Android 9 包含一个供应商测试套件 (VTS) 基础架构,用于在搭载 AOSP 通用系统映像 (GSI) 的合作伙伴设备上自动运行 VTS、CTS 或其他测试。以前,运行这些测试需要大量手动操作,而新的 VTS 测试基础架构可支持每天在多个设备上自动运行测试多次。
架构
VTS 自动化测试基础架构采用以下架构:
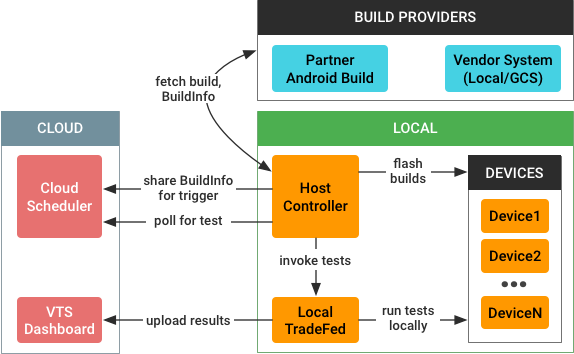
触发测试后,VTS 自动化测试基础架构会执行以下任务:
- 从不同位置获取 build 工件和测试资源:
- 合作伙伴 Android build (PAB)。针对 GSI、VTS 框架以及一些其他 build。
- 本地文件系统、Google Cloud Storage 或其他特定于供应商的构建系统。针对不在 Google 云服务中存储 build 的合作伙伴。
- 将 build 工件(来自设备)和 GSI(来自 AOSP)刷写到连接的设备。
- 使用本地 TradeFed 或云端的 TradeFed 运行 VTS 测试。
- 向 VTS 信息中心报告测试结果
该进程由 VTS 主机控制器 (HC) 进行协调。HC 是实验室中的一台机器,用于指导所有已连接的受测设备的行为。HC 负责获取最新 build、将其刷写到设备上,以及调用测试(本地调用或通过命令工具调用)。HC 还会与云端调度器通信,并在调度器和在 HC 上运行的 TradeFed 实例(或一些其他测试框架)之间引导流量。如需详细了解主机控制器,请参阅主机控制器架构。
资源提供程序
自动化测试需要各种资源,例如系统 build、测试文件和 VTS 工件。虽然可以使用源代码构建这些资源,但更简单的方式是定期使用最新代码进行构建,然后发布工件以供下载。
合作伙伴可以在以下位置访问自动化资源:
- 合作伙伴 Android build。按账号授予的程序化访问权限。
- 本地文件系统(或类似位置)。针对不使用合作伙伴 Android build 的合作伙伴。
为了在以后刷写设备时使用,资源中包含这两个选项的 build 提供程序(从在本地临时目录中存储 build 的单个 build_provider.py 扩展而来)。
合作伙伴 Android build
在 Android 8.1 及更低版本中,Android 合作伙伴需要访问合作伙伴 Android build 网站 (https://partner.android.com/build),转到自己的账号,然后通过界面获取最新的系统映像。为了帮助合作伙伴避免这种缓慢且耗费人力的过程,Android 9 支持在提供相关凭据后自动从 PAB 下载这些资源。
建立访问权限
程序化访问权限使用 Google API 中的 OAuth2 来访问所需的 RPC。如需借助标准方法生成 OAuth2 凭据,合作伙伴必须通过 Google 设置客户 ID/密钥对。PartnerAndroidBuildClient 在首次指向该密钥时,会打开一个浏览器窗口供用户登录 Google 账号,以生成继续操作所需的 OAuth2 凭据。这些凭据(访问令牌和刷新令牌)存储在本地,这意味着合作伙伴只需登录一次即可。
网址 POST 请求
点击 PAB 中的资源链接即会发送一个 POST 请求,其中包含相应资源的必要数据,这些数据包括:
- build id、构建目标
- 资源名称
- 分支
- 候选版本名称,以及候选版本是不是内部 build
buildsvc RPC 的 downloadBuildArtifact 方法会接收 POST 请求,并返回用于访问资源的网址。
- 对于 Clockwork Companion APK 资源,该网址是在 PAB 上托管的可读取网址(设有 auth 验证机制,可凭相关 OAuth2 凭据获取)。
- 对于其他资源,该网址是来自内部 Android build API 的不受保护的长网址(5 分钟后即会过期)。
获取网址
为了防止跨网站请求伪造,buildsvc RPC 需要一个 XSRF 令牌才能与其他参数一起进行 POST。虽然该令牌能够让这一过程更安全,但由于现在访问也需要该令牌(仅在 PAB 页面的 JavaScript 中提供),因此程序化访问就变得更困难了。
为了避免这一问题,Android 9 重新设计了所有文件(不仅仅是 APK)的网址命名方案,以使用可预测的网址名称来访问工件列表和工件网址。现在,PAB 使用一种方便的网址格式,让合作伙伴能够轻松下载资源;HC 脚本可以轻松地下载这些 APK,因为网址格式是已知的,并且 HC 可以绕过 XSRF/Cookie 问题,因为 HC 不需要 buildsvc RPC。
本地文件系统
在获得包含工件列表(或 zip 文件)的目录后,build 提供程序会根据该目录中的内容设置相关映像。您可以使用 gsutil 工具将文件从 Google Cloud Storage 复制到本地目录。
刷写 build
将最新的设备映像下载到主机后,必须将这些映像刷写到设备上。您需要根据 build 提供程序存储的临时文件路径,使用标准 adb 和 fastboot 命令以及 Python 子进程完成相关操作。
支持的操作:
- 仅刷写 GSI
- 刷写来自主系统的单个映像(例如
fastboot flash boot boot.img) - 刷写来自主系统的所有映像,示例:
fastboot flashall(使用内置的flashall实用程序)fastboot flash(一次一个)
运行测试
在 Android 9 中,VTS 自动化测试基础架构仅支持 TradeFed 测试框架,但未来可能会支持其他框架。
设备准备完毕后,您可以使用以下任一选项来调用测试:
- 在本地使用 TradeFed 时,请在主机控制器中使用
test命令,该命令会接受 VTS 测试计划的名称(例如vts-selftest)并运行测试。 - 在使用 TradeFed Cluster(可以选择连接到 MTT)时,请在主机控制器控制台中使用
lease命令,以查找未完成运行的测试。
如果使用 TradeFedCluster,TradeFed 便会作为远程管理器在本地运行。如果未使用,则使用 Python 子进程来调用测试。
报告结果
VtsMultiDeviceTest 会自动将测试结果报告给一些 VTS 信息中心项目。
