מכשירי Android מכילים כמה מחיצות או חלקים ספציפיים בנפח האחסון שמשמשים לאחסון חלקים ספציפיים בתוכנה של המכשיר. כל מחיצה מכילה תמונת מחיצה (קובץ IMG) או תמונת מצב של כל התוכנה של המחיצה. איור 1 מציג את הפריסה של מחיצות הליבה במכשיר:
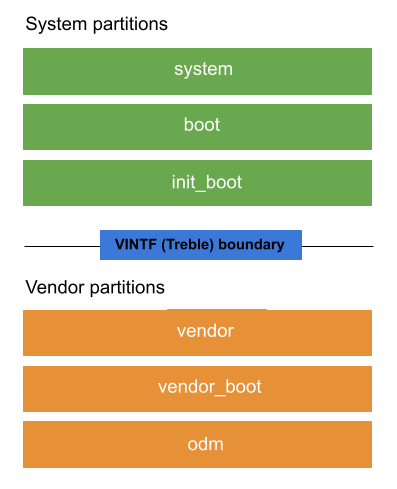
איור 1. פריסה של מחיצות ליבה.
המחיצות מסווגות לשלוש קטגוריות:
מחיצות מערכת הן מחיצות שמתעדכנות כשמעדכנים את מערכת ההפעלה ותכונות אחרות.
system,bootו-init_bootהן מחיצות של מערכת הליבה.מחיצות של ספקים מכילות קוד ספציפי למכשיר ולחומרה, שאולי לא יעודכן אף פעם אחרי ההשקה הראשונית. המחיצות
vendor,vendor_bootו-odmהן מחיצות ליבה של הספק.מחיצות שלא ניתן לעדכן הן מחיצות שהתוכן שלהן לא מתעדכן או מתעדכן בנתוני משתמשים.
קוד במחיצות של המערכת והספק יכול ליצור אינטראקציה באמצעות ממשק יציב שנקרא ממשק הספק (VINTF).
מחיצות מערכת
בהמשך מפורטת רשימה של כל מחיצות המערכת והשימוש בהן:
bootמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה תמונת ליבה גנרית (GKI). המחיצה הזו מכילה גם את ה-ramdisk הגנרי במכשירים שהושקו עם Android מגרסה 12 ומטה. מידע נוסף על ramdisk גנרי זמין במאמר בנושא תוכן של תמונת ramdisk גנרית.מחיצת
init_boot(Android מגרסה 13 ואילך). המחיצה הזו מכילה ramdisk כללי. ב-Android 11 וב-Android 12, ה-ramdisk הכללי נמצא במחיצהboot.systemמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה את תמונת המערכת שמשמשת למוצרי OEM.system_extמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה משאבי מערכת ומודולים קנייניים של המערכת שמרחיבים את תמונת המערכת המשותפת במחיצהsystem.system_dlkmמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה מודולים של GKI. מידע נוסף על החלוקה הזו זמין במאמר הטמעה של חלוקת מודולים ב-GKI.productמחיצה. המחיצה הזו יכולה להכיל מודולים ספציפיים למוצר שלא נכללים בחבילה עם מחיצות אחרות.pvmfwמחיצה. במחיצה הזו מאוחסן קושחת המכונה הווירטואלית המוגנת (pvmfw), שהוא הקוד הראשון שפועל במכונות וירטואליות מוגנות. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר Protected Virtual Machine Firmware.generic_bootloaderמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה את טוען האתחול הגנרי.
