Android 10 では、ConfigStore HAL はビルドフラグを使用して vendor パーティション内に構成値を格納し、system パーティション内のサービスは HIDL を使用してそれらの値にアクセスします(この動作は Android 9 でも同様です)。ただし、メモリの消費量が多く、使用することが困難であるため、ConfigStore HAL は非推奨になりました。
ConfigStore HAL は、従来のベンダー パーティションをサポートするために AOSP に残されます。Android 10 以降を搭載したデバイスでは、surfaceflinger が最初にシステム プロパティを読み取ります。「SurfaceFlingerProperties.sysprop」の構成項目でシステム プロパティが定義されていない場合、「surfaceflinger」は ConfigStore HAL にフォールバックします。
Android 8.0 では、モノリシックだった Android OS が、汎用パーティション(system.img)とハードウェア固有のパーティション(vendor.img と odm.img)に分割されています。この変更により、システム パーティションにインストールされたモジュールから条件付きコンパイルを削除する必要があり、それらのモジュールは実行時にシステムの構成を決定する必要があります(構成に応じて挙動は異なります)。
ConfigStore HAL は、Android フレームワークの構成に使用する読み取り専用の構成アイテムにアクセスするための API セットを提供します。このページでは、ConfigStore HAL の設計(およびこの目的でシステム プロパティが使用されなかった理由)について説明します。このセクションの他のページでは、HAL インターフェース、サービスの実装、クライアント側の使用方法について詳しく説明しています。これらはすべて例として surfaceflinger を用いています。ConfigStore インターフェース クラスのヘルプについては、インターフェース クラスとアイテムの追加をご覧ください。
システム プロパティを使用しない理由
システム プロパティの使用を検討しましたが、次のようないくつかの根本的な問題が見つかりました。
- 値の長さの制限。システム プロパティには、値の長さに厳密な制限があります(92 バイト)。さらに、この制限は C マクロとして Android アプリに直接公開されているため、長さを長くすると下位互換性の問題が発生する可能性があります。
- 型のサポートがない。すべての値は基本的に文字列で、API は単に文字列を
intまたはboolに解析します。他の複合データ型(配列や構造体など)は、クライアントがエンコードまたはデコードする必要があります(たとえば、"aaa,bbb,ccc"は 3 つの文字列の配列としてコード化できます)。 - 上書きされる。読み取り専用のシステム プロパティは 1 回だけ書き込み可能なプロパティとして実装されているため、AOSP 定義の読み取り専用値をオーバーライドするベンダーと ODM は、AOSP 定義の読み取り専用値の前に独自の読み取り専用値をインポートする必要があります。これにより、ベンダー定義の書き換え可能な値は、AOSP 定義の値によって上書きされることになります。
- アドレス空間の要件。システム プロパティは、各プロセスで比較的大量のアドレス空間を使用します。システム プロパティは 128 KB の固定サイズの
prop_areaユニットにグループ化され、その中の 1 つのシステム プロパティのみがアクセスされる場合でも、すべてのシステム プロパティがプロセスのアドレス空間に割り当てられます。これにより、アドレス空間が貴重な 32 ビットデバイスで問題が発生する可能性があります。
互換性を犠牲にすることなくこれらの制限を克服しようとしましたが、読み取り専用の構成アイテムへのアクセスをサポートするようにシステム プロパティが設計されていないことが引き続き懸念されました。最終的に、システム プロパティは動的に更新される少数のアイテムをすべての Android でリアルタイムに共有するのに適しており、読み取り専用の構成アイテムへのアクセス専用の新しいシステムが必要であると判断しました。
ConfigStore HAL の設計
基本的な設計はシンプルです。
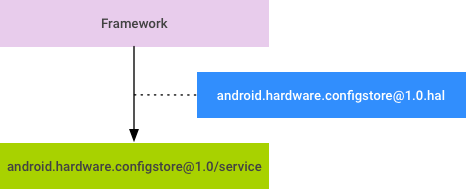
図 1. ConfigStore HAL の設計
- ビルドフラグ(現在はフレームワークの条件付きコンパイルに使用)を HIDL で記述します。
- ベンダーと OEM は、HAL サービスを実装して、ビルドフラグに SoC およびデバイス固有の値を提供します。
- HAL サービスを使用して実行時に構成アイテムの値を見つけるように、フレームワークを変更します。
フレームワークによって現在参照されている構成アイテムは、バージョニングされる HIDL パッケージ(android.hardware.configstore@1.0)に含まれています。ベンダーと OEM は、このパッケージにインターフェースを実装して構成アイテムに値を提供し、フレームワークは構成アイテムの値を取得する必要がある場合にインターフェースを使用します。
セキュリティ上の考慮事項
同じインターフェースで定義されたビルドフラグは、同じ SELinux ポリシーの影響を受けます。1 つ以上のビルドフラグが異なる SELinux ポリシーを持つ場合、それらを別のインターフェースに分離する必要があります。分離されたインターフェースは下位互換性がなくなるため、これには android.hardware.configstore package の大幅な修正が必要になる場合があります。
