Android 권한은 사용자 인지도를 높이고 민감한 정보에 대한 앱의 액세스를 제한하는 제어 기능을 제공합니다. Android 8.0 이하에서 권한을 구성하는 과정에는 허용 목록 추가 작업도 포함됩니다. 여기서는 권한이 있는 앱이 priv-app 경로에 위치한 경우에도 사용 중지되지 않습니다. Android 9 이상에서는 제대로 허용 목록에 추가되지 않은 앱을 사용하려고 시도하는 기기가 부팅되지 않습니다.
Android 10에서는 특정 요구사항 및 권한과 연결된 시스템 내의 고유한 이름인 역할이라는 개념을 도입했습니다. 앱에 역할을 할당하여 특정 목적으로 권한을 부여하고 플랫폼 구성 리소스를 사용하여 기본 역할을 구성합니다.
잠재적으로 위험한 앱(PHA)에 관한 향상된 보호 기능은 다음을 개선합니다.
- 잠재적으로 위험한 앱 동작에 관한 투명성
- 사용자의 앱 동작 제어
- 권한에 의해 보호된 비공개 데이터 사용 시의 앱 개발자 재량
패키지 설치 및 권한
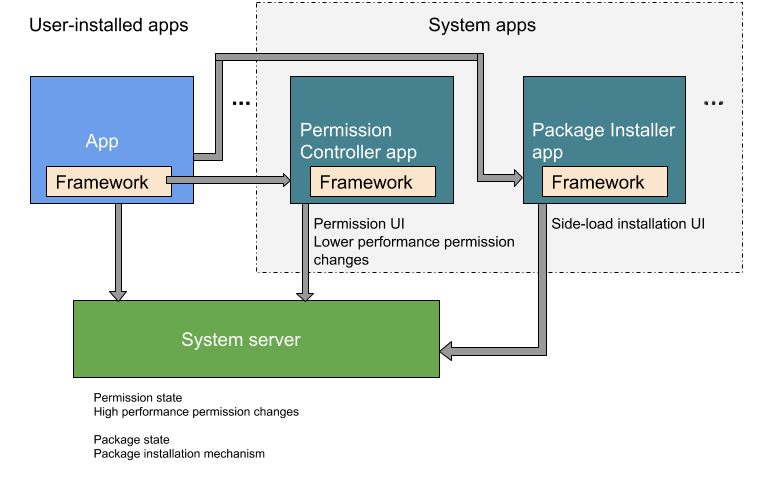
Android 9 이하에서는 패키지 설치 및 권한 제어 기능이 PackageInstaller 패키지(//packages/apps/PackageInstaller)에 포함되었습니다. Android 10 이상에서는 권한 제어 기능이 별도의 패키지인 PermissionController(//packages/apps/PermissionController)에 상주합니다. 그림 1은 두 패키지가 Android 10의 어느 위치에서 상주하는지 보여줍니다.
허용 목록 및 액세스
Android 6.0 이상에서는 앱이 런타임 시 위험한 권한에 대한 액세스를 요청합니다. Android 10에는 사용자에게 위험한 권한을 수정하거나 허용하도록 요청하는 활동 감지(AR) 런타임 권한이 추가됩니다.
Android 8.0에서는 /etc/permissions 디렉터리의 시스템 구성 XML 파일에서 권한 있는 앱을 명시적으로 허용 목록에 추가해야 했습니다.
Android 9 이상에서는 권한 있는 앱을 허용 목록에 추가하지 않으면 기기가 부팅되지 않습니다.
Android 7.0에는 내부 API 가시성을 제한하고 앱이 실수로 플랫폼 라이브러리에 액세스하는 일이 없도록 네이티브 라이브러리용 네임스페이스가 도입되었습니다. 이는 시스템 라이브러리를 애플리케이션 라이브러리로부터 구분하며, 기기 제조업체가 자체 네이티브 라이브러리를 추가할 수 있습니다.
Android 10부터는 앱에 서명 권한 및 사용자 동의가 둘 다 있어야 기기 화면 콘텐츠에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 스크린샷 캡처와 같은 무음 캡처 기능에 의존하는 권한 있는 앱은 MediaProjection 클래스를 대신 사용해야 합니다.
투명성 및 개인 정보 보호
Android 6.0 이상에서는 Wi-Fi 서비스 제공업체 및 패킷 분석업체에서 액세스할 수 없도록 기기의 공장 출고 시 MAC 주소가 보호됩니다. Android 10부터 적용되는 추가 제한사항은 앱이 독점 권한 허용 목록에 추가되지 않은 이상 변경할 수 없는 기기 식별자(ID)에 액세스할 수 없도록 하고 있습니다. 연결 섹션에서는 이동통신사에 영향을 미치는 기기 식별자와 관련된 토론을 제공합니다.
Android 9 이하에서는 사용자가 앱에 위치 액세스 권한을 부여할 때마다 계속 선택을 해야 합니다. Android 10부터 사용자가 tristate 위치 정보 액세스 권한을 통해 제공되는 세 가지 옵션 중 하나를 선택하여 앱이 기기 위치에 액세스하도록 허용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 권한 요구사항은 타겟 SDK와 상관없이 Android 10의 앱에 적용됩니다.
Android 10부터 도입된 다른 투명성 및 개인 정보 보호 기능에 관한 권한도 구성합니다.
- 백그라운드 액세스 위치 알림은 앱이 언제 백그라운드에서
ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION권한을 사용하여 기기 위치에 액세스하는지를 사용자에게 보여줍니다. - 연락처 제공자 구성요소에 의해 관리되는 관심 연락처 관련 데이터는 다른 방식으로 액세스됩니다. 앱은 데이터베이스의 관심 연락처 데이터에서 쓰고 읽을 수 없습니다. 이는 호출자 관련 API에 영향을 미칩니다.
간소화된 구성
Android 6.0 이상의 권한 구성이 간소화되었습니다.
init에 의해 실행되는 서비스의 주변 기능이 단일.rc파일 내 서비스 구성의 모든 관점을 유지합니다.init에 의해 실행되지 않는 서비스의 기능을 설정할 때는 대신fs_config.c를 사용하여 파일 시스템 기능을 구성합니다.- Android 7.x 이하에서는 Android ID(AID) 메커니즘이 확장되며, 이때 기기별
android_filesystem_config.h파일을 사용하여 파일 시스템 기능 및 맞춤 기기 제조업체 AID를 지정합니다. Android 8.0 이상에서는 파일 시스템 기능 확장을 위한 새로운 방식을 지원합니다. - Android 8.0에서는 USB 명령어 취급이 기기별
init스크립트(HAL 레이어 대체)에서 네이티브 USB 데몬으로 이전되었습니다. USB HAL 인터페이스는 Android 8.0 이상에서 실행되는 모든 기기에 구현해야 합니다.
