כדי להטמיע את העדכונים האלחוטיים (OTA), תוכנת האתחול צריכה להיות מסוגלת לגשת לדיסק RAM של שחזור במהלך האתחול. אם המכשיר משתמש בתמונה לשחזור של AOSP שלא שונתה, תוכנת האתחול קוראת את 32 הבייטים הראשונים במחיצה misc. אם הנתונים שם תואמים ל-boot-recovery, תוכנת האתחול מבצעת אתחול לתמונה recovery. השיטה הזו מאפשרת להמשיך את כל פעולות השחזור שממתינות (לדוגמה, החלת עדכון OTA או הסרת נתונים) עד להשלמתן.
פרטים על התוכן של בלוק ב-flash שמשמש לתקשורת על ידי recovery ו-bootloader מופיעים ב-bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h.
מכשירים עם עדכוני A/B
כדי לתמוך בעדכוני OTA במכשירים שמשתמשים בעדכוני A/B, צריך לוודא שתוכנת האתחול של המכשיר עומדת בקריטריונים הבאים.
קריטריונים כלליים
אפשר לעדכן את כל המחיצות באמצעות OTA בזמן שהמערכת הראשית מופעלת (ולא מתעדכנת בשחזור).
כדי להפעיל את המחיצה
system, טוען האתחול מעביר את הערך הבא בשורת הפקודה של ליבת המערכת:ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/init.באחריות של מסגרת Android לקרוא ל-
markBootSuccessfulמ-HAL. תוכנת האתחול לא אמורה לסמן מחיצה ככזו שהאתחול שלה הושלם.
תמיכה ב-HAL של בקרת אתחול
טוען האתחול חייב לתמוך ב-boot_control HAL כפי שמוגדר ב-hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h. הכלי לעדכון שולח שאילתה ל-HAL של בקר האתחול, מעדכן את משבצת האתחול שלא נמצאת בשימוש, משנה את המשבצת הפעילה באמצעות ה-HAL ומבצע אתחול מחדש למערכת ההפעלה המעודכנת. פרטים נוספים מופיעים במאמר בנושא הטמעה של HAL לבקרת אתחול.
תמיכה במשבצות
טוען האתחול חייב לתמוך בפונקציונליות שקשורה למחיצות ולמשבצות, כולל:
שמות המחיצות צריכים לכלול סיומת שמזהה לאיזה משבצת במנהל האתחול שייכות המחיצות. לכל מחיצה כזו יש משתנה תואם
has-slot:partition base nameעם ערך שלyes. המשבצות מקבלות שמות לפי סדר האלפבית: a, b, c וכן הלאה, בהתאם למחיצות עם הסיומת_a,_b,_cוכן הלאה. תוכנת האתחול צריכה להודיע למערכת ההפעלה איזו משבצת הופעלה באמצעות מאפיין שורת הפקודהandroidboot.slot_suffix. המאפיין הזה מוגדר באמצעות bootconfig למכשירים שמופעלים עם Android מגרסה 12 ואילך.הערך של
slot-retry-countמאופס לערך חיובי (בדרך כלל3), באמצעות קריאה חוזרת (callback) שלsetActiveBootSlotדרך HAL של בקר האתחול או באמצעות הפקודהfastboot set_active. כשמשנים מחיצה שהיא חלק מחריץ, תוכנת האתחול מוחקת את ההגדרה 'האתחול בוצע בהצלחה' ומאפסת את מספר הניסיונות החוזרים של החריץ.
תוכנת האתחול צריכה גם לקבוע איזה חריץ לטעון. באיור מוצגת דוגמה לתהליך קבלת החלטות.
