造商的 32 位库)和/system/lib64(对于设备制造商的 64 位库)
.txt 文件是:
/vendor/etc/public.libraries.txt(对于芯片供应商的库)/system/etc/public.libraries-COMPANYNAME.txt(对于设备制造商的库),其中COMPANYNAME指的是制造商的名称(例如awesome.company)。COMPANYNAME应符合[A-Za-z0-9_.-]+格式(字母数字字符 , _, .(点)和 -。如果某些库来自外部解决方案提供商,则可以在设备中包含多个此类 .txt 文件。
设备制造商公开的 system 分区中的原生库必须命名为 lib*COMPANYNAME.so,例如 libFoo.awesome.company.so。
换句话说,没有公司名称后缀的 libFoo.so 不得公开。库文件名中的 COMPANYNAME 必须与列出库名称的 txt 文件名称中的 COMPANYNAME 匹配。
作为 AOSP 一部分的原生库不得公开(默认情况下公开的标准公共原生库除外)。只有芯片供应商或设备制造商添加的其他库可供应用访问。
从 Android 8.0 开始,供应商的公共库需要遵循以下额外限制,并且需要进行相应的设置:
- 供应商的原生库必须添加适当的标签,以供应用访问。如有任何应用(包括第三方应用)要求访问原生库,则该库必须在供应商专用的
file_contexts文件中标记为same_process_hal_file,具体如下所示:/vendor/lib(64)?/libnative.so u:object_r:same_process_hal_file:s0
libnative.so为原生库的名称。 - 该库不得依赖(无论是直接依赖,还是通过其依赖关系间接依赖)VNDK-SP 库和 LLNDK 库之外的任何系统库。在
development/vndk/tools/definition/tool/datasets/eligible-list-<version>-release.csv中找到 VNDK-SP 库和 LLNDK 库的列表。
从 Android 15 开始,供应商公共库可以放入供应商 APEX 中。如果已将库打包到供应商 APEX 中,请在 APEX 清单的 provideNativeLibs 属性中列出这些库。
更新应用,使其不使用非公共原生库
仅针对目标 SDK 版本为 24 或更高的应用启用了此功能;如需了解向后兼容性,请参阅表 1。 当应用关联到私有原生库时会发生什么情况。 CDD 第 3.1.1 节列出了可供应用访问的 Android 原生库(又称为公共原生库)。支持版本 24 或更高版本且使用任何非公共库的应用应进行更新。如需了解详情,请参阅链接到平台库的 NDK 应用。
更新应用以获取其原生库依赖项
以 SDK 版本 31 (Android 12) 或更高版本为目标平台的应用必须在应用清单中使用 <uses-native-library> 标记显式指定其原生共享库依赖项。如果设备上不存在所请求库的任何部分,则未安装应用。应用安装时,系统仅向他们提供已请求的原生共享库。这意味着,应用无法访问应用清单中未显示的原生共享库。
