
يوفر نظام التشغيل Android حزمة بروتوكولات بلوتوث تلقائية تتوافق مع كل من البلوتوث الكلاسيكي والبلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة (BLE). باستخدام البلوتوث، يمكن لأجهزة Android إنشاء شبكات منطقة شخصية لإرسال البيانات واستلامها من أجهزة البلوتوث القريبة.
في الإصدار 4.3 من نظام التشغيل Android والإصدارات الأحدث، تتيح حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث في Android إمكانية تنفيذ تقنية البلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة (BLE). لاستخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات البلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة بشكل كامل، اتّبِع متطلبات واجهة HCI للبلوتوث على Android. يمكن لأجهزة Android التي تحتوي على مجموعة شرائح مؤهَّلة استخدام تقنية البلوتوث العادية أو كلتا التقنيتَين، أي البلوتوث العادي وBLE. لا تتوافق تقنية البلوتوث المنخفض الطاقة (BLE) مع شرائح تعريف البلوتوث القديمة.
في نظام التشغيل Android 8.0، تكون حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث مؤهَّلة بالكامل لاستخدام البلوتوث 5. لاستخدام ميزات البلوتوث 5 المتاحة، يجب أن يتضمّن الجهاز مجموعة شرائح مؤهَّلة لاستخدام البلوتوث 5.
هندسة Android
يتواصل تطبيق البلوتوث مع عملية البلوتوث من خلال Binder. تستخدم عملية البلوتوث واجهة Java الأصلية (JNI) للتواصل مع حزمة بروتوكولات البلوتوث، وتتيح للمطوّرين الوصول إلى العديد من ملفات تعريف البلوتوث. يوضّح هذا الرسم التخطيطي البنية العامة لحزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث:
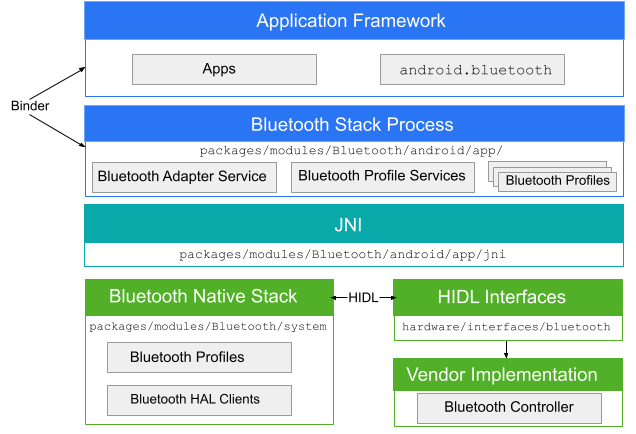
الشكل 1. بنية البلوتوث في Android
- إطار عمل التطبيق
- على مستوى إطار عمل التطبيق، يوجد رمز التطبيق الذي يستخدم واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
android.bluetoothللتفاعل مع أجهزة البلوتوث. داخليًا، يستدعي هذا الرمز عملية البلوتوث من خلال آلية Binder IPC. - تطبيق البلوتوث
- يتم تجميع تطبيق البلوتوث، المتوفّر في
packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app، كتطبيق Android، ويتم تنفيذ ملفات تعريف البلوتوث في طبقة إطار عمل Android. يتصل هذا التطبيق بمجموعة برامج البلوتوث من خلال JNI. - JNI
- يقع رمز JNI المرتبط بـ
android.bluetoothفيpackages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app/jni. يتم استدعاء رمز JNI إلى حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث عند حدوث عمليات بلوتوث معيّنة، مثل عند اكتشاف الأجهزة. - حزمة بروتوكولات البلوتوث
- يتم توفير حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث التلقائية في مشروع Android المفتوح المصدر (AOSP) وتقع في
packages/modules/Bluetooth/system. تنفّذ الحزمة طبقة تجريد الأجهزة (HAL) العامة للبلوتوث وتخصّصها باستخدام الإضافات وتغييرات الإعدادات. - تنفيذ المورّد تتفاعل أجهزة المورِّد
- مع حزمة برامج البلوتوث باستخدام لغة تعريف واجهة HAL (HIDL).
HIDL
تحدِّد HIDL الواجهة بين حزمة Bluetooth وتنفيذ المورِّد. لإنشاء ملفات Bluetooth HIDL، مرِّر ملفات واجهة Bluetooth إلى أداة إنشاء HIDL. توجد ملفات الواجهة في
hardware/interfaces/bluetooth.
تطوير حزمة البلوتوث
حزمة بلوتوث Android هي حزمة بلوتوث مؤهَّلة بالكامل. تتوفّر قائمة المؤهلات على موقع Bluetooth SIG الإلكتروني (يجب تسجيل الدخول) ضمن QDID 169365.
تتوفّر حزمة البلوتوث الأساسية في
packages/modules/Bluetooth.
يتم التطوير في AOSP، ونرحّب بالمساهمات.
