Android デバイスの消費電力とパフォーマンスを管理することにより、さまざまなハードウェアでアプリが安定してスムーズに動作することを保証できます。Android 7.0 以降では、OEM はパフォーマンス維持のヒントのサポートを実装できます。これにより、アプリの実行中に安定したデバイス パフォーマンスを維持することや、CPU を集中的に使用するフォアグラウンド アプリのパフォーマンスを改善するために専用コアを指定することが可能になりました。
パフォーマンス維持
アプリ(ゲーム、カメラ、RenderScript、オーディオ処理など)を長時間実行していると、デバイスの温度制限に達してシステム オン チップ(SoC)エンジンがスロットリングされ、パフォーマンスが大きく変動することがあります。長時間実行される高パフォーマンスのアプリを作成するアプリ デベロッパーは、デバイスが過熱し始めると基盤プラットフォームのパフォーマンスが変動して目標値を定められないという制約を受けます。
こうした制約に対処するため、Android 7.0 ではパフォーマンス維持のサポートが導入され、OEM は長時間実行されるアプリ向けにデバイスのパフォーマンス能力に関するヒントを提供できるようになりました。アプリ デベロッパーは、こうしたヒントを利用して、デバイスが長期間にわたり予測可能な一定のパフォーマンス レベルを維持できるようにアプリを調整できます。
アーキテクチャ
Android アプリは、Android デバイスが一定レベルのパフォーマンスを長時間にわたって維持できるパフォーマンス維持モードに入るようプラットフォームに要求できます。
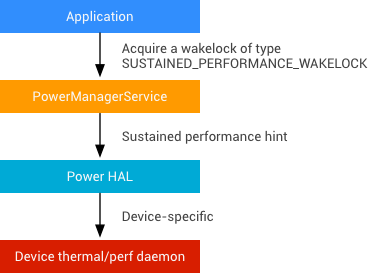
図 1. パフォーマンス維持モードのアーキテクチャ
実装
Android 7.0 以降でパフォーマンス維持をサポートするには、OEM は次のことを行う必要があります。
- 電力 HAL にデバイス固有の変更を加えて、最大 CPU / GPU 周波数をロックする。または、サーマル スロットリングを防ぐために他の最適化を行う。
- 電力 HAL に新しいヒント
POWER_HINT_SUSTAINED_PERFORMANCEを実装する。 isSustainedPerformanceModeSupported()API で TRUE を返すことにより、サポートを宣言する。Window.setSustainedPerformanceModeを実装する。
Nexus のリファレンス実装では、電力ヒントによって、最高の維持レベルで CPU と GPU の最大周波数が制限されます。CPU / GPU 周波数の最大値を示すバーを下げるとフレームレートが低下しますが、このモードでは持続性に優れた低いフレームレートが優先されます。たとえば、通常の最大クロック数で動作するデバイスでは、60 FPS でのレンダリングを数分間実行できますが、30 分経過してデバイスが加熱すると 30 FPS にスロットリングされることがあります。維持モードを使用すると、このデバイスは 30 分の間、常に 45 FPS でレンダリングできます。目標は、このモードを使用しない場合のフレームレートと同等(またはそれ以上)のフレームレートを実現することと、デベロッパーがフレームレートの変動を追いかけなくてすむように長時間にわたってフレームレートを安定させることです。
デバイスが最大限のパフォーマンス維持を実現できる維持モードを実装することを強くおすすめします。テストに合格するための最小要件(たとえば、長時間にわたるサーマル スロットリングを発生させないための最大周波数制限の選択など)では不十分です。
注: 維持モードを実装する場合、最大クロックレートの上限を設ける必要はありません。
検証
OEM は、CTS テスト(Android 7.0 以降)を使用して、パフォーマンス維持 API の実装を検証できます。このテストは、約 30 分間ワークロードを実行し、維持モードを有効にした場合と無効にした場合のパフォーマンスをベンチマーク評価します。
- 維持モードを有効にした場合のフレームレートがほぼ一定に保たれることが必要です(テストでは、フレームレートの経時的な変動率を測定し、5% 未満であれば合格とします)。
- 維持モードを有効にした場合のフレームレートが、維持モードを無効にした場合の 30 分経過後のフレームレートを下回らないことが必要です。
さらに、CPU と GPU を集中的に使用するワークロードをいくつか実行して、手動で実装をテストします。これにより、30 分経過後にデバイスでサーマル スロットリングが発生しないことを確認します。Google の内部テストでは、ゲームアプリとベンチマーク アプリ(gfxbench など)を含むサンプル ワークロードを使用しました。
専用コア
CPU を集中的に使用する緊急のワークロードの場合、別のスレッドによってプリエンプトされると、フレーム期限を守れるかどうかという問題が生じます。遅延とフレームレートの要件が厳格なアプリ(オーディオ アプリやバーチャル リアリティ アプリなど)では、専用の CPU コアを用意することで、許容可能なレベルのパフォーマンスを確保できます。
Android 7.0 以降を搭載したデバイスでは、トップ フォアグラウンド アプリ用に 1 つのコアを明示的に予約できます。これにより、高負荷のワークロードを実行するアプリは CPU コア間の作業割り当てをよりきめ細かく制御できるようになりました。
デバイスで専用コアをサポートするには:
cpusetsを有効にし、トップ フォアグラウンド アプリのみを含むcpusetを構成します。- この
cpusetからのスレッド用に 1 つのコア(これが専用コアです)を予約します。 - 専用コアのコア番号を返す getExclusiveCores API を実装します。
どのプロセスがどのコアでスケジュール設定されているかを特定するには、ワークロードの実行時に systrace を使用し、トップ フォアグラウンド アプリ以外のアプリからのユーザー空間スレッドが専用コアでスケジュール設定されていないことを確認します。
Nexus 6P 向けのリファレンス実装を確認するには、android//device/huawei/angler/power/power.c をご覧ください。