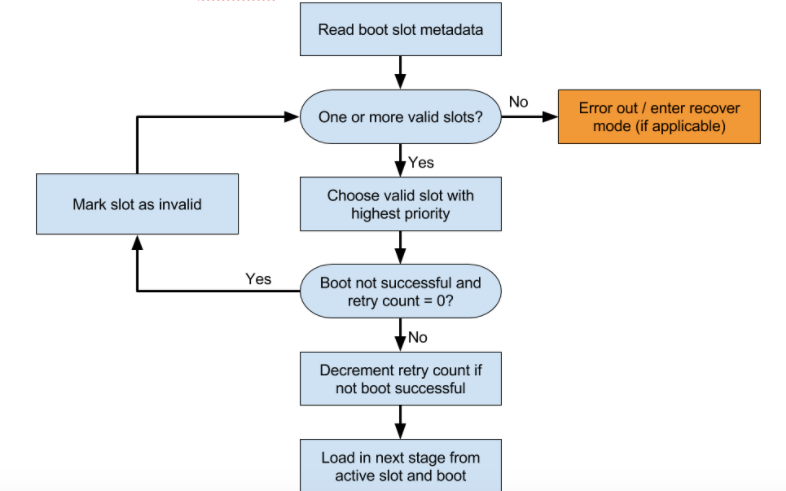
קובעים באיזה משבצת זמן לנסות. אל תנסו לטעון משבצת שסומנה כ-
slot-unbootable. המשבצת הזו צריכה להיות עקבית עם הערכים שמוחזרים על ידי fastboot, והיא נקראת המשבצת הנוכחית.אם המשבצת הנוכחית לא מסומנת כ-
slot-successfulויש להslot-retry-count = 0, מסמנים את המשבצת הנוכחית כ-slot-unbootable. אחר כך בוחרים יחידת קיבולת אחרת שלא מסומנת בסימןunbootableומסומנת בסימןslot-successful. יחידת הקיבולת הזו היא עכשיו יחידת הקיבולת שנבחרה. אם אין משבצת זמינה, צריך לבצע אתחול למצב שחזור או להציג למשתמש הודעת שגיאה משמעותית.בוחרים את
boot.imgהמתאים וכוללים את הנתיב למחיצת המערכת הנכונה בשורת הפקודה של ליבת המערכת.מאכלסים את הפרמטר
slot_suffixשל שורת הפקודה של ליבת המערכת.אתחול. אם לא מסומן
slot-successful, מפחיתים את הערך שלslot-retry-count.
כלי השירות fastboot קובע איזו מחיצה להפעיל כשמריצים פקודות הפעלה. לדוגמה, הפעלת הפקודה fastboot flash system system.img תבצע קודם שאילתה על המשתנה current-slot ואז תשרשר את התוצאה למערכת כדי ליצור את שם המחיצה שצריך להעביר (system_a, system_b וכו').
כשמגדירים את הסלוט הנוכחי באמצעות הפקודה set_active של fastboot או הפקודה setActiveBootSlot של boot control HAL, טוען האתחול צריך לעדכן את הסלוט הנוכחי, לנקות את slot-unbootable ואת slot-successful ולאפס את מספר הניסיונות (זו הדרך היחידה לנקות את slot-unbootable).
מכשירים ללא עדכוני A/B
כדי לתמוך בעדכוני OTA במכשירים שלא משתמשים בעדכוני A/B (ראו מכשירים שאפשר לעדכן אבל לא מסוג A/B), צריך לוודא שטוען האתחול של המכשיר עומד בקריטריונים הבאים.
המחיצה
recoveryצריכה להכיל תמונה שיכולה לקרוא תמונת מערכת ממחיצה נתמכת כלשהי (cache,userdata) ולכתוב אותה במחיצהsystem.טוען האתחול צריך לתמוך באתחול ישירות למצב שחזור.
אם יש תמיכה בעדכוני תמונות של רדיו, גם למחיצה
recoveryצריכה להיות אפשרות להפעיל את הרדיו. אפשר לעשות זאת באחת משתי דרכים:תוכנת האתחול מפעילה את הרדיו. במקרה כזה, אמורה להיות אפשרות להפעיל מחדש ממחיצת השחזור בחזרה לתוכנת האתחול כדי להשלים את העדכון.
קובץ האימג' לשחזור המערכת מפעיל את הרדיו. הפונקציונליות הזו יכולה להינתן כספרייה בינארית או ככלי.
