साल 2026 से, हम अपने ट्रंक स्टेबल डेवलपमेंट मॉडल के साथ अलाइन होने के लिए, दूसरी और चौथी तिमाही में AOSP पर सोर्स कोड पब्लिश करेंगे. इससे यह पक्का किया जा सकेगा कि प्लैटफ़ॉर्म, पूरे सिस्टम के लिए स्थिर बना रहे. हमारा सुझाव है कि AOSP को बनाने और उसमें योगदान देने के लिए, aosp-main के बजाय android-latest-release का इस्तेमाल करें. android-latest-release मेनिफ़ेस्ट ब्रांच, हमेशा AOSP पर पुश की गई सबसे नई रिलीज़ का रेफ़रंस देगी. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, AOSP में हुए बदलाव लेख पढ़ें.
होस्ट कंट्रोलर का आर्किटेक्चर
संग्रह की मदद से व्यवस्थित रहें
अपनी प्राथमिकताओं के आधार पर, कॉन्टेंट को सेव करें और कैटगरी में बांटें.
वीटीएस टेस्ट फ़्रेमवर्क का आर्किटेक्चर, क्लाउड पर आधारित टेस्ट
सर्विसिंग सेवा के साथ इंटिग्रेट होता है. वीटीएस होस्ट कंट्रोलर, होस्ट मशीन पर चलता है और टेस्ट हार्नेस (उदाहरण के लिए, Tradefed) के इंस्टेंस को कंट्रोल करता है. इसे यहां दिखाया गया है:
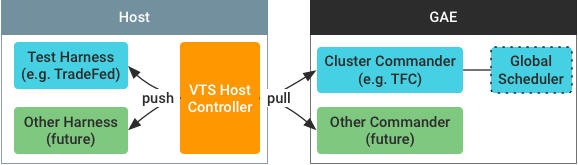
पहली इमेज. वीटीएस होस्ट कंट्रोलर का आर्किटेक्चर.
कंट्रोलर, Google App Engine (GAE) इंस्टेंस के तौर पर चल रहे क्लस्टर कमांडर से निर्देश लेता है. इसके बाद, यह अपने क्लस्टर कमांडर और टेस्ट हार्नेस इंस्टेंस के बीच निर्देश और जवाब भेजता है.
इस आर्किटेक्चर के ये फ़ायदे हैं:
- यह किसी भी टेस्ट हार्नेस इंस्टेंस से अलग होता है. इसलिए, यह अलग-अलग तरह के टेस्ट हार्नेस को कंट्रोल कर सकता है और ज़्यादा मज़बूत होता है. वैकल्पिक डिज़ाइन (टेस्ट हार्नेस में होस्ट कंट्रोल लॉजिक को एम्बेड करना) से, गड़बड़ियों को फैलने से नहीं रोका जा सकता.
- पुल-आधारित कमांड-एंड-कंट्रोल (सी ऐंड सी) मॉडल का इस्तेमाल करने की वजह से, यह अलग-अलग तरह के क्लाउड-साइड क्लस्टर कमांडर के साथ-साथ फ़ायरवॉल के पीछे मौजूद होस्ट के साथ भी काम कर सकता है. ऐसा इनग्रेस कनेक्शन के लिए होता है. पुश-आधारित C&C मॉडल वाले वैकल्पिक डिज़ाइन में, ऐसा हो सकता है कि क्लाउड कमांडर को निजी नेटवर्क में मौजूद होस्ट कंप्यूटर पर होस्ट कंट्रोलर इंस्टेंस को ऐक्सेस करने की अनुमति न मिले.
इस पेज पर मौजूद कॉन्टेंट और कोड सैंपल कॉन्टेंट के लाइसेंस में बताए गए लाइसेंस के हिसाब से हैं. Java और OpenJDK, Oracle और/या इससे जुड़ी हुई कंपनियों के ट्रेडमार्क या रजिस्टर किए हुए ट्रेडमार्क हैं.
आखिरी बार 2025-12-03 (UTC) को अपडेट किया गया.
[[["समझने में आसान है","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["मेरी समस्या हल हो गई","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["अन्य","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["वह जानकारी मौजूद नहीं है जो मुझे चाहिए","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["बहुत मुश्किल है / बहुत सारे चरण हैं","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["पुराना","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["अनुवाद से जुड़ी समस्या","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["सैंपल / कोड से जुड़ी समस्या","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["अन्य","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["आखिरी बार 2025-12-03 (UTC) को अपडेट किया गया."],[],[]]

