Kablosuz (OTA) güncellemeleri uygulamak için bootloader'ın başlatma sırasında kurtarma RAM diskine erişebilmesi gerekir. Cihaz, değiştirilmemiş bir AOSP kurtarma görüntüsü kullanıyorsa bootloader, misc bölümündeki ilk 32 baytı okur. Buradaki veriler boot-recovery ile eşleşirse bootloader, recovery görüntüsüne önyükleme yapar. Bu yöntem, bekleyen kurtarma işlemlerinin (ör. OTA uygulama veya veri kaldırma) tamamlanmasını sağlar.
Kurtarma ve önyükleyici tarafından iletişim için kullanılan flaş bellekteki bir bloğun içeriğiyle ilgili ayrıntılar için bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h adresine bakın.
A/B güncellemeleri olan cihazlar
A/B güncellemelerini kullanan cihazlarda OTA güncellemelerini desteklemek için cihaz önyükleyicisinin aşağıdaki ölçütleri karşıladığından emin olun.
Genel ölçütler
OTA üzerinden güncellenen tüm bölümler, ana sistem başlatılırken (ve kurtarma modunda güncellenmezken) güncellenebilir olmalıdır.
Önyükleyici,
systembölümünü önyüklemek için çekirdek komut satırında şu değeri iletir:ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/init.HAL'den
markBootSuccessfulişlevini çağırmak Android çerçevesinin sorumluluğundadır. Bootloader, hiçbir zaman bir bölümü başarıyla başlatılmış olarak işaretlememelidir.
Önyükleme kontrolü HAL'si için destek
Bootloader, boot_control HAL'ı desteklemelidir. Bu HAL, hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h içinde tanımlanmıştır. Güncelleyici, boot control
HAL'yi sorgular, kullanılmayan önyükleme yuvasını günceller, HAL'yi kullanarak etkin yuvayı değiştirir ve güncellenen işletim sisteminde yeniden başlatılır. Ayrıntılı bilgi için Başlatma kontrolü HAL'sini uygulama başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
Slotlar için destek
Bootloader, aşağıdakiler de dahil olmak üzere bölümler ve yuvalarla ilgili işlevleri desteklemelidir:
Bölüm adları, hangi bölümlerin önyükleyicideki belirli bir yuvaya ait olduğunu tanımlayan bir sonek içermelidir. Bu tür her bölüm için
has-slot:partition base namedeğerine sahip bir değişkenyesvardır. Aralıklar,_a,_b,_cvb. sonekine sahip bölümlere karşılık gelecek şekilde alfabetik olarak adlandırılır. Önyükleyici,androidboot.slot_suffixkomut satırı özelliğini kullanarak hangi aralığın başlatıldığını işletim sistemine bildirmelidir. Bu özellik, Android 12 veya sonraki sürümlerle kullanıma sunulan cihazlar için bootconfig üzerinden ayarlanır.slot-retry-countdeğeri,setActiveBootSlotgeri çağırma yoluyla önyükleme kontrolü HAL'si veyafastboot set_activekomutu aracılığıyla pozitif bir değere (genellikle3) sıfırlanır. Bir yuvaya ait olan bölüm değiştirildiğinde önyükleyici, "başarıyla başlatıldı"yı temizler ve yuvanın yeniden deneme sayısını sıfırlar.
Bootloader, hangi yuvanın yükleneceğini de belirlemelidir. Şekilde örnek bir karar verme süreci gösterilmektedir.
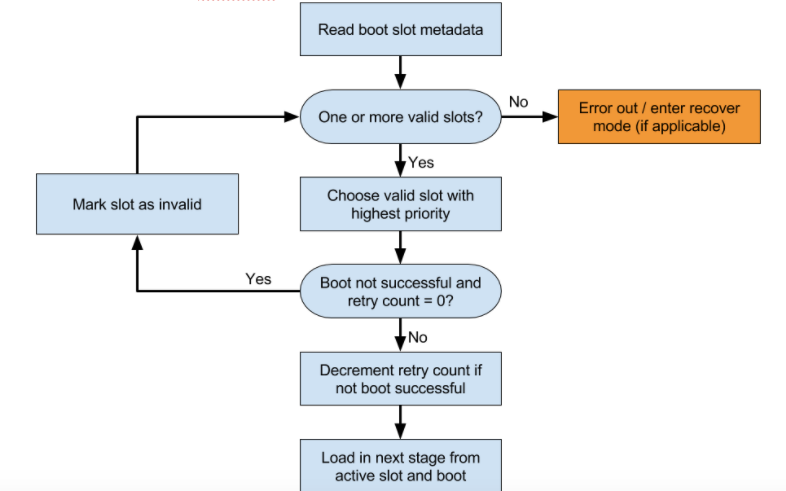
Hangi yerin denenmesi gerektiğini belirleyin.
slot-unbootableolarak işaretlenmiş bir yuva yüklemeye çalışmayın. Bu yuva, fastboot tarafından döndürülen değerlerle tutarlı olmalı ve mevcut yuva olarak adlandırılır.Mevcut yuva
slot-successfulolarak işaretlenmemişse veslot-retry-count = 0içeriyorsa mevcut yuvayıslot-unbootableolarak işaretleyin. Ardından,unbootableolarak işaretlenmemiş veslot-successfulolarak işaretlenmiş farklı bir yuva seçin. Bu yuva artık seçili yuvadır. Mevcut bir yuva yoksa kurtarma modunda başlatın veya kullanıcıya anlamlı bir hata mesajı gösterin.Uygun
boot.imgseçeneğini belirleyin ve çekirdek komut satırında doğru sistem bölümünün yolunu ekleyin.Çekirdek komut satırı
slot_suffixparametresini doldurun.Başlatma
slot-successfulolarak işaretlenmemişseslot-retry-countdeğerini azaltın.
fastboot yardımcı programı, herhangi bir flash komutu çalıştırıldığında hangi bölümün flash'leneceğini belirler. Örneğin, fastboot flash system system.img
komutunu çalıştırmak önce current-slot değişkenini sorgular, ardından sonucu birleştirerek
sisteme aktarılacak bölümün adını oluşturur
(system_a, system_b vb.).
Geçerli yuva, fastboot set_active komutu veya
boot control HAL setActiveBootSlot komutu kullanılarak ayarlandığında önyükleyici geçerli yuvayı güncellemeli, slot-unbootable ve slot-successful değerlerini temizlemeli ve yeniden deneme sayısını sıfırlamalıdır (slot-unbootable değerini temizlemenin tek yolu budur).
A/B güncellemeleri olmayan cihazlar
A/B güncellemelerini kullanmayan cihazlarda OTA güncellemelerini desteklemek için (bkz. Non-A/B updatable devices) cihaz önyükleyicisinin aşağıdaki ölçütleri karşıladığından emin olun.
recoverybölümü, desteklenen bir bölümden (cache,userdata) sistem görüntüsünü okuyabilen vesystembölümüne yazabilen bir görüntü içermelidir.Bootloader, doğrudan kurtarma moduna önyüklemeyi desteklemelidir.
Radyo görüntüsü güncellemeleri destekleniyorsa
recoverybölümü de radyoyu flaşlayabilmelidir. Bu işlem iki şekilde yapılabilir:Bootloader, radyoyu flaşlar. Bu durumda, güncellemeyi tamamlamak için kurtarma bölümünden yeniden başlatarak bootloader'a geri dönmek mümkün olmalıdır.
Kurtarma görüntüsü, radyoyu yanıp söner. Bu işlev, ikili kitaplık veya yardımcı program olarak sağlanabilir.
