Android 9 รองรับการรับชื่อบริการของอินสแตนซ์ HAL ที่ระบุตามอุปกรณ์ที่ชุดทดสอบของผู้ให้บริการ (VTS) ทำงานอยู่ การเรียกใช้การทดสอบ VTS HAL ที่รับรู้ชื่อบริการ ช่วยให้นักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์สามารถทำการทดสอบส่วนขยายของผู้ให้บริการ, HAL หลายรายการ และ อินสแตนซ์ HAL หลายรายการโดยอัตโนมัติในการทดสอบ VTS ทั้งฝั่งเป้าหมายและฝั่งโฮสต์
เกี่ยวกับชื่อบริการ
อินสแตนซ์แต่ละรายการของบริการ HAL ที่ทำงานจะลงทะเบียนตัวเองด้วยชื่อบริการ
ใน Android เวอร์ชันก่อนหน้า นักพัฒนาแอปที่เรียกใช้การทดสอบ VTS HAL จะต้องตั้งชื่อบริการที่ถูกต้องสำหรับไคลเอ็นต์ทดสอบใน
getService() หรือปล่อยให้ชื่อว่างไว้และกลับไปใช้ชื่อบริการเริ่มต้น
ข้อเสียของแนวทางนี้ ได้แก่
- การพึ่งพาความรู้ของนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ทดสอบในการตั้งชื่อบริการที่ถูกต้อง
- โดยค่าเริ่มต้นจะจำกัดไว้ที่การทดสอบกับอินสแตนซ์บริการเดียว
- การบำรุงรักษาชื่อบริการด้วยตนเอง (กล่าวคือ เนื่องจากชื่อมีการฮาร์ดโค้ด จึงต้องอัปเดตด้วยตนเองหากชื่อบริการมีการเปลี่ยนแปลง
ใน Android 9 นักพัฒนาแอปจะรับชื่อบริการสำหรับอินสแตนซ์ HAL ที่กำหนดโดยอัตโนมัติตามอุปกรณ์ที่อยู่ระหว่างการทดสอบได้ ข้อดีของแนวทางนี้รวมถึงการรองรับการทดสอบมีดังนี้
- ส่วนขยาย HAL ของผู้จำหน่าย ตัวอย่างเช่น เมื่อผู้ให้บริการมีการ ติดตั้งใช้งาน HAL ของ camera.provider ที่ทำงานบนอุปกรณ์ของผู้ให้บริการที่มี ชื่อบริการที่กำหนดเอง VTS จะระบุอินสแตนซ์ของผู้ให้บริการและเรียกใช้การทดสอบ กับอินสแตนซ์นั้นได้
- HAL หลายอินสแตนซ์ ตัวอย่างเช่น เมื่อ
graphics.composerHAL มี 2 อินสแตนซ์ (อินสแตนซ์หนึ่งมีชื่อบริการ "default" และอีกอินสแตนซ์หนึ่งมีชื่อบริการ "vr") VTS จะระบุทั้ง 2 อินสแตนซ์และเรียกใช้การทดสอบกับแต่ละอินสแตนซ์ได้ - การทดสอบ HAL หลายรายการ ใช้เมื่อทดสอบ HAL หลายรายการที่มีอินสแตนซ์หลายรายการ เช่น เมื่อเรียกใช้การทดสอบ VTS ที่ตรวจสอบว่า HAL ของ KeyMint (เดิมคือ Keymaster) และ Gatekeeper ทำงานร่วมกันอย่างไร VTS จะทดสอบชุดค่าผสมทั้งหมดของอินสแตนซ์บริการสำหรับ HAL เหล่านั้นได้
การทดสอบฝั่งเป้าหมาย
Android 9 มีสภาพแวดล้อมการทดสอบที่ปรับแต่งได้ (VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase) เพื่อให้มีอินเทอร์เฟซสำหรับทำสิ่งต่อไปนี้
เพื่อเปิดใช้การรับรู้ชื่อบริการสำหรับการทดสอบฝั่งเป้าหมาย
- ลงทะเบียน HAL ของการกำหนดเป้าหมายในการทดสอบ
- แสดงรายการ HAL ที่ลงทะเบียนทั้งหมด
- รับชื่อบริการสำหรับ HAL ที่ลงทะเบียนซึ่งเฟรมเวิร์ก VTS จัดเตรียมไว้ให้
นอกจากนี้ เฟรมเวิร์ก VTS ยังรองรับรันไทม์สำหรับรายการต่อไปนี้
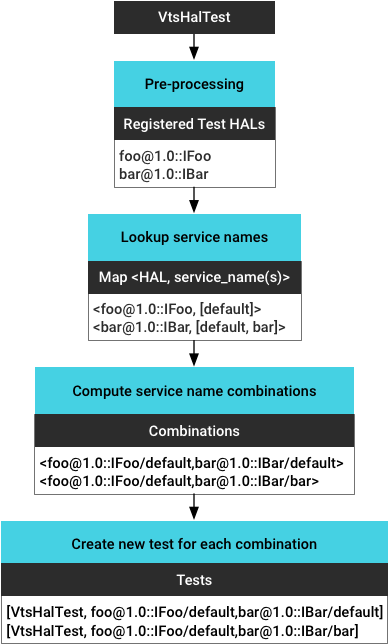
- ประมวลผลไบนารีทดสอบล่วงหน้าเพื่อรับ HAL การทดสอบที่ลงทะเบียนทั้งหมด
- ระบุอินสแตนซ์บริการที่ทำงานทั้งหมดและรับชื่อบริการสำหรับ
แต่ละอินสแตนซ์ (ดึงข้อมูลตาม
vendor/manifest.xml) - คำนวณชุดค่าผสมของอินสแตนซ์ทั้งหมด (เพื่อรองรับการทดสอบ HAL หลายรายการ )
- สร้างการทดสอบใหม่สำหรับอินสแตนซ์บริการ (ชุดค่าผสม) แต่ละรายการ
ตัวอย่าง
ตั้งค่าการทดสอบฝั่งเป้าหมายที่รับรู้ชื่อบริการ
วิธีตั้งค่าสภาพแวดล้อมการทดสอบสำหรับการทดสอบที่รับรู้ชื่อบริการฝั่งเป้าหมาย
- กำหนด
testEnvironmentตามVtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBaseและลงทะเบียน HAL การทดสอบ#include <VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase.h> class testEnvironment : public::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase { virtual void registerTestServices() override { registerTestService<IFoo>(); } };
- ใช้
getServiceName()ที่สภาพแวดล้อมการทดสอบระบุเพื่อส่งชื่อบริการ::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestBase::getService<IFoo>(testEnv->getServiceName<IFoo>("default")); // "default" is the default service name you want to use.
