ה-Vendor Native Development Kit (VNDK) מחייב לבצע כמה שינויים בבסיס הקוד כדי להפריד בין הדאגות של הספק לבין אלה של המערכת. כדי להפעיל את VNDK בבסיס קוד של ספק או יצרן ציוד מקורי, נעזרים במדריך הבא.
יצירת ספריות מערכת
מערכת ה-build מכילה כמה סוגים של אובייקטים, כולל ספריות (משותפות, סטטיות או כותרות) וקבצים בינאריים.
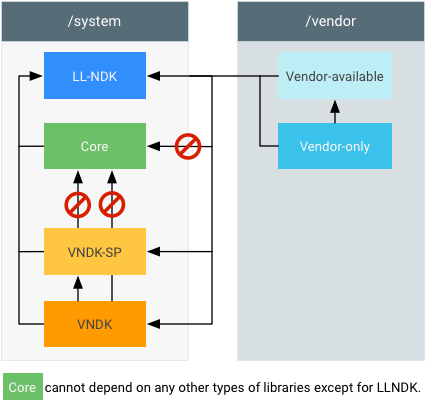
איור 1. יצירת ספריות מערכת.
coreספריות משמשות את תמונת המערכת, בתמונת המערכת. אי אפשר להשתמש בספריות האלה בספריותvendor,vendor_available,vndkאוvndk-sp.cc_library { name: "libThatIsCore", ... }
- ספריות
vendor-only(אוproprietary) משמשות את תמונת הספק, בתמונת הספק.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorOnly", proprietary: true, # or: vendor: true, # (for things in AOSP) ... }
- ספריות
vendor_availableמשמשות לתמונת הספק, בתמונת הספק (יכול להיות שהן מכילות כפילויות שלvendor_available).corecc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorAvailable", vendor_available: true, ... }
- ספריות
vndkנמצאות בקובץ האימג' של הספק, בקובץ האימג' של המערכת.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndk", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, } ... }
- ספריות
vndk-spנמצאות בשימוש בתמונת הספק, וגם בתמונת המערכת באופן עקיף.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndkSp", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, support_system_process: true, } ... }
- ספריות
llndkמשמשות גם את המערכת וגם את תמונות הספק.cc_library { name: "libThatIsLlndk", llndk: { symbol_file: "libthatisllndk.map.txt" } ... }
כשספרייה מסומנת ב-vendor_available:true, היא נבנית פעמיים:
- פעם אחת לפלטפורמה (ולכן מותקן ב-
/system/lib) - פעם אחת לספק (ולכן מותקן ב-
/vendor/libאו ב-VNDK APEX)
גרסאות הספק של ספריות נוצרות באמצעות -D__ANDROID_VNDK__.
רכיבי מערכת פרטיים שעשויים להשתנות באופן משמעותי בגרסאות עתידיות של Android מושבתים באמצעות הדגל הזה. בנוסף, ספריות שונות מייצאות קבוצה שונה של כותרות (כמו liblog). אפשר לציין אפשרויות ספציפיות לגרסת ספק של יעד בקובץ Android.bp במיקום:
target: { vendor: { … } }הפעלת VNDK בבסיס קוד
כדי להפעיל את VNDK בבסיס קוד:
- כדי לקבוע את הזכאות, מחשבים את הגדלים הנדרשים של מחיצות
vendor.imgו-system.img. - מפעילים את
BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current. אפשר להוסיף אותו ל-BoardConfig.mkאו ליצור איתו רכיבים ישירות (לדוגמה,m -j BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current MY-LIB).
אחרי שמפעילים את BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current, מערכת ה-build אוכפת את הדרישות הבאות לגבי יחסי תלות וכותרות.
ניהול יחסי תלות
אובייקט vendor שתלוי ברכיב core שלא קיים ב-vndk או כאובייקט vendor, צריך לפתור את הבעיה באחת מהדרכים הבאות:
- אפשר להסיר את התלות.
- אם הרכיב
coreנמצא בבעלותvendor, אפשר לסמן אותו כ-vendor_availableאו כ-vendor. - שינוי שהופך את אובייקט הליבה לחלק מ-
vndkעשוי להיות מועבר ל-Google.
בנוסף, אם לרכיב core יש תלות ברכיב vendor, צריך להפוך את רכיב vendor לרכיב core או להסיר את התלות בדרך אחרת (לדוגמה, על ידי הסרת התלות או העברת התלות לרכיב vendor).
ניהול כותרות
צריך להסיר את התלות בכותרת הגלובלית כדי שמערכת ה-build תוכל לדעת אם לבצע build של הכותרות עם -D__ANDROID_VNDK__ או בלי.
לדוגמה, עדיין אפשר לגשת לכותרות של libutils כמו utils/StrongPointer.h באמצעות ספריית הכותרות libutils_headers.
אי אפשר יותר לכלול באופן טרנזיטיבי כותרות מסוימות (כמו unistd.h), אבל אפשר לכלול אותן באופן מקומי.
לבסוף, החלק הציבורי של private/android_filesystem_config.h הועבר אל cutils/android_filesystem_config.h. כדי לנהל את הכותרות האלה, מבצעים אחת מהפעולות הבאות:
- כדי להסיר את התלות ב-
private/android_filesystem_config.h, מחליפים את כל פקודות המאקרוAID_*בקריאותgetgrnam/getpwnam, אם אפשר. לדוגמה:-
(uid_t)AID_WIFIהופך ל-getpwnam("wifi")->pw_uid. -
(gid_t)AID_SDCARD_Rהופך ל-getgrnam("sdcard_r")->gr_gid.
private/android_filesystem_config.h. -
- אם ה-AIS מוטמע בקוד, צריך לכלול את המחרוזת
cutils/android_filesystem_config.h.
