Android Runtime (ART) 包含一个具备代码分析功能的即时 (JIT) 编译器,该编译器可以在 Android 应用运行时持续提高其性能。JIT 编译器对 Android 运行组件当前的预先 (AOT) 编译器进行了补充,可以提升运行时性能,节省存储空间,加快应用和系统更新速度。相较于 AOT 编译器,JIT 编译器的优势也更为明显,因为在应用自动更新期间或在无线下载 (OTA) 更新期间重新编译应用时,它不会拖慢系统速度。
尽管 JIT 和 AOT 使用相同的编译器,它们所进行的一系列优化也较为相似,但它们生成的代码可能会有所不同。JIT 会利用运行时类型信息,可以更高效地进行内联,并可让堆栈替换 (OSR) 编译成为可能,而这一切都会使其生成的代码略有不同。
JIT 架构
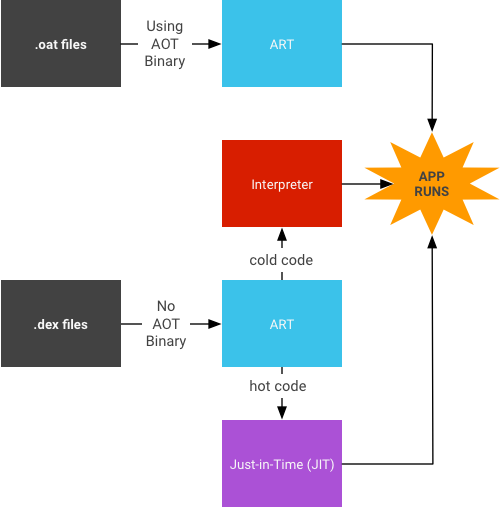
JIT 编译
JIT 编译涉及以下活动:
- 用户运行应用,此举随后触发 ART 加载
.dex文件。- 如果有
.oat文件(即.dex文件的 AOT 二进制文件),ART 会直接使用该文件。虽然.oat文件会定期生成,但文件中不一定会包含经过编译的代码(即 AOT 二进制文件)。 - 如果
.oat文件不含经过编译的代码,ART 会通过 JIT 和解释器执行.dex文件。
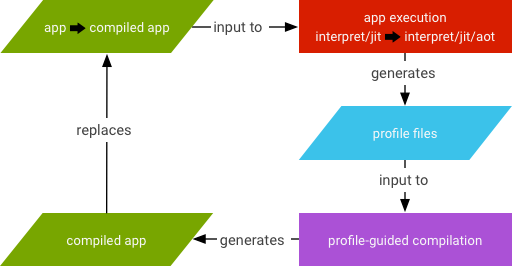
- 如果有
- 针对任何未根据
speed编译过滤器编译的应用启用 JIT(也就是说,要尽可能多地编译应用中的代码)。 - 将 JIT 配置文件数据转储到只有该应用可以访问的系统目录下的文件中。
- AOT 编译 (
dex2oat) 守护程序通过解析该文件来推进其编译。
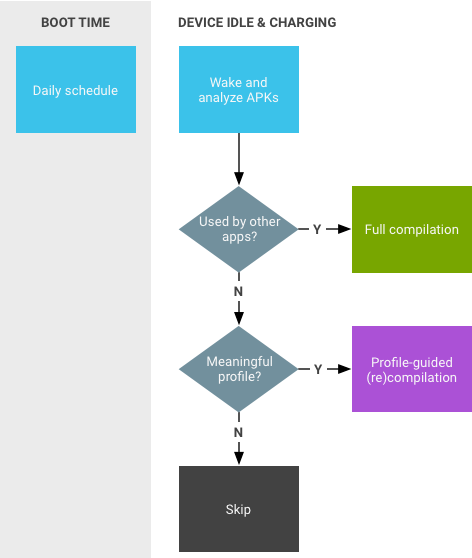
图 3. JIT 守护程序 activity。
举例来说,Google Play 服务就是一种由其他应用使用的类似于共享库的服务。
JIT 工作流程
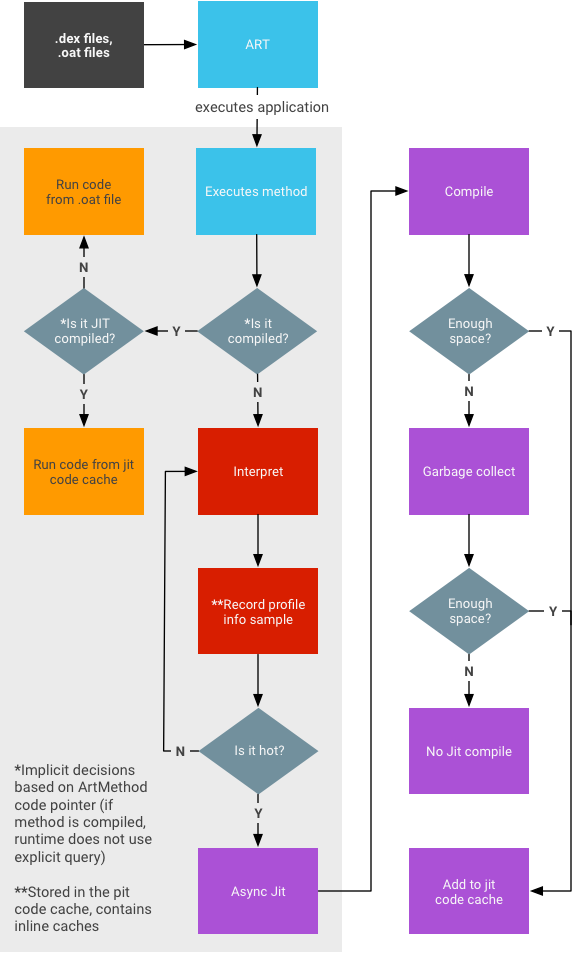
- 分析信息会存储在代码缓存中,并会在内存紧张时作为垃圾被回收。
- 无法保证在应用处于后台运行状态时所捕获的快照能够包含完整的数据(即 JIT 编译的所有内容)。
- 该过程不会尝试确保记录所有内容(因为这会影响运行时性能)。
- 方法可能有三种不同的状态:
- 已经过解释(dex 代码)
- 已经过 JIT 编译
- 已经过 AOT 编译
