デバイス メーカーは通常、デバイスごとに作成されたプライベート アセットの所有者とみなされます。したがって、エンジニアリングの取り組みは、デバイス単位で行われることが多く、エコシステム内の他のデバイスとの一貫性に対する取り組みはほとんど、あるいはまったく行われません。
これとは正反対に、デベロッパーは各デバイスの技術仕様に関係なく、エコシステム内のすべての Android スマートフォンで動作するアプリを作成することを目指します。このようなアプローチの違いにより、断片化の問題が発生することがあります。たとえば、特定のスマートフォンのハードウェア機能が、アプリ デベロッパーの想定と一致しないことがあります。一部の Android スマートフォンで動作するハプティクス API が他の Android スマートフォンでは動作しない場合、結果として一貫性のないエコシステムとなります。こうした理由により、メーカーが Android ハプティクス API をすべてのデバイスに実装できるようにするうえで、ハードウェア構成が重要な役割を果たします。
このページでは、Android ハプティクス API を最大限活用するためにハードウェア コンプライアンスを設定する方法について、詳細なチェックリストをご紹介します。
下図は、デバイス メーカーとデベロッパーの間で共通の知識を構築するプロセスを示しています。これは、一貫性のあるエコシステムを構築するうえで重要なステップです。
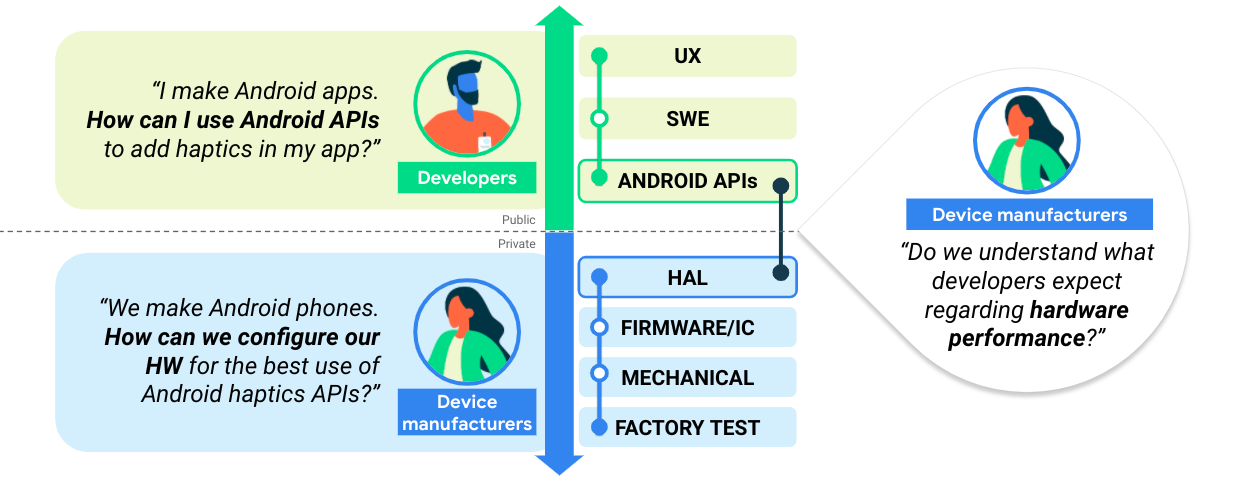
図 1. デバイス メーカーとデベロッパーの間の知識の構築
ハプティクス実装チェックリスト
-
- ハプティクスを実装する定数のリスト。
-
- HAL 合成プリミティブの実装ガイダンス。
-
- 公開 API 定数(フレームワークの名前付きプレースホルダ)と、プレースホルダを実装する HAL 定数との間のマッピングの推奨事項。
- このプロセスについて詳しくは、推奨されるマッピングの指針となる設計原則をご覧ください。
-
- ターゲットとする触覚効果についての説明。これにより、ハードウェアのクイック チェックを行います。