- ลงทะเบียนสภาพแวดล้อมการทดสอบใน
main()และinitTestโดยทำดังนี้int main(int argc, char** argv) { testEnv = new testEnvironment(); ::testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(testEnv); ::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); testEnv->init(argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); }
ดูตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติมได้ที่
VtsHalCameraProviderV2_4TargetTest.cpp
การทดสอบฝั่งโฮสต์ของ VTS
การทดสอบฝั่งโฮสต์ของ VTS จะเรียกใช้สคริปต์ทดสอบในฝั่งโฮสต์แทนไบนารีทดสอบใน อุปกรณ์เป้าหมาย หากต้องการเปิดใช้การรับรู้ชื่อบริการสำหรับการทดสอบเหล่านี้ คุณสามารถ ใช้เทมเพลตฝั่งโฮสต์เพื่อเรียกใช้สคริปต์การทดสอบเดียวกันหลายครั้งกับ พารามิเตอร์ต่างๆ (คล้ายกับการทดสอบที่กำหนดพารามิเตอร์ gtest)

hal_hidl_host_test
(คลาสย่อยของ param_test) จะใช้ HAL การทดสอบที่ลงทะเบียนจาก
สคริปต์ทดสอบ ระบุชื่อบริการที่เกี่ยวข้องสำหรับ HAL การทดสอบ
จากนั้นสร้างชุดชื่อบริการ (สำหรับการทดสอบแบบหลาย HAL) เป็นพารามิเตอร์การทดสอบ นอกจากนี้ ยังมีเมธอด getHalServiceName() ซึ่ง
แสดงผลชื่อบริการที่เกี่ยวข้องตามพารามิเตอร์ที่ส่งไปยัง
กรณีทดสอบปัจจุบันตั้งค่าการทดสอบฝั่งโฮสต์ที่รับรู้ชื่อบริการ
วิธีตั้งค่าสภาพแวดล้อมการทดสอบสำหรับการทดสอบที่รับรู้ชื่อบริการฝั่งโฮสต์
- ระบุบริการ HAL เป้าหมายในสคริปต์ทดสอบ
TEST_HAL_SERVICES = { "android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo" }
- โทรหา
getHalServiceName()แล้วส่งชื่อไปยัง init halself.dut.hal.InitHidlHal( target_type='foo', target_basepaths=self.dut.libPaths, target_version=1.0, target_package='android.hardware.foo', target_component_name='IFoo', hw_binder_service_name =self.getHalServiceName("android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo"), bits=int(self.abi_bitness))
ดูตัวอย่างเพิ่มเติมได้ที่
VtsHalMediaOmxStoreV1_0HostTest.py
ลงทะเบียน HAL ทดสอบ
ใน Android เวอร์ชันก่อนหน้า VTS จะระบุ HAL ที่ใช้ทดสอบโดยใช้ตัวเลือก <precondition-lshal> ที่กำหนดค่าไว้ใน AndroidTest.xml วิธีนี้ดูแลรักษายาก (เนื่องจากต้องอาศัยนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ในการกำหนดค่าการทดสอบอย่างถูกต้องและอัปเดตการกำหนดค่าตามนั้น) และไม่ถูกต้อง (เนื่องจากมีเฉพาะข้อมูลแพ็กเกจและเวอร์ชัน ไม่ใช่ข้อมูลอินเทอร์เฟซ)
ใน Android 9 VTS จะระบุ HAL ที่ทดสอบโดยใช้ การรับรู้ชื่อบริการ นอกจากนี้ HAL การทดสอบที่ลงทะเบียนแล้วยังมีประโยชน์สำหรับสิ่งต่อไปนี้ด้วย
- การตรวจสอบข้อกำหนดเบื้องต้น ก่อนที่จะเรียกใช้การทดสอบ HAL นั้น VTS สามารถ ยืนยันว่า HAL ที่จะทดสอบพร้อมใช้งานในอุปกรณ์เป้าหมายและข้ามการทดสอบ หากไม่พร้อมใช้งาน (ดูการตรวจสอบความสามารถในการทดสอบของ VTS)
- การวัดการครอบคลุม VTS รองรับการวัดความครอบคลุมของโค้ดข้ามกระบวนการ ผ่านความรู้เกี่ยวกับบริการ HAL ของการทดสอบที่ต้องการ วัด (เช่น เพื่อล้างความครอบคลุมสำหรับกระบวนการบริการ HAL)