- 在不影响前台应用性能的情况下运行 JIT 所需的内存取决于相关应用。大型应用比小型应用需要更多内存。一般来说,大型应用所需的内存稳定维持在 4 MB 左右。
打开 JIT 日志记录
要开启 JIT 日志记录,请运行以下命令:
adb rootadb shell stopadb shell setprop dalvik.vm.extra-opts -verbose:jitadb shell start
停用 JIT
要停用 JIT,请运行以下命令:
adb rootadb shell stopadb shell setprop dalvik.vm.usejit falseadb shell start
强制编译
要强制编译,请运行以下命令:
adb shell cmd package compile
强制编译特定软件包的常见用例:
- 基于配置文件:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed-profile -f my-package
- 全面:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed -f my-package
强制编译所有软件包的常见用例:
- 基于配置文件:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed-profile -f -a
- 全面:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed -f -a
清除配置文件数据
在 Android 13 或更低版本中
如需清除本地配置文件数据并移除经过编译的代码,请运行以下命令:
adb shell pm compile --reset
在 Android 14 或更高版本中
若要仅清除本地配置文件数据,请执行以下操作:
adb shell pm art clear-app-profiles
注意:与适用于 Android 13 或更低版本的命令不同,此命令不会清除随应用一起安装的外部配置文件数据(“.dm”)。
如需清除本地配置文件数据并移除根据本地配置文件数据生成的已编译代码(即重置安装状态),请运行以下命令:
adb shell pm compile --reset
注意:此命令不会移除随应用一起安装的外部配置文件数据(“.dm”)生成的已编译代码。
如需清除所有已编译代码,请运行以下命令:
adb shell cmd package compile -m verify -f
注意:此命令会保留本地配置文件数据。
