Android 9 支援根據執行供應商測試套件 (VTS) 測試的裝置,取得特定 HAL 執行個體的服務名稱。執行可識別服務名稱的 VTS HAL 測試,開發人員就能在目標端和主機端 VTS 測試執行作業中,自動測試供應商擴充功能、多個 HAL 和多個 HAL 執行個體。
關於服務名稱
每個 HAL 服務執行個體都會以服務名稱註冊。
在舊版 Android 中,執行 VTS HAL 測試的開發人員必須在 getService() 中為測試用戶端設定正確的服務名稱,或將名稱留空並回退至預設服務名稱。這種做法的缺點包括:
- 依賴測試開發人員的知識來設定正確的服務名稱。
- 預設只能針對單一服務執行個體進行測試。
- 手動維護服務名稱 (即名稱經過硬式編碼,因此如果服務名稱變更,就必須手動更新)。
在 Android 9 中,開發人員可根據測試中的裝置,自動取得特定 HAL 執行個體的服務名稱。這種做法的優點包括支援測試:
- 供應商 HAL 擴充功能。舉例來說,如果供應商實作的 camera.provider HAL 在供應商裝置上執行,且使用自訂服務名稱,VTS 就能識別供應商執行個體,並對其執行測試。
- 多個 HAL 執行個體。舉例來說,如果
graphics.composerHAL 有兩個執行個體 (一個的服務名稱為「default」,另一個為「vr」),VTS 可以識別這兩個執行個體,並針對每個執行個體執行測試。 - 多個 HAL 測試。用於測試多個 HAL 和多個執行個體。舉例來說,執行 VTS 測試來驗證 KeyMint (先前為 Keymaster) 和 Gatekeeper HAL 如何協同運作時,VTS 可以測試這些 HAL 的所有服務執行個體組合。
目標端測試
如要為目標端測試啟用服務名稱感知功能,Android 9 包含可自訂的測試環境 (VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase),提供下列介面:
- 在測試中註冊目標 HAL。
- 列出所有已註冊的 HAL。
- 取得 VTS 架構提供的已註冊 HAL 服務名稱。
此外,VTS 架構還提供下列項目的執行階段支援:
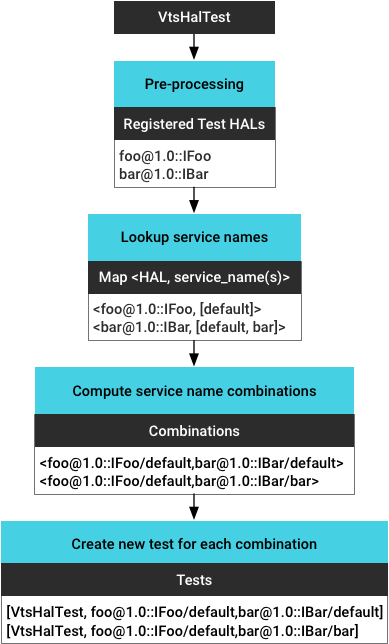
- 預先處理測試二進位檔,取得所有已註冊的測試 HAL。
- 找出所有正在執行的服務執行個體,並取得每個執行個體的服務名稱 (根據
vendor/manifest.xml擷取)。 - 計算所有執行個體組合 (支援多個 HAL 測試)。
- 為每個服務執行個體 (組合) 產生新的測試。
範例如下:
設定可識別服務名稱的目標端測試
如要設定目標端服務名稱感知測試的測試環境,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 根據
VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase定義testEnvironment,並註冊測試 HAL:#include <VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase.h> class testEnvironment : public::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase { virtual void registerTestServices() override { registerTestService<IFoo>(); } };
- 使用測試環境提供的
getServiceName()傳遞服務名稱:::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestBase::getService<IFoo>(testEnv->getServiceName<IFoo>("default")); // "default" is the default service name you want to use.
- 在
main()和initTest中註冊測試環境:int main(int argc, char** argv) { testEnv = new testEnvironment(); ::testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(testEnv); ::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); testEnv->init(argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); }
如需其他範例,請參閱 VtsHalCameraProviderV2_4TargetTest.cpp。
VTS 主機端測試
VTS 主機端測試會在主機端執行測試指令碼,而不是在目標裝置上執行測試二進位檔。如要為這些測試啟用服務名稱感知功能,可以使用主機端範本,針對不同參數多次執行相同測試指令碼 (類似於 gtest 參數化測試)。

- hal test 指令碼會在測試中指定目標 HAL 服務。
hal_hidl_host_test(param_test的子類別) 會從測試指令碼中取得已註冊的測試 HAL,找出測試 HAL 的對應服務名稱,然後產生服務名稱組合 (適用於多個 HAL 的測試),做為測試參數。此外,這個類別也提供getHalServiceName()方法,可根據傳遞至目前測試案例的參數,傳回對應的服務名稱。- param_test 範本支援邏輯,可接受參數清單,並針對每個參數執行所有指定的測試案例。也就是說,系統會為每個測試案例產生 N 個新的參數化測試案例 (N = 參數大小),每個案例都有指定的參數。
設定可識別服務名稱的主機端測試
如要設定主機端服務名稱感知測試的測試環境,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 在測試指令碼中指定目標 HAL 服務:
TEST_HAL_SERVICES = { "android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo" }
- 呼叫
getHalServiceName()並將名稱傳遞至 init hal:self.dut.hal.InitHidlHal( target_type='foo', target_basepaths=self.dut.libPaths, target_version=1.0, target_package='android.hardware.foo', target_component_name='IFoo', hw_binder_service_name =self.getHalServiceName("android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo"), bits=int(self.abi_bitness))
如需其他範例,請參閱 VtsHalMediaOmxStoreV1_0HostTest.py。
註冊測試 HAL
在舊版 Android 中,VTS 會使用 AndroidTest.xml 中設定的 <precondition-lshal> 選項,識別測試 HAL。這種做法難以維護 (因為需要開發人員正確設定測試,並相應更新設定),而且不準確 (因為只包含套件和版本資訊,不含介面資訊)。
在 Android 9 中,VTS 會使用服務名稱感知功能識別測試 HAL。註冊的測試 HAL 也可用於:
- 先決條件檢查。執行 HAL 測試前,VTS 可以確認目標裝置上是否有可用的測試 HAL,如果沒有,則會略過測試 (請參閱 VTS 可測試性檢查)。
- 涵蓋範圍評估:VTS 支援跨程序程式碼涵蓋範圍測量,方法是瞭解要測量的測試 HAL 服務 (也就是要清除 HAL 服務程序的涵蓋範圍)。

