기기 트리(DT)는 검색할 수 없는 하드웨어를 설명하는 이름이 지정된 노드와 속성의 데이터 구조입니다. Android에서 사용되는 Linux 커널과 같은 커널은 DT를 사용하여 Android 기반 기기에 사용되는 광범위한 하드웨어 구성을 지원합니다. 하드웨어 공급업체는 자체 기기 트리 소스(DTS) 파일을 제공합니다. 이 파일은 기기 트리 컴파일러를 사용하여 기기 트리 Blob(DTB) 파일로 컴파일됩니다. 그러면 부트로더에서 이 파일을 사용합니다. DTB 파일에는 바이너리 형식의 평면화된 기기 트리가 포함되어 있습니다.
기기 트리 오버레이(DTO)는 중앙 기기 트리 Blob(DTB)을 기기 트리에 오버레이할 수 있도록 지원합니다. DTO를 사용하는 부트로더는 단일 칩 시스템(SoC) DT를 유지하고 기기별 DT를 동적으로 오버레이하여 노드를 트리에 추가하고 기존 트리의 속성을 변경할 수 있습니다.
DTBO: 오버레이용 기기 트리 Blob
Android 9 출시에 포함된 업데이트
Android 9에서는 통합 기기 트리 blob을 커널에 전달하기 전에 부트로더가 기기 트리 오버레이에 정의된 속성을 수정하면 안 됩니다.
기기 트리 로드
부트로더에 기기 트리를 로드하는 과정에는 빌드, 파티션 나누기 및 실행이 포함됩니다.
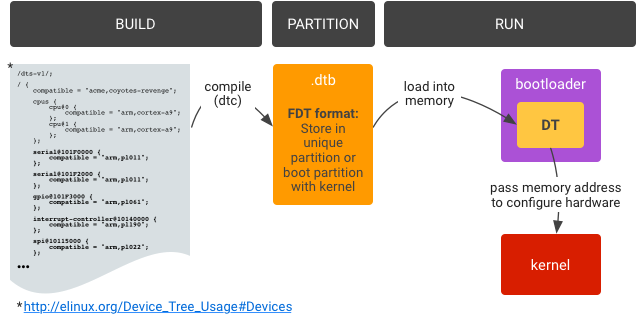
기기 트리 blob을 만들고 플래시하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
1a. 기기 트리 컴파일러(
dtc>)를 사용하여 기기 트리 소스(.dts)를 기기 트리 blob(.dtb)에 컴파일합니다. 기기 트리 blob은 평면화된 기기 트리로 형식이 지정됩니다. 1b..dtb파일을 부트로더 런타임으로 액세스 가능한 위치에 플래시합니다(자세한 내용은 아래 참고).파티션을 분할하려면 플래시 메모리에서 부트로더 런타임으로 액세스 가능한 신뢰할 수 있는 위치를 파악하여
.dtb를 배치합니다. 위치의 예는 다음과 같습니다.부팅 파티션 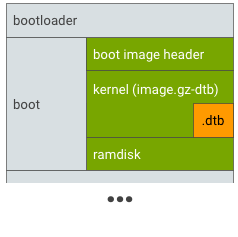
그림 2. .dtb를image.gz에 추가하고 'kernel'로mkbootimg에 전달하여 부팅 파티션에 배치합니다.고유 파티션 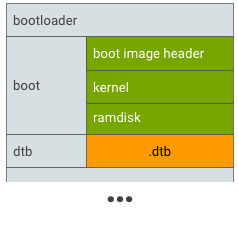
그림 3. .dtb를 고유 파티션(예:dtb파티션)에 배치기기 트리 blob을 로드하고 커널을 시작하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
.dtb를 저장소에서 메모리로 로드합니다.- 로드된 DT의 메모리 주소를 사용하여 커널을 시작합니다.
다음 단계
이 페이지에서는 DT를 로드하기 위한 일반적인 부트로더 워크플로에 관해 자세히 설명하고 일반적인 DT 용어 목록을 제공합니다. 이 섹션의 다른 페이지에서는 부트로더 지원을 구현하는 방법과 DTO를 컴파일하고 확인하고 최적화하는 방법, 다중 DT를 사용하는 방법을 설명합니다. 또한 DTO 문법 및 필수 DTO/DTBO 파티션 형식 지정에 관한 자세한 내용도 확인할 수 있습니다.