מחיצות של ספקים
בהמשך מופיעה רשימה של כל המחיצות של הספקים והשימוש בהן:
vendor_bootמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה קוד הפעלה ספציפי לספק. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא מחיצות אתחול של ספקים.recoveryמחיצה. במחיצה הזו מאוחסנת תמונת השחזור, שממנה מתבצעת האתחול במהלך תהליך העדכון דרך האוויר (OTA). במכשירים שתומכים בעדכונים חלקים, אפשר לאחסן את תמונות השחזור כ-ramdisk שכלול בתמונתbootאוinit_boot. מידע נוסף על עדכונים ללא הפרעה זמין במאמר עדכוני A/B (ללא הפרעה).miscמחיצה. המחיצה הזו משמשת את מחיצת השחזור והיא בגודל 4 KB או יותר.vbmetaמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה את המידע על אתחול מאומת לכל המחיצות. המידע הזה מאמת שהתמונות שהותקנו בכל מחיצה הן מהימנות. מידע נוסף על אתחול מאומת זמין במאמר בנושא אתחול מאומת.vendorמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה קובץ בינארי ספציפי לספק שלא מספיק כללי כדי להפיץ אותו ל-AOSP.vendor_dlkmמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה מודולים של ליבת הספק. אחסון מודולי ליבת הספק במחיצה הזו במקום במחיצהvendorמאפשר לעדכן את מודולי הליבה בלי לעדכן את המחיצהvendor. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא מחיצות DKLM של ספקים ו-ODM.odmמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה התאמות אישיות של יצרן עיצוב מקורי (ODM) לחבילות תמיכה בלוח (BSP) של ספק מערכת על שבב (SoC). התאמות אישיות כאלה מאפשרות ליצרני ODM להחליף או להתאים אישית רכיבי SoC, ולהטמיע מודולים של ליבת מערכת ההפעלה עבור רכיבים ספציפיים ללוח, תהליכי רקע ותכונות ספציפיות ל-ODM בשכבות הפשטה של חומרה (HAL). המחיצה הזו היא אופציונלית. בדרך כלל המחיצה הזו משמשת להכללת התאמות אישיות, כדי שמכשירים יוכלו להשתמש בתמונה יחידה של ספק עבור כמה מק"טים של חומרה. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא מחיצות ODM.odm_dlkmמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מיועדת לאחסון מודולים של ליבת ODM. אחסון מודולים של ליבת ODM במחיצה הזו, במקום במחיצהodm, מאפשר לעדכן מודולים של ליבת ODM בלי לעדכן את המחיצהodm. מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא מחיצות DKLM של ספקים ו-ODM.radioמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה את תמונת הרדיו והיא נדרשת רק למכשירים שכוללים רדיו עם תוכנה ספציפית לרדיו במחיצה ייעודית.
מחיצות שלא ניתן לעדכן
בהמשך מופיעה רשימה של כל המחיצות שלא ניתן לעדכן והשימוש בהן:
cacheמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה נתונים זמניים והיא אופציונלית אם המכשיר משתמש בעדכונים חלקים. המחיצה הזו לא צריכה להיות ניתנת לכתיבה מתוכנת האתחול, אבל היא צריכה להיות ניתנת למחיקה. גודל המחיצה תלוי בסוג המכשיר ובנפח האחסון הזמין ב-userdata. בדרך כלל, נפח של 50 עד 100 MB מספיק.userdataמחיצה. המחיצה הזו מכילה אפליקציות ונתונים שהמשתמש התקין, כולל נתוני התאמה אישית.metadataמחיצה. אם המכשיר משתמש בהצפנת מטא-נתונים, המחיצה הזו מכילה את המפתח להצפנת המטא-נתונים. גודל המחיצה הזו הוא 16MB או יותר, היא לא מוצפנת והנתונים שלה לא מצולמים. המחיצה הזו נמחקת כשמבצעים איפוס להגדרות המקוריות של המכשיר.
כללים והמלצות לעדכון מחיצות
מומלץ לעדכן את כל מחיצות המערכת כמכלול אחד ואת כל מחיצות הספק כמכלול אחר. כשמעדכנים את קבוצת המחיצות כמכלול, אפשר לבדוק כדי לוודא שהממשקים בין התמונות בכל מחיצה נשארים יציבים.
לא משנה איך מעדכנים את המחיצות, צריך לעדכן את המחיצות הבאות בגלל תלות הדוקה בין רכיבים וחוסר בממשקי API יציבים:
- המחיצות
bootו-system_dlkm - המחיצות
init_boot,system,system_extו-product
מחיצות דינמיות
מכשירים עם Android 11 ואילך יכולים לתמוך במחיצות דינמיות, שהן מערכת חלוקה למחיצות במרחב המשתמש ב-Android, שמאפשרת ליצור, לשנות את הגודל או למחוק מחיצות במהלך עדכונים דרך האוויר (OTA). מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא מחיצות דינמיות.
וריאציות של מוצרים ב-Soong
מערכת ה-build של Soong משתמשת בווריאציות של תמונות כדי לפצל את יחסי התלות של ה-build. מודולים מקוריים (/build/soong/cc) יכולים לשנות מודולים של תהליכי מערכת למודולים של תהליכי ספק ליבה, ומודולים של תהליכי ספק למודולים של תהליכי ספק וריאנט; מודול בווריאציה אחת של תמונה לא יכול לקשר למודולים אחרים בווריאציה אחרת של תמונה.
ב-Android מגרסה 12 ואילך, מודול מערכת עם vendor_available: true יוצר וריאנט של הספק בנוסף לווריאנט הליבה. כדי ליצור וריאציית מוצר, צריך להגדיר את product_available: true. חלק מספריות VNDK ללא product_available: true לא זמינות למודולים של מוצרים.
